Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Fe
Fe O
O grown on Al
grown on Al O
O ; Effects of postdeposition annealing studied by XMCD
; Effects of postdeposition annealing studied by XMCD野中 洋亮*; 若林 勇希*; 芝田 悟朗; 坂本 祥哉*; 池田 啓祐*; Chi, Z.*; Wan, Y.*; 鈴木 雅弘*; 田中 新*; 田中 雅明*; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(4), p.044413_1 - 044413_10, 2023/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We study the electronic and magnetic states of as-grown and annealed  Fe
Fe O
O (111)/Al
(111)/Al O3(111) (
O3(111) (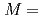 Co, Ni) thin films with various thicknesses grown on Si(111) substrates with the
Co, Ni) thin films with various thicknesses grown on Si(111) substrates with the  -Al
-Al O
O (111)buffer layers by using X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), to investigate magnetically dead layers in these films. Although the magnetically dead layers in the as-grown samples are formed near the interface with the Al
(111)buffer layers by using X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), to investigate magnetically dead layers in these films. Although the magnetically dead layers in the as-grown samples are formed near the interface with the Al O
O buffer layer, we reveal that ferrimagnetic order is partially recovered by postdeposition annealing at 973 K for 48 hours in air. By analyzing the line shapes of the XAS and XMCD spectra, we conclude that, in the dead layers, there are a significant number of vacancies at the
buffer layer, we reveal that ferrimagnetic order is partially recovered by postdeposition annealing at 973 K for 48 hours in air. By analyzing the line shapes of the XAS and XMCD spectra, we conclude that, in the dead layers, there are a significant number of vacancies at the 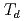 sites of the spinel structure, which may be the microscopic origin of the degraded ferrimagnetic order in the
sites of the spinel structure, which may be the microscopic origin of the degraded ferrimagnetic order in the  Fe
Fe O
O thin films.
thin films.
 TaS
TaS のX線磁気円二色性による研究; Fe
のX線磁気円二色性による研究; Fe TiS
TiS との比較
との比較芝田 悟朗; Won, C.*; Kim, J.*; 野中 洋亮*; 池田 啓祐*; Wan, Y.*; 鈴木 雅弘*; 小出 常晴*; 田中 新*; Cheong, S.-W.*; et al.
Photon Factory Activity Report 2022 (インターネット), 2 Pages, 2023/00
Feをインターカレートした遷移金属ダイカルコゲナイド化合物Fe TiS
TiS およびFe
およびFe TaS
TaS は、巨大な保磁力および垂直磁気異方性を示す強磁性体になることが知られている。我々は以前、Fe
は、巨大な保磁力および垂直磁気異方性を示す強磁性体になることが知られている。我々は以前、Fe TiS
TiS についてのX線磁気円二色性(XMCD)実験の結果から、Fe
についてのX線磁気円二色性(XMCD)実験の結果から、Fe の凍結していない軌道磁気モーメントが結晶場の1次摂動によって直接磁気異方性エネルギーを生むことを明らかにした。今回、Fe
の凍結していない軌道磁気モーメントが結晶場の1次摂動によって直接磁気異方性エネルギーを生むことを明らかにした。今回、Fe TiS
TiS よりもさらに強い磁気異方性を示す遷移金属ダイカルコゲナイドFe
よりもさらに強い磁気異方性を示す遷移金属ダイカルコゲナイドFe TaS
TaS について同様にXMCD実験を行い、磁気異方性の強さが何によって左右されているかを探ることを試みた。
について同様にXMCD実験を行い、磁気異方性の強さが何によって左右されているかを探ることを試みた。
 Mn
Mn Te studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
Te studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroismVerma, V.*; 坂本 祥哉*; 石川 弘一郎*; Singh, V. R.*; 石上 啓介*; 芝田 悟朗; 門野 利治*; 小出 常晴*; 黒田 真司*; 藤森 淳*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 642, p.414129_1 - 414129_5, 2022/10
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:53.42(Physics, Condensed Matter)The prototypical diluted magnetic semiconductor Cd Mn
Mn Te is a spin glass (
Te is a spin glass (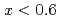 ) or an antiferromagnet (
) or an antiferromagnet (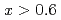 ) but becomes ferromagnetic upon doping with a small amount of Cr atoms. To investigate the origin of the ferromagnetism in Cd
) but becomes ferromagnetic upon doping with a small amount of Cr atoms. To investigate the origin of the ferromagnetism in Cd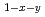 Mn
Mn Cr
Cr Te, we have studied its element specific magnetic properties by X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD). Measured XAS and XMCD spectra indicate that both Cr and Mn atoms are divalent and that the magnetic moments of Cr and Mn are aligned parallel. By analyzing the element-specific magnetization curves, we conclude that Cr doping leads to the formation of ferromagnetic or superparamagnetic clusters consisting of several Cr ions surrounded by a much larger number of Mn ions.
Te, we have studied its element specific magnetic properties by X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD). Measured XAS and XMCD spectra indicate that both Cr and Mn atoms are divalent and that the magnetic moments of Cr and Mn are aligned parallel. By analyzing the element-specific magnetization curves, we conclude that Cr doping leads to the formation of ferromagnetic or superparamagnetic clusters consisting of several Cr ions surrounded by a much larger number of Mn ions.
 K
K (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )
) As
As studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering鈴木 博人*; Zhao, G.*; 岡本 淳*; 坂本 祥哉*; Chen, Z.-Y.*; 野中 洋亮*; 芝田 悟朗; Zhao, K.*; Chen, B.*; Wu, W.-B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(6), p.064710_1 - 064710_5, 2022/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The magnetic properties and the electronic excitations of the new diluted magnetic semiconductor Ba K
K (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )
) As
As have been studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS). The sum rule analysis of the XMCD spectra indicates that the Mn atoms are in the high-spin configurations of
have been studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS). The sum rule analysis of the XMCD spectra indicates that the Mn atoms are in the high-spin configurations of 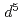 , whereas the presence of competing ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic interactions between the Mn ions reduces the net spin moment. Based on a comparison of the RIXS line shapes with those of Ga
, whereas the presence of competing ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic interactions between the Mn ions reduces the net spin moment. Based on a comparison of the RIXS line shapes with those of Ga Mn
Mn As, it is concluded that the ground state of Mn in Ba
As, it is concluded that the ground state of Mn in Ba K
K (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )
) As
As consists of both the
consists of both the 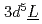 and
and 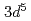 electron configurations.
electron configurations.
小林 正起*; Anh, L. D.*; 鈴木 雅弘*; 金田-高田 真悟*; 竹田 幸治; 藤森 伸一; 芝田 悟朗*; 田中 新*; 田中 雅明*; 大矢 忍*; et al.
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 15(6), p.064019_1 - 064019_10, 2021/06
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:27.71(Physics, Applied)A fundamental understanding of the interfacial magnetic properties in ferromagnetic heterostructures is essential for utilizing ferromagnetic materials for spintronic device applications. Here, we investigate the interfacial magnetic and electronic structures of epitaxial single-crystalline LaAlO (LAO)/La
(LAO)/La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO (LSMO)/Nb:SrTiO
(LSMO)/Nb:SrTiO (Nb:STO) heterostructures with varying LSMO layer thicknesses, in which the magnetic anisotropy strongly changes with the LSMO thickness due to the delicate balance between strains originating from both the Nb:STO and LAO layers, using X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and photoemission spectroscopy. We successfully detect the clear change of the magnetic behavior of the Mn ions concomitant with the thickness-dependent metal-insulator transition. Our results suggest that the double-exchange interaction induces ferromagnetism in the metallic LSMO film under tensile strain caused by the STO substrate, while the superexchange interaction determines the magnetic behavior in the insulating LSMO film under compressive strain originating from the top LAO layer. The change in strain, depending on LSMO layer thickness, is confirmed by scanning transmission electron microscopy. Based on those findings, the formation of a magnetic dead layer near the LAO/LSMO interface is attributed to competition between the superexchange interaction via Mn
(Nb:STO) heterostructures with varying LSMO layer thicknesses, in which the magnetic anisotropy strongly changes with the LSMO thickness due to the delicate balance between strains originating from both the Nb:STO and LAO layers, using X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and photoemission spectroscopy. We successfully detect the clear change of the magnetic behavior of the Mn ions concomitant with the thickness-dependent metal-insulator transition. Our results suggest that the double-exchange interaction induces ferromagnetism in the metallic LSMO film under tensile strain caused by the STO substrate, while the superexchange interaction determines the magnetic behavior in the insulating LSMO film under compressive strain originating from the top LAO layer. The change in strain, depending on LSMO layer thickness, is confirmed by scanning transmission electron microscopy. Based on those findings, the formation of a magnetic dead layer near the LAO/LSMO interface is attributed to competition between the superexchange interaction via Mn 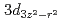 orbitals under compressive strain and the double-exchange interaction via the
orbitals under compressive strain and the double-exchange interaction via the 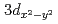 orbitals. These findings provide key aspects of ferromagnetic oxide heterostructures for the development of spintronic device applications.
orbitals. These findings provide key aspects of ferromagnetic oxide heterostructures for the development of spintronic device applications.
 ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb; X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studies
ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb; X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studies坂本 祥哉*; Tu, N. T.*; 竹田 幸治; 藤森 伸一; Hai, P. N.*; Anh, L. D.*; 若林 勇希*; 芝田 悟朗*; 堀尾 眞史*; 池田 啓祐*; et al.
Physical Review B, 100(3), p.035204_1 - 035204_8, 2019/07
The electronic structure and the magnetism of the ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb, whose Curie temperature  can exceed room temperature, were investigated by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), and resonance photoemission spectroscopy (RPES). The line-shape analyses of the XAS and XMCD spectra suggest that the ferromagnetism is of intrinsic origin. The orbital magnetic moments deduced using XMCD sum rules were found to be large, indicating that there is a considerable 3
can exceed room temperature, were investigated by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), and resonance photoemission spectroscopy (RPES). The line-shape analyses of the XAS and XMCD spectra suggest that the ferromagnetism is of intrinsic origin. The orbital magnetic moments deduced using XMCD sum rules were found to be large, indicating that there is a considerable 3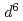 contribution to the ground state of Fe. From RPES, we observed a strong dispersive Auger peak and nondispersive resonantly enhanced peaks in the valence-band spectra. The latter is a fingerprint of the correlated nature of Fe 3
contribution to the ground state of Fe. From RPES, we observed a strong dispersive Auger peak and nondispersive resonantly enhanced peaks in the valence-band spectra. The latter is a fingerprint of the correlated nature of Fe 3 electrons, whereas the former indicates their itinerant nature. It was also found that the Fe 3
electrons, whereas the former indicates their itinerant nature. It was also found that the Fe 3 states have a finite contribution to the density of states at the Fermi energy. These states, presumably consisting of majority-spin
states have a finite contribution to the density of states at the Fermi energy. These states, presumably consisting of majority-spin  -
- hybridized states or minority-spin e states, would be responsible for the ferromagnetic order in this material.
hybridized states or minority-spin e states, would be responsible for the ferromagnetic order in this material.
 ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb; X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studies
ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb; X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studies坂本 祥哉*; Tu, N. T.*; 竹田 幸治; 藤森 伸一; Hai, P. N.*; Anh, L. D.*; 若林 勇希*; 芝田 悟朗*; 堀尾 眞史*; 池田 啓祐*; et al.
Physical Review B, 100(3), p.035204_1 - 035204_8, 2019/07
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:66.08(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The electronic structure and the magnetism of the ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga,Fe)Sb, whose Curie temperature  can exceed room temperature, were investigated by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), and resonance photoemission spectroscopy (RPES). The line-shape analyses of the XAS and XMCD spectra suggest that the ferromagnetism is of intrinsic origin. The orbital magnetic moments deduced using XMCD sum rules were found to be large, indicating that there is a considerable 3
can exceed room temperature, were investigated by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD), and resonance photoemission spectroscopy (RPES). The line-shape analyses of the XAS and XMCD spectra suggest that the ferromagnetism is of intrinsic origin. The orbital magnetic moments deduced using XMCD sum rules were found to be large, indicating that there is a considerable 3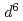 contribution to the ground state of Fe. From RPES, we observed a strong dispersive Auger peak and nondispersive resonantly enhanced peaks in the valence-band spectra. The latter is a fingerprint of the correlated nature of Fe 3
contribution to the ground state of Fe. From RPES, we observed a strong dispersive Auger peak and nondispersive resonantly enhanced peaks in the valence-band spectra. The latter is a fingerprint of the correlated nature of Fe 3 electrons, whereas the former indicates their itinerant nature. It was also found that the Fe 3
electrons, whereas the former indicates their itinerant nature. It was also found that the Fe 3 states have a finite contribution to the density of states at the Fermi energy. These states would be responsible for the ferromagnetic order in this material.
states have a finite contribution to the density of states at the Fermi energy. These states would be responsible for the ferromagnetic order in this material.
 VFeAsO
VFeAsO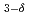 studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism堀尾 眞史*; 竹田 幸治; 並木 宏允*; 片桐 隆雄*; 若林 勇希*; 坂本 祥哉*; 野中 洋亮*; 芝田 悟朗*; 池田 啓祐*; 斎藤 祐児; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(10), p.105001_1 - 105001_2, 2018/10
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:21.2(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have performed X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) measurements on the iron-based superconductor Sr VFeAsO
VFeAsO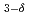 to study the origin of weak ferromagnetism (WFM) reported for this compound. While Fe 3d electrons show a magnetic response similar to the other iron pnictides, signals from V 3d electrons remain finite at zero magnetic field and may be responsible for the WFM.
to study the origin of weak ferromagnetism (WFM) reported for this compound. While Fe 3d electrons show a magnetic response similar to the other iron pnictides, signals from V 3d electrons remain finite at zero magnetic field and may be responsible for the WFM.
 Co
Co )Fe
)Fe O
O (x=0-1) layers on Si(111) studied by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
(x=0-1) layers on Si(111) studied by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism若林 勇希*; 野中 洋亮*; 竹田 幸治; 坂本 祥哉*; 池田 啓祐*; Chi, Z.*; 芝田 悟朗*; 田中 新*; 斎藤 祐児; 山上 浩志; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 2(10), p.104416_1 - 104416_12, 2018/10
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:37.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We study the electronic structure and magnetic properties of epitaxial (Ni Co
Co )Fe
)Fe O
O (111) layers with thicknesses
(111) layers with thicknesses  = 1.7 - 5.2 nm grown on Al
= 1.7 - 5.2 nm grown on Al O
O (111)/Si(111) structures. We revealed the crystallographic (octahedral
(111)/Si(111) structures. We revealed the crystallographic (octahedral 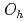 or tetrahedral
or tetrahedral 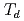 ) sites and the valences of the Fe, Co, and Ni cations using experimental soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism spectra and configuration-interaction cluster-model calculation.
) sites and the valences of the Fe, Co, and Ni cations using experimental soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism spectra and configuration-interaction cluster-model calculation.
 Mn
Mn granular thin films
granular thin films若林 勇希*; 秋山 了太*; 竹田 幸治; 堀尾 眞史*; 芝田 悟朗*; 坂本 祥哉*; 伴 芳祐*; 斎藤 祐児; 山上 浩志; 藤森 淳*; et al.
Physical Review B, 95(1), p.014417_1 - 014417_6, 2017/01
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:45.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ge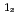 Mn
Mn (GeMn) granular thin films are a unique and promising material for spintronic applications owing to their large positive magnetoresistance (MR). The microscopic origin of the MR has not yet been clarified. Here, we develop a method to separately investigate the magnetic properties of the nanoparticles and the matrix, utilizing the extremely high sensitivity of X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) to the local magnetic state of each atom. We find that the MR ratio is proportional to the product of the magnetizations originating from the nanoparticles and the matrix. This result indicates that the spin-polarized holes in the nanoparticles penetrate into the matrix and that these holes undergo first order magnetic scattering by the paramagnetic Mn atoms in the matrix, which induces the large MR.
(GeMn) granular thin films are a unique and promising material for spintronic applications owing to their large positive magnetoresistance (MR). The microscopic origin of the MR has not yet been clarified. Here, we develop a method to separately investigate the magnetic properties of the nanoparticles and the matrix, utilizing the extremely high sensitivity of X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) to the local magnetic state of each atom. We find that the MR ratio is proportional to the product of the magnetizations originating from the nanoparticles and the matrix. This result indicates that the spin-polarized holes in the nanoparticles penetrate into the matrix and that these holes undergo first order magnetic scattering by the paramagnetic Mn atoms in the matrix, which induces the large MR.
 -type ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As:Be studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
-type ferromagnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As:Be studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism坂本 祥哉*; Anh, L. D.*; Hai, P. N.*; 芝田 悟朗*; 竹田 幸治; 小林 正起*; 高橋 文雄*; 小出 常晴*; 田中 雅明*; 藤森 淳*
Physical Review B, 93(3), p.035203_1 - 035203_6, 2016/01
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:63.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to investigate the mechanism of ferromagnetic ordering in the new  -type magnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As codoped with Be, we have performed X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) studies. The spectral line shapes suggest that the ferromagnetism is intrinsic, originating from Fe atoms incorporated into the zinc-blende-type InAs lattice. The magnetization curves of Fe measured by XMCD were well reproduced by the superposition of a Langevin function representing superparamagnetic (SPM) behavior of nanoscale ferromagnetic domains and a
-type magnetic semiconductor (In,Fe)As codoped with Be, we have performed X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) studies. The spectral line shapes suggest that the ferromagnetism is intrinsic, originating from Fe atoms incorporated into the zinc-blende-type InAs lattice. The magnetization curves of Fe measured by XMCD were well reproduced by the superposition of a Langevin function representing superparamagnetic (SPM) behavior of nanoscale ferromagnetic domains and a  -linear function representing Curie-Weiss paramagnetism even much above the Curie temperatures. The data at 20 K showed a deviation from the Langevin behavior, suggesting a gradual establishment of macroscopic ferromagnetism on lowering temperature. The existence of nanoscale ferromagnetic domains indicated by the SPM behavior suggests spatial fluctuations of Fe concentration on the nanoscale.
-linear function representing Curie-Weiss paramagnetism even much above the Curie temperatures. The data at 20 K showed a deviation from the Langevin behavior, suggesting a gradual establishment of macroscopic ferromagnetism on lowering temperature. The existence of nanoscale ferromagnetic domains indicated by the SPM behavior suggests spatial fluctuations of Fe concentration on the nanoscale.
 thin films
thin films石上 啓介*; 吉松 公平*; 豊田 大介*; 滝沢 優*; 吉田 鉄平*; 芝田 悟朗*; 原野 貴幸*; 高橋 文雄*; 門野 利治*; Verma, V. K.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 92(6), p.064402_1 - 064402_5, 2015/08
被引用回数:45 パーセンタイル:84.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Thin films of the ferromagnetic metal SrRuO (SRO) show a varying easy magnetization axis depending on the epitaxial strain, and undergo a metal-to-insulator transition with decreasing film thickness. We have investigated the magnetic properties of SRO thin films with varying thicknesses fabricated on SrTiO
(SRO) show a varying easy magnetization axis depending on the epitaxial strain, and undergo a metal-to-insulator transition with decreasing film thickness. We have investigated the magnetic properties of SRO thin films with varying thicknesses fabricated on SrTiO (001) substrates by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism at the Ru M2,3 edge. Results have shown that, with decreasing film thickness, the film changes from ferromagnetic to nonmagnetic at around 3 monolayer thickness, consistent with previous magnetization and magneto-optical Kerr effect measurements. The orbital magnetic moment perpendicular to the film was found to be 0.1
(001) substrates by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism at the Ru M2,3 edge. Results have shown that, with decreasing film thickness, the film changes from ferromagnetic to nonmagnetic at around 3 monolayer thickness, consistent with previous magnetization and magneto-optical Kerr effect measurements. The orbital magnetic moment perpendicular to the film was found to be 0.1 B/Ru, and remained nearly unchanged with decreasing film thickness while the spin magnetic moment decreases. A mechanism for the formation of the orbital magnetic moment is discussed based on the electronic structure of the compressively strained SRO film.
B/Ru, and remained nearly unchanged with decreasing film thickness while the spin magnetic moment decreases. A mechanism for the formation of the orbital magnetic moment is discussed based on the electronic structure of the compressively strained SRO film.
 -coated FePt nanoparticles studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
-coated FePt nanoparticles studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism高橋 文雄*; 門野 利治*; 山本 真平*; Singh, V. R.*; Verma, V.*; 石上 啓介*; 芝田 悟朗*; 原野 貴幸*; 竹田 幸治; 岡根 哲夫; et al.
Physical Review B, 90(2), p.024423_1 - 024423_5, 2014/07
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:44.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have investigated the spin and orbital magnetic moments of Fe in FePt nanoparticles in the 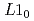 -ordered phase coated with SiO
-ordered phase coated with SiO by X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) measurements at the Fe
by X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) measurements at the Fe 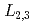 absorption edges. The magnetic coercivity (H
absorption edges. The magnetic coercivity (H ) was found to be as large as 1.8 T at room temperature, 3 times larger than the thin film value and 50 times larger than that of the gas phase condensed nanoparticles. The hysteresis curve is well explained by the Stoner-Wohlfarth model for noninteracting single-domain nanoparticles with the H
) was found to be as large as 1.8 T at room temperature, 3 times larger than the thin film value and 50 times larger than that of the gas phase condensed nanoparticles. The hysteresis curve is well explained by the Stoner-Wohlfarth model for noninteracting single-domain nanoparticles with the H distributed from 1 to 5 T.
distributed from 1 to 5 T.
 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO thin films studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
thin films studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism芝田 悟朗*; 吉松 公平*; 坂井 延寿*; Singh, V. R.*; Verma, V.*; 石上 啓介*; 原野 貴幸*; 門野 利治*; 竹田 幸治; 岡根 哲夫; et al.
Physical Review B, 89(23), p.235123_1 - 235123_5, 2014/06
被引用回数:23 パーセンタイル:66.6(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Metallic transition-metal oxides undergo a metal-to-insulator transition (MIT) as the film thickness decreases across a critical thickness of several monolayers (MLs), but its driving mechanism remains controversial. We have studied the thickness-dependent MIT of the ferromagnetic metal La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO by X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism. The results suggest that the ferromagnetic phase gradually and most likely inhomogeneously turns into the paramagnetic phase and both phases abruptly become insulating at the critical thickness.
by X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism. The results suggest that the ferromagnetic phase gradually and most likely inhomogeneously turns into the paramagnetic phase and both phases abruptly become insulating at the critical thickness.
芝田 悟朗
no journal, ,
Layered transition-metal dichalcogenides with the 1T-CdI -type crystal structure are known to exhibit a wide variety of electric and magnetic properties by intercalating various transition-metal atoms of different concentrations between adjacent layers. Among them, iron-intercalated titanium disulfides Fe
-type crystal structure are known to exhibit a wide variety of electric and magnetic properties by intercalating various transition-metal atoms of different concentrations between adjacent layers. Among them, iron-intercalated titanium disulfides Fe TiS
TiS and tantalum disulfides Fe
and tantalum disulfides Fe TaS
TaS are ferromagnets which exhibits strong perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) with large coercive fields of a few tesla. It is reported that Fe
are ferromagnets which exhibits strong perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) with large coercive fields of a few tesla. It is reported that Fe TaS
TaS shows stronger PMA than Fe
shows stronger PMA than Fe TiS
TiS , presumably due to the stronger spin-orbit interaction (SOI) of Ta. In the present study, in order to elucidate the microscopic origin of the strong PMA in these compounds, the electronic structure and magnetism of single-crystalline Fe
, presumably due to the stronger spin-orbit interaction (SOI) of Ta. In the present study, in order to elucidate the microscopic origin of the strong PMA in these compounds, the electronic structure and magnetism of single-crystalline Fe TiS
TiS and Fe
and Fe TaS
TaS have been investigated via X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD). From the spectral line shapes of XAS and XMCD, the valence of Fe is shown to be essentially 2+, whereas Ti is in an itinerant electronic state between 3+ and 4+. This shows that electrons are doped from the intercalated Fe atoms into the host TiS
have been investigated via X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD). From the spectral line shapes of XAS and XMCD, the valence of Fe is shown to be essentially 2+, whereas Ti is in an itinerant electronic state between 3+ and 4+. This shows that electrons are doped from the intercalated Fe atoms into the host TiS and TaS
and TaS . Notably, clear differences in the spectral line shapes of XMCD at the Fe
. Notably, clear differences in the spectral line shapes of XMCD at the Fe 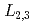 edges are observed between Fe
edges are observed between Fe TiS
TiS and Fe
and Fe TaS
TaS despite the similarity of the crystal structures. This may be attributed to the different SOI strength between these compounds. Based on the configuration-interaction cluster-model calculations, the observed changes in the spectral line shapes can be qualitatively reproduced by virtually increasing SOI of Fe 3
despite the similarity of the crystal structures. This may be attributed to the different SOI strength between these compounds. Based on the configuration-interaction cluster-model calculations, the observed changes in the spectral line shapes can be qualitatively reproduced by virtually increasing SOI of Fe 3 electrons.
electrons.
 CaOsO
CaOsO の磁気転移・多極子秩序に関する研究
の磁気転移・多極子秩序に関する研究芝田 悟朗; 林 浩章*; 河村 直己*; 岡本 淳*; Huang, D.-J.*; Streltsov, S.*; 山浦 一成*; 藤森 淳*
no journal, ,
近年、スピン-軌道相互作用(SOI)の強い立方晶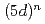 電子系における多極子秩序状態が盛んに議論されている。その中で
電子系における多極子秩序状態が盛んに議論されている。その中で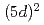 系ダブルペロブスカイト(DP)型酸化物Ba
系ダブルペロブスカイト(DP)型酸化物Ba CaOsO
CaOsO は、
は、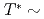 50Kで帯磁率の異常を示し、
50Kで帯磁率の異常を示し、 SRによる
SRによる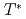 以下での時間反転対称性の破れも確認されている一方で、中性子散乱では
以下での時間反転対称性の破れも確認されている一方で、中性子散乱では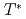 以下で反強磁性ピークが観測されないという特異な磁性を示す。これと結晶構造が最低温まで立方晶であることから、磁気八極子秩序の可能性が指摘されており、その理論的な予言もなされているが、DP型結晶で
以下で反強磁性ピークが観測されないという特異な磁性を示す。これと結晶構造が最低温まで立方晶であることから、磁気八極子秩序の可能性が指摘されており、その理論的な予言もなされているが、DP型結晶で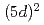 系は四極子秩序を示すという理論予測もあり、
系は四極子秩序を示すという理論予測もあり、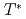 以下での秩序状態について合意は得られていない。本研究では、Os
以下での秩序状態について合意は得られていない。本研究では、Os 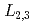 端硬X線磁気円二色性(XMCD)により、磁場中におけるBa
端硬X線磁気円二色性(XMCD)により、磁場中におけるBa CaOsO
CaOsO 多結晶のOs 5
多結晶のOs 5 電子状態の解明を試みた。観測されたXMCDスペクトルは、3
電子状態の解明を試みた。観測されたXMCDスペクトルは、3 , 4
, 4 電子系のXMCDスペクトルと異なり、
電子系のXMCDスペクトルと異なり、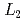 端で比較的大きなXMCD (
端で比較的大きなXMCD ( 1%)を示すのに対して
1%)を示すのに対して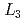 端のXMCDは弱く(
端のXMCDは弱く( 0.1%)、強いSOIによる大きな軌道磁気モーメントの存在が示唆された。X線吸収(XAS), XMCDスペクトルの概形は立方晶を仮定した原子多重項計算によって再現することができ、XASの2本のピーク分裂が
0.1%)、強いSOIによる大きな軌道磁気モーメントの存在が示唆された。X線吸収(XAS), XMCDスペクトルの概形は立方晶を仮定した原子多重項計算によって再現することができ、XASの2本のピーク分裂が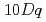 (
( 4eV)を反映していること、他の5
4eV)を反映していること、他の5 電子系と同様にクーロン相互作用は弱くSOIが強いことが示された。
電子系と同様にクーロン相互作用は弱くSOIが強いことが示された。
竹田 幸治; 土井 玲祐; 芝田 悟朗; 矢板 毅
no journal, ,
日本原子力研究開発機構は、大型放射光施設SPring-8において放射性物質の取り扱いが可能なRI実験棟に引き込まれた硬X線(BL22XU)および軟X線(BL23SU)の2本の専用ビームラインを運用している。本発表ではRI実験棟のBL23SUの最下流に設置・整備してきた走査型透過X線顕微鏡(STXM)装置を紹介する。本装置は、福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉作業に資するための放射性微粒子の分析や希土類抽出技術の開発、アクチノイド基礎科学研究等の展開を目的として導入された。本装置概要とこれまでの立ち上げ状況、および今後の計画について報告する。
 CaOsO
CaOsO のXMCDによる研究
のXMCDによる研究芝田 悟朗
no journal, ,
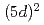 系ダブルペロブスカイト(DP)型酸化物Ba
系ダブルペロブスカイト(DP)型酸化物Ba CaOsO
CaOsO は、
は、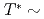 50Kで帯磁率の異常を示し、
50Kで帯磁率の異常を示し、 SRによる
SRによる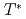 以下での時間反転対称性の破れも確認されている一方で、中性子散乱では
以下での時間反転対称性の破れも確認されている一方で、中性子散乱では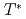 以下でも反強磁性ピークが観測されないという特異な磁性を示す。これと結晶構造が最低温まで立方晶であることから、磁気八極子秩序の可能性が理論的に指摘されているが、これに反する理論予測もあり、合意は得られていない。本研究では、Os
以下でも反強磁性ピークが観測されないという特異な磁性を示す。これと結晶構造が最低温まで立方晶であることから、磁気八極子秩序の可能性が理論的に指摘されているが、これに反する理論予測もあり、合意は得られていない。本研究では、Os 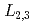 端硬X線磁気円二色性(XMCD)により、磁場中におけるBa
端硬X線磁気円二色性(XMCD)により、磁場中におけるBa CaOsO
CaOsO 多結晶のOs
多結晶のOs 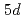 電子状態の解明を試みた。観測されたX線吸収(XAS)およびXMCDスペクトルは、
電子状態の解明を試みた。観測されたX線吸収(XAS)およびXMCDスペクトルは、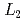 端で比較的大きなXMCDを示すのに対して
端で比較的大きなXMCDを示すのに対して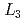 端のXMCDは弱く、強いスピン軌道相互作用(SOI)による大きな軌道磁気モーメントの存在が示唆された。XAS, XMCDスペクトルの概形は立方晶を仮定した原子多重項計算によって再現することができ、XASの2本のピーク分裂が結晶場分裂を反映していること、他の
端のXMCDは弱く、強いスピン軌道相互作用(SOI)による大きな軌道磁気モーメントの存在が示唆された。XAS, XMCDスペクトルの概形は立方晶を仮定した原子多重項計算によって再現することができ、XASの2本のピーク分裂が結晶場分裂を反映していること、他の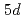 電子系と同様にクーロン相互作用は弱くSOIが強いことが示された。
電子系と同様にクーロン相互作用は弱くSOIが強いことが示された。
竹田 幸治; 土井 玲祐; 芝田 悟朗; 矢板 毅
no journal, ,
SPring-8 RI実験棟BL23SUに設置・整備をしてきた走査型透過X線顕微鏡(STXM)のスペックと立ち上げ状況を報告する。

芝田 悟朗
no journal, ,
The transparent conducting oxide InGaZnO (IGZO) has been studied extensively because of its high conductivity and large optical band gap. In order to reveal the intrinsic electronic structures of the bulk single-crystalline IGZO crystals, which were very recently synthesized, we performed hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HX-PES) experiments of these crystals. We find that oxygen vacancies are preferentially located around In atoms in as grown crystals, which are filled out by post annealing in an oxygen atmosphere. We also find the presence of intrinsic hydroxy bonds, which persists even after oxygen annealing. We also show that the "subgap states" near the valence band maximum (VBM) are much weaker than those in the previous study even without oxygen annealing, suggesting that the crystallinity is more relevant to the near VBM subgap states than the oxygen vacancies.
(IGZO) has been studied extensively because of its high conductivity and large optical band gap. In order to reveal the intrinsic electronic structures of the bulk single-crystalline IGZO crystals, which were very recently synthesized, we performed hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HX-PES) experiments of these crystals. We find that oxygen vacancies are preferentially located around In atoms in as grown crystals, which are filled out by post annealing in an oxygen atmosphere. We also find the presence of intrinsic hydroxy bonds, which persists even after oxygen annealing. We also show that the "subgap states" near the valence band maximum (VBM) are much weaker than those in the previous study even without oxygen annealing, suggesting that the crystallinity is more relevant to the near VBM subgap states than the oxygen vacancies.