Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Daido, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Tomonori; Saruta, Koichi; Miyabe, Masabumi; Ito, Chikara; Shibata, Takuya; Inoue, Kaoru*; Terabayashi, Ryohei*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Physica Scripta, 98(3), p.035112_1 - 035112_22, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Characterization of kW class quasi-continuous wave (a pulse duration of 10 ms) laser interaction with metal targets and those with metal oxide targets are presented in respect to the laser induced breakdown and the successive laser induced melting and evaporation coupled with a mechanical response followed by ejection of various kinds of particles and fragments. An experiment was performed using fiber lasers coupled with a high-speed camera to observe dynamics of the interaction. Ejected fine particles were collected using a cascade impactor and a home-made collector and were observed with electron microscopes. Shapes of irradiation marks were observed with a digital optical microscope. We also measured total ejected mass from a target. The experimental results reveal that firstly the laser threshold intensity of the interaction with the metal target was lower and more stable than those with the metal oxide targets. Secondly, in the stainless steel targets, the dynamics of molten layer created by thermal conduction from the laser heated thin layer and successive particle ejection with less mechanical response by the adjacent solid layer are dominant processes, while in the metal oxide targets, the fracturing in the relatively deeper interaction region coupled with brittle material response having relatively large laser shot to shot fluctuation appears to play a significant role in addition to the laser induced melting.
Daido, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Tomonori; Furukawa, Hiroyuki*; Ito, Chikara; Miyabe, Masabumi; Shibata, Takuya; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of Laser Applications, 33(1), p.012001_1 - 012001_16, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.88(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Satoh, Daiki; Maeda, Yoshikazu*; Tameshige, Yuji*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Shibata, Tokushi*; Endo, Akira; Tsuda, Shuichi; Sasaki, Makoto*; Maekawa, Motokazu*; Shimizu, Yasuhiro*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 49(11), p.1097 - 1109, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:73.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)At the Fukui Prefectural Hospital Proton Therapy Center, neutron doses behind concrete shields and at maze have been measured by using radiation monitors, DARWIN, Wendi-2, a rem meter, and solid state nuclear track detectors. The measured data were compared with the estimations by analytical models and Monte Carlo code PHITS. The analytical model with the parameters employed in shielding design of the facility gave considerably larger estimates than the measured data. This means that the facility was designed with an enough safety margin. The calculation results of PHITS were less than those of the analytical model, and were about 3 times larger than the measured data. From the view point of a safety policy with conservative estimation for shielding design, Monte Carlo simulation is a better tool for estimating radiation safety at accelerator-based proton treatment facilities.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Aizawa, Kazuya; Suzuya, Kentaro; Shibata, Kaoru; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(Suppl.B), p.SB028_1 - SB028_6, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:142 Percentile:95.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary)AMATERAS is a cold-neutron disk-chopper spectrometer in MLF, J-PARC. The construction of main part of the spectrometer has been completed in spring of 2009. Soon after that, we have started the commissioning work on AMATERAS. The performance of AMATERAS has been examined by test experiments in the course of commissioning. In parallel to these works, we have started the user program on AMATERAS from December 2009 and we are getting scientific results from our spectrometer. In this presentation, we will report the current status of AMATERAS including the results of performance tests and some of examples of scientific outputs.
Obara, Satoshi*; Kobayashi, Ryoei*; Yagi, Shuichi*; Toyama, Yuko*; Kutluk, G.*; Osawa, Tetsutaro*; Ogura, Koichi; Shibata, Takemasa; Azuma, Yoshiro*; Nagata, Tetsuo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 269(3), p.263 - 271, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)A crossed photon-atom beam apparatus has been constructed for absolute measurement of total photoionization cross sections of isolated and neutral metallic atoms. Using this apparatus, measurements on Ba and Eu atoms have been made at their 4d giant resonance regions 110-140 eV and 140-180 eV, respectively. The target atom density was determined using the deposition rate on a quartz crystal sensor and the average velocity of the atoms obtained by a time-of-flight method combined with a pulsed electron gun. The number of photons was determined with use of a double ion chamber. The comparison of the measured cross-section values with previous experimental and theoretical results is reasonable, indicating that the crossed photon-atom beam method is fairly promising technique.
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Mizuno, Fumio; Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Nakatani, Takeshi; Maruyama, Ryuji; Soyama, Kazuhiko; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(Suppl.B), p.SB025_1 - SB025_6, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:114 Percentile:94.55(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Enomoto, Shuichi*; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Shirakawa, Yoshiyuki*; Nakanishi, Tomoko*; Nakamura, Kayoko*; Yano, Tsuneo*; Ido, Tatsuo*; Shibata, Tokushi
Isotope News, (657), p.2 - 11, 2009/01
The view of the future and the necessity of the system construction such as supply systems were shown about production of the medical diagnostics  Mo and the silicon semiconductor on JMTR.
Mo and the silicon semiconductor on JMTR.
Kumamoto, Yuichiro*; Aramaki, Takafumi*; Watanabe, Shuichi*; Yoneda, Minoru*; Shibata, Yasuyuki*; Togawa, Orihiko; Morita, Masatoshi*; Shitashima, Kiminori*
Journal of Oceanography, 64(3), p.429 - 441, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:24.36(Oceanography)In 1995 and 2000, radiocarbon ratio (
 C) of total dissolved inorganic carbon was measured in the Japan Sea, a semi-closed marginal sea in the western North Pacific, where deep and bottom waters are formed in itself. Compiling them with historical radiocarbon data in the Japan Sea, temporal and spatial variations of the radiocarbon in the bottom water below 2000 m depth were elucidated.
C) of total dissolved inorganic carbon was measured in the Japan Sea, a semi-closed marginal sea in the western North Pacific, where deep and bottom waters are formed in itself. Compiling them with historical radiocarbon data in the Japan Sea, temporal and spatial variations of the radiocarbon in the bottom water below 2000 m depth were elucidated. 
 C in the bottom waters in the western Japan and Yamato Basins increased by about 20 ‰ between 1977/79 and 1995 and did not changed between 1995 and 1999/2000, suggesting penetration of surface bomb-produced radiocarbon into the bottom waters due to bottom ventilation in the earlier period and stagnation of the bottom ventilation in the following period, respectively. In the eastern Japan Basin, the bottom
C in the bottom waters in the western Japan and Yamato Basins increased by about 20 ‰ between 1977/79 and 1995 and did not changed between 1995 and 1999/2000, suggesting penetration of surface bomb-produced radiocarbon into the bottom waters due to bottom ventilation in the earlier period and stagnation of the bottom ventilation in the following period, respectively. In the eastern Japan Basin, the bottom 
 C increased by about 10 ‰ between 1977/79 and 2002, suggesting less ventilation of the bottom water in the basin. The temporal changes of the radiocarbon, tritium, and dissolved oxygen suggest sporadic occurrences of the bottom ventilation between 1979 and 1984 and its stagnation between 1984 and 2004 in the eastern Japan and Yamato Basins. The former is probably due to spreading of a newly ventilated bottom water in the western Japan Basin in the severe winter of 1976-1977 along the abyssal circulation in the Japan Sea. The latter does not conflict with temporal changes of bomb-produced
C increased by about 10 ‰ between 1977/79 and 2002, suggesting less ventilation of the bottom water in the basin. The temporal changes of the radiocarbon, tritium, and dissolved oxygen suggest sporadic occurrences of the bottom ventilation between 1979 and 1984 and its stagnation between 1984 and 2004 in the eastern Japan and Yamato Basins. The former is probably due to spreading of a newly ventilated bottom water in the western Japan Basin in the severe winter of 1976-1977 along the abyssal circulation in the Japan Sea. The latter does not conflict with temporal changes of bomb-produced  Cs and chlorofluorocarbon-11 in the bottom water.
Cs and chlorofluorocarbon-11 in the bottom water.
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Mizuno, Fumio; Nakajima, Kenji; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Kawamura, Seiko; Maruyama, Ryuji; Soyama, Kazuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Mizuno, Fumio; Nakajima, Kenji; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Kawamura, Seiko; Maruyama, Ryuji; Soyama, Kazuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Mizuno, Fumio; Nakajima, Kenji; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Kawamura, Seiko; Maruyama, Ryuji; Soyama, Kazuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Aizawa, Kazuya; Suzuya, Kentaro; et al.
no journal, ,
AMATERAS is a cold-neutron disk-chopper spectrometer in Materials and Life science Facility in J-PARC. By combination of high-peak intensity from a H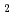 -coupled moderator source and newly developed high-speed disk-choppers (the maximum revolution: 350Hz, the minimum burst time: 7.6
-coupled moderator source and newly developed high-speed disk-choppers (the maximum revolution: 350Hz, the minimum burst time: 7.6  sec.) for pulse shaping and monochromating, the spectrometer realizes both high-resolution (
sec.) for pulse shaping and monochromating, the spectrometer realizes both high-resolution (
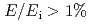 ) and high-intensity (one order of magnitude higher than the present state-of-the-art chopper spectrometers) in the range of
) and high-intensity (one order of magnitude higher than the present state-of-the-art chopper spectrometers) in the range of 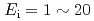 meV, and can show sufficient performance up to
meV, and can show sufficient performance up to 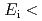 80 meV. Construction of AMTERAS has been completed in March 2009 and the spectrometer is at commissioning phase. In this presentation, we will report the current status of AMATERAS including the first results obtained at commissioning.
80 meV. Construction of AMTERAS has been completed in March 2009 and the spectrometer is at commissioning phase. In this presentation, we will report the current status of AMATERAS including the first results obtained at commissioning.
Yano, Tetsuji*; Akagi, Naoto*; Shibata, Shuichi*; Amamoto, Ippei
no journal, ,
In order to clarify the origins of the high chemical durability of iron phosphate glasses and find more stable glass composition, the transition metal oxides were added by the replacement of a part of the iron oxide, prepared the glasses by melt-quenching method and their thermal properties and chemical durabilities were measured. The structures of the glasses and their surfaces were analyzed using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The bulk samples were fractured in vacuum to obtain pristine surfaces, and the photoelectrons emitted from the analyzed surface by the monochromatic X-ray irradiation were collected. From the result, the dissolution rates of the sample glasses were correlated with the structural factors obtained from the XPS data, and strong correlations with the chemical shifts of the core electron spectra of oxygen and phosphorus ions were found, which are on the different trends found in general phosphate glass system like alkali phosphate glass.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Aizawa, Kazuya; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Amamoto, Ippei; Myochin, Munetaka; Akai, Naoto*; Yano, Tetsuji*; Shibata, Shuichi*
no journal, ,
The chemical durability of iron phosphate glasses was investigated by substituting MnO or CoO for a part of Fe
or CoO for a part of Fe O
O and by addition of pseudo nuclear waste (NW). The glass structure was also analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The substitution of MnO
and by addition of pseudo nuclear waste (NW). The glass structure was also analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The substitution of MnO and CoO decreased chemical durability of the glass without NW, while NW remarkably increased the chemical durability of glasses substituted by MnO
and CoO decreased chemical durability of the glass without NW, while NW remarkably increased the chemical durability of glasses substituted by MnO and CoO. According to XPS measurement, the substitution of MnO
and CoO. According to XPS measurement, the substitution of MnO and CoO increased bridging oxygen ratio and NW decreased it. The fraction of bridging oxygen is suggested to be one of the factors to affect the improvement of chemical durability.
and CoO increased bridging oxygen ratio and NW decreased it. The fraction of bridging oxygen is suggested to be one of the factors to affect the improvement of chemical durability.
Amamoto, Ippei; Myochin, Munetaka; Yano, Tetsuji*; Akagi, Naoto*; Segawa, Hiroyo*; Shibata, Shuichi*
no journal, ,
Phosphate glasses have received much attention for the development of new low-melting glasses with low environmental load. However, their low chemical durability prevents their application for practical use. Recently, the addition of Fe O
O was found to improve their chemical durability. Due to their high durability and high capacity of solution of dopants, iron phosphate glass system has been suggested to be utilized as new materials. In this work, the effect of the addition of other transition metal oxides on the properties of iron phosphate glass was investigated. In addition, the pseudo fission products as nuclear waste was added and their glass formation and chemical durability were investigated. All the glass batches formed homogenous melts at 1250 in the centigrade scale and vitrified without crystallization by pouring on the carbon plate. It was found that the substitution of a part of Fe
was found to improve their chemical durability. Due to their high durability and high capacity of solution of dopants, iron phosphate glass system has been suggested to be utilized as new materials. In this work, the effect of the addition of other transition metal oxides on the properties of iron phosphate glass was investigated. In addition, the pseudo fission products as nuclear waste was added and their glass formation and chemical durability were investigated. All the glass batches formed homogenous melts at 1250 in the centigrade scale and vitrified without crystallization by pouring on the carbon plate. It was found that the substitution of a part of Fe O
O by MnO
by MnO or CoO did not cause large changes in the thermal properties.
or CoO did not cause large changes in the thermal properties.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Osakabe, Toyotaka; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Ito, Shinichi*; Aizawa, Kazuya; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kajimoto, Ryoichi*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Aizawa, Kazuya; Suzuya, Kentaro; Shibata, Kaoru*; et al.
no journal, ,
AMATERAS is a cold-neutron disk-chopper spectrometer installed at beam-line No. 14 at Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at J-PARC. Owing to the use of newly developed high-speed disk choppers and the high peak intensity from the coupled moderator source of MLF, the AMATERAS design to realize high-intensity and fine and flexible energy resolution measurements in quasielastic and inelastic neutron scattering experiments in cold and sub-thermal neutron energy region. In this presentation, we will show the current status of AMATEAS including the results of performance tests and some of examples of scientific outputs.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawamura, Seiko; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kajimoto, Ryoichi*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Aizawa, Kazuya; Suzuya, Kentaro; Shibata, Kaoru*; et al.
no journal, ,
AMATERAS is a disk-chopper-type spectrometer installed at beam-line No. 14 at Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) of J-PARC. AMATERAS is equipped with an extra chopper for pulse shaping at the upstream position, in addition to a monochromating chopper. Owing to the use of these choppers and the high peak intensity from a coupled moderator source at MLF, AMATERAS is designed to realize high-intensity and fine and flexible energy resolution measurements in quasielastic and inelastic neutron scattering experiments in cold and sub-thermal neutron energy region. The spectrometer had the first neutron beam in May 2009 and user program started from December, 2009. During the course of commissioning and users' experiments, the performance of the spectrometer was confirmed by conducting test experiments. In this presentation, we will show the current status of AMATEAS including the results of performance tests and some of examples of scientific outputs.
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Mizuno, Fumio; Nakajima, Kenji; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Kawamura, Seiko; Maruyama, Ryuji; Soyama, Kazuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English