Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Nb by activation method and half-life of
Nb by activation method and half-life of  Nb by mass analysis
Nb by mass analysisNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1361 - 1371, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross section (
 ) and resonance integral (I
) and resonance integral (I ) for
) for  Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of
Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of  Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25-
Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25- m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of
m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of 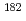 Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by
Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by  -ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the
-ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the 
 and I
and I values were derived as 1.11
values were derived as 1.11 0.04 barn and 10.5
0.04 barn and 10.5 0.6 barn, respectively. After the
0.6 barn, respectively. After the  -ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both
-ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both  -ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of
-ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of  Nb was derived as (2.00
Nb was derived as (2.00 0.15)
0.15) 10
10 years.
years.
Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Kimura, Atsushi; Endo, Shunsuke; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(9), p.1133 - 1142, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In recent years, research has been advanced on lead-cooled fast reactors and accelerator drive systems, and it is required to improve the accuracy of the neutron capture cross section of Pb isotopes. Although  Pb has a small natural abundance, it is of importance because it produces the long-lived radionuclide
Pb has a small natural abundance, it is of importance because it produces the long-lived radionuclide  Pb (17.3 million years) by neutron capture reaction. However, it is difficult to measure its cross section by a conventional activation method using a nuclear reactor because the induced radioactivity of
Pb (17.3 million years) by neutron capture reaction. However, it is difficult to measure its cross section by a conventional activation method using a nuclear reactor because the induced radioactivity of  Pb is weak. Hence, the cross-section measurement was performed by applying mass spectrometry. This presentation gives the details of the experiment and the results obtained in the neutron capture cross-section measurement of
Pb is weak. Hence, the cross-section measurement was performed by applying mass spectrometry. This presentation gives the details of the experiment and the results obtained in the neutron capture cross-section measurement of  Pb using mass spectroscopy.
Pb using mass spectroscopy.
Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2022, P. 73, 2023/07
The present study is concerned with the neutron capture cross-sections that contribute to the evaluation of the amount of radionuclides possessing problems in decommissioning. In this study,  Sc,
Sc,  Cu,
Cu,  Zn,
Zn,  Ag,
Ag,  In and
In and  W were selected among the objective nuclides, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured using TC-Pn equipment of the KUR of the Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. High purity metal samples were prepared. A gold-aluminum ally wire, cobalt and molybdenum foils were used to monitor the neutron flux at the irradiation position of TC-Pn. The flux monitors and metal samples were irradiated for 1 hour at 1-MW operation of the KUR. After irradiation, the irradiation capsule was opened, samples and flux monitors were enclosed in a vinyl bag one by one, and then
W were selected among the objective nuclides, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured using TC-Pn equipment of the KUR of the Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. High purity metal samples were prepared. A gold-aluminum ally wire, cobalt and molybdenum foils were used to monitor the neutron flux at the irradiation position of TC-Pn. The flux monitors and metal samples were irradiated for 1 hour at 1-MW operation of the KUR. After irradiation, the irradiation capsule was opened, samples and flux monitors were enclosed in a vinyl bag one by one, and then  rays emitted from the samples and monitors were measured with a high-purity Ge detector. The thermal-neutron flux component was derived with the reaction rates of flux monitors (
rays emitted from the samples and monitors were measured with a high-purity Ge detector. The thermal-neutron flux component was derived with the reaction rates of flux monitors ( Au,
Au,  Co and
Co and  Mo) on the basis of Westcott's convention, and found to be (5.92
Mo) on the basis of Westcott's convention, and found to be (5.92 0.10)
0.10) 10
10 n/cm
n/cm /sec at the irradiation position. The measured reaction rate for each metal sample divided by the evaluated thermal-neutron capture cross-section should give the same value of the thermal-neutron flux component if the cross section is suitable. This time, we found that the cross sections of
/sec at the irradiation position. The measured reaction rate for each metal sample divided by the evaluated thermal-neutron capture cross-section should give the same value of the thermal-neutron flux component if the cross section is suitable. This time, we found that the cross sections of  Sc and
Sc and  Zn were consistent with the evaluated one, but those of other nuclides were inconsistent with their evaluated ones; that is, it turned out that their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections should be modified.
Zn were consistent with the evaluated one, but those of other nuclides were inconsistent with their evaluated ones; that is, it turned out that their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections should be modified.
 Gd and
Gd and  Gd in the thermal energy region with the Li-glass detectors and NaI(Tl) spectrometer installed in J-PARC
Gd in the thermal energy region with the Li-glass detectors and NaI(Tl) spectrometer installed in J-PARC MLF
MLF ANNRI
ANNRIKimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Terada, Kazushi*; Hori, Junichi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.678 - 696, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hori, Junichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Nakamura, Shoji; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Endo, Shunsuke; Shibahara, Yuji*; Terada, Kazushi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 281, p.00014_1 - 00014_4, 2023/03
Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1388 - 1398, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The present study selected  Np among radioactive nuclides and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section for
Np among radioactive nuclides and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section for  Np in a well-thermalized neutron field by an activation method. A
Np in a well-thermalized neutron field by an activation method. A  Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. A thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with neutron flux monitors:
Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. A thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with neutron flux monitors:  Sc,
Sc,  Co,
Co,  Mo,
Mo,  Ta and
Ta and  Au. The
Au. The  Np sample and flux monitors were irradiated together for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped with the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was carried out twice. After the irradiations, the
Np sample and flux monitors were irradiated together for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped with the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was carried out twice. After the irradiations, the  Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma ray emitted from
Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma ray emitted from  Pa in a radiation equilibrium with
Pa in a radiation equilibrium with  Np. The reaction rates of
Np. The reaction rates of  Np were obtained from gamma-ray peak net counts given by
Np were obtained from gamma-ray peak net counts given by  Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np was found to be 173.8
Np was found to be 173.8 4.4 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within the limit of uncertainty.
4.4 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within the limit of uncertainty.
 Np(n,
Np(n,  ) reaction with TC-Pn in KUR
) reaction with TC-Pn in KURNakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2021, P. 93, 2022/07
In terms of nuclear transmutation studies of minor actinides in nuclear wastes, the present work selected  Np among them and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np among them and aimed to measure the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np using a well-thermalized neutron field by a neutron activation method because there have been discrepancies among reported cross-section data. A
Np using a well-thermalized neutron field by a neutron activation method because there have been discrepancies among reported cross-section data. A  Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. The thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with flux monitors:
Np standard solution was used for irradiation samples. The thermal-neutron flux at an irradiation position was measured with flux monitors:  Sc,
Sc,  Co,
Co,  Mo,
Mo,  Ta and
Ta and  Au. The
Au. The  Np sample was irradiated together with the flux monitors for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped in the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was repeated once more to confirm the reproducibility of the results. After irradiation, the
Np sample was irradiated together with the flux monitors for 30 minutes in the graphite thermal column equipped in the Kyoto University Research Reactor. The similar irradiation was repeated once more to confirm the reproducibility of the results. After irradiation, the  Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma-ray emitted from
Np samples were quantified using 312-keV gamma-ray emitted from  Pa in radiation equilibrium with
Pa in radiation equilibrium with  Np. The reaction rates of
Np. The reaction rates of  Np were obtained from the peak net counts of gamma-rays emitted from generated
Np were obtained from the peak net counts of gamma-rays emitted from generated  Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of
Np, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross-section of  Np was found to be 173.8
Np was found to be 173.8 4.7 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within a limit of uncertainty.
4.7 barn by averaging the results obtained by the two irradiations. The present result was in agreement with the reported data given by a time-of-flight method within a limit of uncertainty.
 Au with a Cr-filtered neutron beam at the ANNRI beamline of MLF/J-PARC
Au with a Cr-filtered neutron beam at the ANNRI beamline of MLF/J-PARCRovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Kodama, Yu*; Nakano, Hideto*; Sato, Yaoki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(5), p.647 - 655, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)Rovira Leveroni, G.; Iwamoto, Osamu; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Endo, Shunsuke; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Terada, Kazushi*; Kodama, Yu*; Nakano, Hideto*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2021-001, p.156 - 161, 2022/03
 Am around 23.5 keV
Am around 23.5 keVKodama, Yu*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hori, Junichi*; Shibahara, Yuji*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(11), p.1159 - 1164, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:56.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(10), p.1061 - 1070, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:56.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)In a well-thermalized neutron field, it is principally possible to drive a thermal-neutron capture cross-section without considering an epithermal neutron component. This was demonstrated by a neutron activation method using the graphite thermal column (TC-Pn) of the Kyoto University Research Reactor. First, in order to confirm that the graphite thermal column was a well-thermalized neutron field, neutron irradiation was performed with neutron flux monitors:  Au,
Au,  Co,
Co,  Sc,
Sc,  Cu, and
Cu, and  Mo. The TC-Pn was confirmed to be extremely thermalized on the basis of Westcott's convention, because the thermal-neutron flux component took a constant value regardless of the sensitivity of each flux monitor to epithermal neutrons. Next, as a demonstration, the thermal-neutron capture cross section of
Mo. The TC-Pn was confirmed to be extremely thermalized on the basis of Westcott's convention, because the thermal-neutron flux component took a constant value regardless of the sensitivity of each flux monitor to epithermal neutrons. Next, as a demonstration, the thermal-neutron capture cross section of  Ta(n,
Ta(n, )
)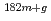 Ta reaction was measured using the graphite thermal column, and then derived to be 20.5
Ta reaction was measured using the graphite thermal column, and then derived to be 20.5 0.4 barn, which supported the evaluated value of 20.4
0.4 barn, which supported the evaluated value of 20.4 0.3 barn. The
0.3 barn. The  Ta nuclide could be useful as a flux monitor that complements the sensitivity between
Ta nuclide could be useful as a flux monitor that complements the sensitivity between  Au and
Au and  Mo monitors.
Mo monitors.
 Np using graphite thermal column
Np using graphite thermal columnNakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2020, P. 94, 2021/08
The present study selected  Np among radioactive nuclides and aimed to converge a contradiction between reported thermal-neutron capture cross sections. Neutron irradiation was carried out using the graphite thermal column equipped with the Kyoto University Research Reactor. A solution equivalent to 950 Bq order of radioactivity was pipetted out of a
Np among radioactive nuclides and aimed to converge a contradiction between reported thermal-neutron capture cross sections. Neutron irradiation was carried out using the graphite thermal column equipped with the Kyoto University Research Reactor. A solution equivalent to 950 Bq order of radioactivity was pipetted out of a  Np standard solution and dropped onto a fiber filter, which was then dried with an infrared lamp to prepare a
Np standard solution and dropped onto a fiber filter, which was then dried with an infrared lamp to prepare a  Np sample. The
Np sample. The  Np sample was quantified using 312-keV gamma ray emitted from
Np sample was quantified using 312-keV gamma ray emitted from  Pa in a radiation equilibrium with
Pa in a radiation equilibrium with  Np. To monitor a thermal-neutron flux component at an irradiation position, the
Np. To monitor a thermal-neutron flux component at an irradiation position, the  Np sample was irradiated together with several stable nuclides as neutron flux monitors:
Np sample was irradiated together with several stable nuclides as neutron flux monitors:  Sc,
Sc,  Co,
Co,  Mo,
Mo,  Ta and
Ta and  Au. The reaction rate of
Au. The reaction rate of  Np was obtained from gamma-ray yields given by
Np was obtained from gamma-ray yields given by  Np and
Np and  Pa, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross section of
Pa, and then the thermal-neutron capture cross section of  Np was derived.
Np was derived.
Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Terada, Kazushi*; Kodama, Yu*; Nakano, Hideto*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1003, p.165318_1 - 165318_10, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:57.13(Instruments & Instrumentation) Am(n,
Am(n, )
)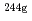 Am and
Am and  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)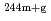 Am reactions
Am reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(3), p.259 - 277, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:53.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Research and development were made for accuracy improvement of neutron capture cross section data on  Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay
Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay  rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of
rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of  Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of
Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of  Am was examined by
Am was examined by  -ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examined by
-ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examined by  -ray measurement. Thermal-neutron capture cross sections and resonance integrals were derived both for the
-ray measurement. Thermal-neutron capture cross sections and resonance integrals were derived both for the  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)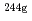 Am and for
Am and for  Am(n,
Am(n, )
)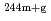 Am reactions.
Am reactions.
Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Hori, Junichi*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Terada, Kazushi*; Tosaka, Kenichi*; Endo, Shunsuke; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2020-001, p.5 - 9, 2020/12
Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hori, Junichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Terada, Kazushi*; Rovira, G.*; Matsuura, Shota*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.01044_1 - 01044_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:86.93(Nuclear Science & Technology) Am(n,
Am(n, )
)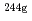 Am,
Am, 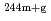 Am reactions
Am reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2019, P. 132, 2020/08
Research and development were made for accuracy improvement of neutron capture cross section data on  Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay
Am among minor actinides. First, the emission probabilities of decay  rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of
rays were obtained with high accuracy, and the amount of the ground state of  Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of
Am produced by reactor neutron irradiation of  Am was examinded by
Am was examinded by  -ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examoned by
-ray measurement. Next, the total amount of isomer and ground states was examoned by  -ray measurement.
-ray measurement.
 Cs
CsShibahara, Yuji*; Nakamura, Shoji; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*; Fukutani, Satoshi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Osamu
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 325(1), p.155 - 165, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:71.58(Chemistry, Analytical)The measurements of isotopic ratios of Cs samples by thermal ionization mass spectrometry were performed for the analysis of their samples used to evaluate nuclear data obtained for  Cs. To obtain a high intensity and stable ion beam, the effects of additive agents on the ionization of Cs were examined. The effect of silicotungstic acid on the ionization of Cs was the largest among the additive agents studied in the present study, while the silicotungstic acid also showed the largest isobaric interference of polyatomic ions. It was demonstrated that as small as 2
Cs. To obtain a high intensity and stable ion beam, the effects of additive agents on the ionization of Cs were examined. The effect of silicotungstic acid on the ionization of Cs was the largest among the additive agents studied in the present study, while the silicotungstic acid also showed the largest isobaric interference of polyatomic ions. It was demonstrated that as small as 2 10
10 g of a Cs sample was sufficient to achieve the analytical precision required to measure the
g of a Cs sample was sufficient to achieve the analytical precision required to measure the  Cs/
Cs/ Cs ratio in the case where an additive agent of TaO/glucose was employed. After examining of the analytical conditions, such as the interference effect due to Ba, the measurements of the isotopic ratios of two Cs samples used in our study using TIMS were conducted, and it was discussed how much the ratios contributed to evaluation of the neutron capture cross-section of
Cs ratio in the case where an additive agent of TaO/glucose was employed. After examining of the analytical conditions, such as the interference effect due to Ba, the measurements of the isotopic ratios of two Cs samples used in our study using TIMS were conducted, and it was discussed how much the ratios contributed to evaluation of the neutron capture cross-section of  Cs.
Cs.
Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Kimura, Atsushi; Iwamoto, Osamu; Uehara, Akihiro*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(4), p.388 - 400, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.89(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross-section ( ) and resonance integral(I
) and resonance integral(I ) were measured for the
) were measured for the  Cs(n,
Cs(n, )
) Cs reaction by an activation method and mass spectrometry. We used
Cs reaction by an activation method and mass spectrometry. We used  Cs contained as an impurity in a normally available
Cs contained as an impurity in a normally available  Cs standard solution. An isotope ratio of
Cs standard solution. An isotope ratio of  Cs and
Cs and  Cs in a standard
Cs in a standard  Cs solution was measured by mass spectrometry to quantify
Cs solution was measured by mass spectrometry to quantify  Cs. The analyzed
Cs. The analyzed  Cs samples were irradiated at the hydraulic conveyer of the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Wires of Co/Al and Au/Al alloys were used as neutron monitors to measure thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indices at an irradiation position. A gadolinium filter was used to measure the
Cs samples were irradiated at the hydraulic conveyer of the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Wires of Co/Al and Au/Al alloys were used as neutron monitors to measure thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indices at an irradiation position. A gadolinium filter was used to measure the  , and a value of 0.133 eV was taken as the cut-off energy. Gamma-ray spectroscopy was used to measure induced activities of
, and a value of 0.133 eV was taken as the cut-off energy. Gamma-ray spectroscopy was used to measure induced activities of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs and monitor wires. On the basis of Westcott's convention, the
Cs and monitor wires. On the basis of Westcott's convention, the  and I
and I values were derived as 8.57
values were derived as 8.57 0.25 barn, and 45.3
0.25 barn, and 45.3 3.2 barn, respectively. The
3.2 barn, respectively. The  obtained in the present study agreed within the limits of uncertainties with the past reported value of 8.3
obtained in the present study agreed within the limits of uncertainties with the past reported value of 8.3 0.3 barn.
0.3 barn.
Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hori, Junichi*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Terada, Kazushi*
JAEA-Conf 2019-001, p.193 - 197, 2019/11