Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shinto, Katsuhiro; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shibata, Takanori*; Nammo, Kesao*; Kawai, Isao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Ueno, Akira
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.928 - 931, 2023/11
J-PARC initiated the operation of the high-intensity rf-driven negative hydrogen (H ) ion source in 2014 autumn. The ion source produces the H
) ion source in 2014 autumn. The ion source produces the H beam with the beam current of 60 mA and the beam energy of 50 keV in order to inject the H
beam with the beam current of 60 mA and the beam energy of 50 keV in order to inject the H beam into the 3 GeV RCS with the beam current of 50 mA and the beam energy of 400 MeV from the J-PARC linac. We have achieved the longest continuous operation time of 4001 hours in the previous (2021/2022) campaign. The 2022/2023 campaign was the first time that the continuous operation of the H
beam into the 3 GeV RCS with the beam current of 50 mA and the beam energy of 400 MeV from the J-PARC linac. We have achieved the longest continuous operation time of 4001 hours in the previous (2021/2022) campaign. The 2022/2023 campaign was the first time that the continuous operation of the H ion source without any exchanges of the ion source until the end of the campaign was examined. We present the operation status of the J-PARC H
ion source without any exchanges of the ion source until the end of the campaign was examined. We present the operation status of the J-PARC H ion source in this campaign as well as the status of the J-PARC-made internal antenna test.
ion source in this campaign as well as the status of the J-PARC-made internal antenna test.
Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Seki, Misaki; Shibata, Akira; Nakamura, Jinichi; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-018, 42 Pages, 2022/03
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) in Oarai Research and Development Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing various reactor materials, irradiation techniques and instruments for more than 30 years. Among them, the development of self-powered neutron detectors (SPNDs) and gamma detectors (SPGDs) has been carried out, and several research results have been reported. However, most of the results are based on the design study of the detector development and the results of in-core irradiation tests and gamma irradiation tests using Cobalt-60. In this report, a numerical code is developed based on the paper "Neutron and Gamma-Ray Effects on Self-Powered In-Core Radiation Detectors" written by H.D. Warren and N.H. Shah in 1974, in order to theoretically evaluate the self-powered radiation detectors.
 ion source
ion sourceOguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Nammo, Kesao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Ueno, Akira
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011008_1 - 011008_7, 2021/03
A cesiated RF-driven negative hydrogen ion source was initiated to operate in September, 2014 in response to the need for upgrading J-PARC's linac beam current. The ion source mainly comprises a stainless-steel plasma chamber, a beam extractor and a large vacuum chamber equipped with two turbo molecular pumps, each having the pumping speed of 1500 L/s, for differential pumping. The user operation was started with the beam current of 33 mA from the ion source. We gradually increased both beam current and continuous operation time of the ion source. In July, 2018 (Run#79), approximately 2,200 hours operation was achieved with the typical beam current, pulse length and repetition rate of 47 mA, 300  s and 25 Hz, respectively. Since October, 2018 (Run#80), the ion source has been delivering a nominal beam current of approximately 60 mA.
s and 25 Hz, respectively. Since October, 2018 (Run#80), the ion source has been delivering a nominal beam current of approximately 60 mA.
Shibata, Takanori*; Sugimura, Takashi*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Sato, Masaharu*; Naito, Fujio*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Hasegawa, Kazuo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011009_1 - 011009_6, 2021/03
Upgrade of beam current in the Linac of Ibaraki Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (iBNCT) is one of the most important requirements to realize clinical trial. By 2018, the measurement of the produced neutrons characteristics and the neutron irradiation experiment for living cells have been done by producing 8-MeV proton beam current at the beryllium target with average current up to 2 mA. In order to satisfy the original clinical trial conditions, 5 mA average beam current is required at the target. For this goal, peak beam current extracted from the ion source should be increased to 60 mA from the present 30 mA with duty factor up to more than 10% (pulse width up to 1 ms and repetition rate up to more than 100 Hz). Stability of the peak current in the macro pulse is also important for the clinical application.
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Shibata, Keiichi; Ichihara, Akira; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.09002_1 - 09002_6, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:99.95(Nuclear Science & Technology) Mo/
Mo/ Tc generator by (n,
Tc generator by (n, ) method
) methodFujita, Yoshitaka; Seki, Misaki; Namekawa, Yoji*; Nishikata, Kaori; Kimura, Akihiro; Shibata, Akira; Sayato, Natsuki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Sano, Tadafumi*; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; et al.
KURNS Progress Report 2018, P. 155, 2019/08
no abstracts in English
 ion source
ion sourceOkoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Nammo, Kesao*; Shibata, Takanori*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Ueno, Akira; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.554 - 557, 2019/07
In September 2014, a cesiated RF-driven negative hydrogen ion (H ) source was initiated to operate at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The extracted H
) source was initiated to operate at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The extracted H beam current and the continuous operation time of the ion source have been improved upon their own records. In the RUN#79 (from April to July 2018), the ion source delivered the H
beam current and the continuous operation time of the ion source have been improved upon their own records. In the RUN#79 (from April to July 2018), the ion source delivered the H beam current of 47 mA to the post-accelerators for 2,201 hours continuously. In October 2018, the beam current from the ion source was increased to 60 mA in order to inject the beam current of 50 mA into the 3 GeV synchrotron. In the RUN#80 (from October to December 2018), the continuous operation time of 1,791 hours was achieved. For the past year, we had the antenna failures twice during the operation, and needed to replace to a spare ion source. We have been developed the J-PARC-made antenna by using a test-stand. Recent experiment result showed the continuous operation time of 2,083 hours was achieved with the J-PARC-made antenna.
beam current of 47 mA to the post-accelerators for 2,201 hours continuously. In October 2018, the beam current from the ion source was increased to 60 mA in order to inject the beam current of 50 mA into the 3 GeV synchrotron. In the RUN#80 (from October to December 2018), the continuous operation time of 1,791 hours was achieved. For the past year, we had the antenna failures twice during the operation, and needed to replace to a spare ion source. We have been developed the J-PARC-made antenna by using a test-stand. Recent experiment result showed the continuous operation time of 2,083 hours was achieved with the J-PARC-made antenna.
 beam dynamics in J-PARC LEBT
beam dynamics in J-PARC LEBTShibata, Takanori*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Liu, Y.*; Miura, Akihiko; Naito, Fujio*; Nammo, Kesao*; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Otani, Masashi*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 29th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2018) (Internet), p.519 - 521, 2019/01
Transport process of negative hydrogen ion (H ) in LEBT (Low Energy Beam Transport) is investigated by comparison of experimental and numerical results. A three dimensional Particle-In-Cell (PIC) particle transport model has been developed in order to take into account (i) axial magnetic field by two solenoids in J-PARC LEBT and (ii) radial electric field by space charge (SC) effect. Ratio of H
) in LEBT (Low Energy Beam Transport) is investigated by comparison of experimental and numerical results. A three dimensional Particle-In-Cell (PIC) particle transport model has been developed in order to take into account (i) axial magnetic field by two solenoids in J-PARC LEBT and (ii) radial electric field by space charge (SC) effect. Ratio of H beam particles inside the RFQ (Radio Frequency Quadrupole) acceptance to the total particles at the RFQ entrance is calculated for different current conditions in LEBT solenoid 1 and 2. The results are compared with RFQ transmission rate measured in the J-PARC linac commissioning. The double peak of RFQ transmission rate to the solenoid applied current seen in the measurement is explained by the calculation results. The results indicate that presence of the LEBT orifice for differential pumping plays a role as a collimator to reduce emittance at RFQ entrance.
beam particles inside the RFQ (Radio Frequency Quadrupole) acceptance to the total particles at the RFQ entrance is calculated for different current conditions in LEBT solenoid 1 and 2. The results are compared with RFQ transmission rate measured in the J-PARC linac commissioning. The double peak of RFQ transmission rate to the solenoid applied current seen in the measurement is explained by the calculation results. The results indicate that presence of the LEBT orifice for differential pumping plays a role as a collimator to reduce emittance at RFQ entrance.
Shinto, Katsuhiro; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shibata, Takanori*; Nammo, Kesao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Namekawa, Yuya*; Ueno, Akira; Oguri, Hidetomo
AIP Conference Proceedings 2052, p.050002_1 - 050002_7, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:93.93(Physics, Applied)In the 2017/2018 campaign, the J-PARC cesiated rf-driven negative hydrogen (H ) ion source producing H
) ion source producing H beam with the beam current of 47 mA accomplished three long-term operations more than 2,000 hours without any serious issues. On the final day of this campaign, the ion source produced an H
beam with the beam current of 47 mA accomplished three long-term operations more than 2,000 hours without any serious issues. On the final day of this campaign, the ion source produced an H beam current of 72 mA so that the linac commissioning group could demonstrate the beam current of 60 mA at the linac exit. We are also conducting an endurance test of a J-PARC-made antenna at a test bench. The antenna achieved the operation time approximately 1,400 hours.
beam current of 72 mA so that the linac commissioning group could demonstrate the beam current of 60 mA at the linac exit. We are also conducting an endurance test of a J-PARC-made antenna at a test bench. The antenna achieved the operation time approximately 1,400 hours.
 filament arc-driven multi-cusp ion source for iBNCT
filament arc-driven multi-cusp ion source for iBNCTShibata, Takanori*; Takagi, Akira*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Sugimura, Takashi*; Nammo, Kesao*; Naito, Fujio*; Kobayashi, Hitoshi*; Kurihara, Toshikazu*; Honda, Yosuke*; Sato, Masaharu*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.385 - 387, 2018/10
 ion source
ion sourceShinto, Katsuhiro; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Shibata, Takanori*; Nammo, Kesao*; Namekawa, Yuya*; Ueno, Akira; Oguri, Hidetomo
AIP Conference Proceedings 2011, p.050018_1 - 050018_3, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:82.15(Physics, Applied)Shibata, Takanori*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Takagi, Akira*; Oguri, Hidetomo; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Nammo, Kesao*; Naito, Fujio*
AIP Conference Proceedings 2011, p.020008_1 - 020008_3, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:91.75(Physics, Applied) pellets for Mo-99 production
pellets for Mo-99 productionFujita, Yoshitaka; Nishikata, Kaori; Namekawa, Yoji*; Kimura, Akihiro; Shibata, Akira; Sayato, Natsuki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Sano, Tadafumi*; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; Zhang, J.*
KURRI Progress Report 2017, P. 126, 2018/08
no abstracts in English
 ion source
ion sourceOkoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Nammo, Kesao*; Shibata, Takanori*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Ueno, Akira; Namekawa, Yuya*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.889 - 892, 2018/08
In 2017-2018 campaign, three times of long-time operation more than 2,000 hours of the J-PARC rf-driven negative hydrogen (H ) ion source producing H
) ion source producing H beam with the beam current of 47 mA were successfully achieved without any serious problems. At the final day of this campaign, the ion source produced an H
beam with the beam current of 47 mA were successfully achieved without any serious problems. At the final day of this campaign, the ion source produced an H beam with the current of 72 mA in order to demonstrate the beam current of 60 mA at the linac exit. We are also conducting an endurance test of a J-PARC-made antenna at a test bench. Approximately 1,400-hour operation with the antenna was successfully performed.
beam with the current of 72 mA in order to demonstrate the beam current of 60 mA at the linac exit. We are also conducting an endurance test of a J-PARC-made antenna at a test bench. Approximately 1,400-hour operation with the antenna was successfully performed.
Shibata, Akira
JAEA-Review 2017-035, 184 Pages, 2018/03
The degradation of materials, the exposing to high-dose neutron and gamma irradiation, the high temperature and the high pressure water environment are important issues for nuclear reactors. Due to the public concern, plants will inevitably be used for a long term, thereby facing problems of degradation materials due to ageing. In addition, "high burn-up" is being promoted. This prolongs period of operation cycles. The major objective of the thesis is to understand the degradation phenomenon of reactor materials and to improve the evaluation test techniques. Zirconium alloys have been used as fuel cladding material. Advanced Zr-Nb alloys gradually replaced Zircaloy-4 in PWR. Corrosion tests under simulated PWR water conditions were conducted on those materials and formation of oxide layers was studied via EIS. Mechanical properties of oxide layers on Zircaloy-4 and M5 were evaluated by Nano indentation with FEM analysis. Stainless steel is widely used as structure material of nuclear reactors. Tensile tests and SSRTs were conducted on specimens irradiated to higher than threshold fluence of IASCC. The integrity and the IASCC susceptibility were evaluated.
 ion source
ion sourceOkoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Takagi, Akira*; Nammo, Kesao*; Ueno, Akira; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 14th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.651 - 654, 2017/12
Operation of a cesiated rf-driven negative hydrogen ion source was initiated in September 2014 in response to the requirements of beam current upgrade in J-PARC linac. Delivery of the required beam current from the ion source to the J-PARC accelerators has been successfully performed. In 2016-2017 campaign, continuous operation of the ion source for approximately 1,845 hours (from April to July 2017) was achieved with beam current of 47 mA.
Iwamoto, Osamu; Shibata, Keiichi; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Ichihara, Akira; Nakayama, Shinsuke
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.02005_1 - 02005_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.21(Nuclear Science & Technology) ion source
ion sourceOguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Asano, Hiroyuki; Shibata, Takanori*; Nammo, Kesao*; Ueno, Akira; Shinto, Katsuhiro
AIP Conference Proceedings 1869, p.030053_1 - 030053_7, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:89.08(Physics, Applied)A cesiated RF-driven negative hydrogen ion source was started to operate in September, 2014 in response to the need for upgrading J-PARC's linac beam current. The ion source mainly comprises a stainless-steel plasma chamber, a beam extractor, and a large vacuum chamber with two turbo molecular pumps of 1500 L/s for differential pumping. The ion source has been successfully providing the required beam current to the accelerator without any significant issues other than a single-incident antenna failure occurred in October, 2014. Continuous operation for approximately 1,000 h was achieved with a beam current and duty factor of 45 mA and 1.25 % (0.5 msec and 25 Hz), respectively. In this paper, we will present the some operation parameters and the beam stability through the long-term user operation.
Shibata, Takanori*; Asano, Hiroyuki; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Naito, Fujio*; Nammo, Kesao*; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Takagi, Akira*; Ueno, Akira
AIP Conference Proceedings 1869, p.030017_1 - 030017_11, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:85.09(Physics, Applied)From September 2014, operation of Cs-seeded, multi-cusp, Radio Frequency (RF), hydrogen negative ion source (J-PARC source) has been started. The operation for 1,000 hours of J-PARC source has been achieved with H beam current 45 mA and duty factor of 1.25 % (0.5 msec and 25 Hz). In the present study, mechanisms of hydrogen plasma ramp-up and H
beam current 45 mA and duty factor of 1.25 % (0.5 msec and 25 Hz). In the present study, mechanisms of hydrogen plasma ramp-up and H production/transport processes in the steady state (which lasts for few 100 us) are investigated by numerical modeling for RF plasma. In the simulation, charged particle (e, H
production/transport processes in the steady state (which lasts for few 100 us) are investigated by numerical modeling for RF plasma. In the simulation, charged particle (e, H , H
, H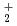 , and Cs
, and Cs ) transport, time variations of inductive and capacitive electromagnetic field, collision processes between charged and neutral (H, H
) transport, time variations of inductive and capacitive electromagnetic field, collision processes between charged and neutral (H, H ) particles are solved simultaneously. The model is applied to KEK parallel computation System-A with 32 nodes and 256 GB memory in order to solve high density RF plasma up to around 10
) particles are solved simultaneously. The model is applied to KEK parallel computation System-A with 32 nodes and 256 GB memory in order to solve high density RF plasma up to around 10 m
m with adequate statisticity. In the presentation, time variations of plasma density distributions and average energy are shown with electromagnetic field variations.
with adequate statisticity. In the presentation, time variations of plasma density distributions and average energy are shown with electromagnetic field variations.
Shibata, Takanori*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Liu, Y.*; Maruta, Tomofumi*; Naito, Fujio*; Takagi, Akira*; Asano, Hiroyuki; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Miura, Akihiko; Oguri, Hidetomo; et al.
Proceedings of 28th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2016) (Internet), p.251 - 253, 2017/05
After upgrade of J-PARC Linac in 2014, Low Energy Beam Transport (LEBT) beam commissioning of the J-PARC LINAC has been made for improving H beam intensity extracted from Linac. Currents of two solenoid coils and steering magnets in LEBT are optimized with extraction and acceleration voltages for static acceleration in ion source (IS) which decides on an initial emittance diagram of H
beam intensity extracted from Linac. Currents of two solenoid coils and steering magnets in LEBT are optimized with extraction and acceleration voltages for static acceleration in ion source (IS) which decides on an initial emittance diagram of H beam. As a result of LEBT and IS parameter optimization, beam transmission rate of RFQ has been reached up to 96% in 50 mA H
beam. As a result of LEBT and IS parameter optimization, beam transmission rate of RFQ has been reached up to 96% in 50 mA H current operation. Moreover, PIC-MC (Particle-In-Cell Monte-Carlo) simulation models developed for H
current operation. Moreover, PIC-MC (Particle-In-Cell Monte-Carlo) simulation models developed for H transport in LEBT. Comparison between experimental and numerical results are presented to clarify beam physics from IS exit to RFQ entrance.
transport in LEBT. Comparison between experimental and numerical results are presented to clarify beam physics from IS exit to RFQ entrance.