Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 dynamics in the H
dynamics in the H conductors LaH
conductors LaH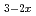 O
O
Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; Fukui, Keiga*; Iimura, Soshi*; Honda, Takashi*; Tada, Tomofumi*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Yamaura, Junichi*; Kuramoto, Yoshio*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Yamada, Takeshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 107(18), p.184114_1 - 184114_8, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.23(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Daido, Hiroyuki*; Yamada, Tomonori; Saruta, Koichi; Miyabe, Masabumi; Ito, Chikara; Shibata, Takuya; Inoue, Kaoru*; Terabayashi, Ryohei*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Physica Scripta, 98(3), p.035112_1 - 035112_22, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.15(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Characterization of kW class quasi-continuous wave (a pulse duration of 10 ms) laser interaction with metal targets and those with metal oxide targets are presented in respect to the laser induced breakdown and the successive laser induced melting and evaporation coupled with a mechanical response followed by ejection of various kinds of particles and fragments. An experiment was performed using fiber lasers coupled with a high-speed camera to observe dynamics of the interaction. Ejected fine particles were collected using a cascade impactor and a home-made collector and were observed with electron microscopes. Shapes of irradiation marks were observed with a digital optical microscope. We also measured total ejected mass from a target. The experimental results reveal that firstly the laser threshold intensity of the interaction with the metal target was lower and more stable than those with the metal oxide targets. Secondly, in the stainless steel targets, the dynamics of molten layer created by thermal conduction from the laser heated thin layer and successive particle ejection with less mechanical response by the adjacent solid layer are dominant processes, while in the metal oxide targets, the fracturing in the relatively deeper interaction region coupled with brittle material response having relatively large laser shot to shot fluctuation appears to play a significant role in addition to the laser induced melting.
 GeP
GeP S
S by quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurements
by quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurementsHori, Satoshi*; Kanno, Ryoji*; Kwon, O.*; Kato, Yuki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Matsuura, Masato*; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Kawakita, Yukinobu
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 126(22), p.9518 - 9527, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:61.15(Chemistry, Physical) Al
Al and Nd
and Nd Pd
Pd Ge
Ge
Metoki, Naoto; Shibata, Kaoru; Matsuura, Masato*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Hagihara, Masato; Frontzek, M. D.*; Matsuda, Masaaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(5), p.054710_1 - 054710_6, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hyperfine splitting of Nd nuclei in NdPd Al
Al has been studied by means of high-resolution neutron spectroscopy. We observed inelastic peaks at
has been studied by means of high-resolution neutron spectroscopy. We observed inelastic peaks at 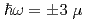 eV coming from the hyperfine splitting in the magnetically ordered phase due to the hyperfine interactions between Nd nuclei (
eV coming from the hyperfine splitting in the magnetically ordered phase due to the hyperfine interactions between Nd nuclei ( =7/2) and the 4
=7/2) and the 4 electrons with
electrons with 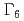 ground state composed of mainly
ground state composed of mainly 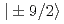 . At very low temperatures, nuclear spin of Nd is polarized with increasing occupation probability of low energy levels and contributes to the enhancement of the antiferromagnetic Bragg intensities: the elastic non-spin-flip channel is dominant. As an application of this phenomenon, we determined the Nd moment and hyperfine splitting from the temperature dependence of an antiferromagnetic Bragg intensities for Nd
. At very low temperatures, nuclear spin of Nd is polarized with increasing occupation probability of low energy levels and contributes to the enhancement of the antiferromagnetic Bragg intensities: the elastic non-spin-flip channel is dominant. As an application of this phenomenon, we determined the Nd moment and hyperfine splitting from the temperature dependence of an antiferromagnetic Bragg intensities for Nd Pd
Pd Ge
Ge .
.
Hashimoto, Shunsuke*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Shibata, Kaoru; Yamada, Takeshi*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 342, p.117580_1 - 117580_8, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:23.35(Chemistry, Physical)Quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) and pulsed-field-gradient nuclear magnetic resonance (PFGNMR) analyses of a nanofluid composed of silicon dioxide (SiO ) nanoparticles and a base fluid of ethylene glycol aqueous solution were performed. The aim was to elucidate the mechanism increase in the thermal conductivity of the nanofluid above its theoretical value. The obtained experimental results indicate that SiO
) nanoparticles and a base fluid of ethylene glycol aqueous solution were performed. The aim was to elucidate the mechanism increase in the thermal conductivity of the nanofluid above its theoretical value. The obtained experimental results indicate that SiO particles may decrease the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules in the ethylene glycol aqueous solution because of their highly restricted motion around these nanoparticles. At a constant temperature, the thermal conductivity increases as the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules decreases in the SiO
particles may decrease the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules in the ethylene glycol aqueous solution because of their highly restricted motion around these nanoparticles. At a constant temperature, the thermal conductivity increases as the self-diffusion coefficient of the liquid molecules decreases in the SiO nanofluids.
nanofluids.
Tominaga, Taiki*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011086_1 - 011086_5, 2021/03
We developed a quartz double cylindrical sample cell optimized for a backscattering neutron spectrometer, especially for BL02 (DNA), MLF in J-PARC. A quartz glass tube, with one end closed, is shaved to obtain a wall thickness of 0.55 mm. The inner tube is properly centered using a protrusion into the outer tube such that the interstice between the outer and inner tubes keeps constant. This quartz cell can be used for samples that should not be in contact with the aluminum surface. We verified cell's background effect between the quartz cell and Al cell by QENS measurements using D O buffer. The elastic intensity profiles of the buffer in a low Q region were identical between both quartz cell and Al cell (A1070). In a high Q region, however, the profiles were different caused by the first sharp diffraction peak of quartz glass. For this region the data should be analyzed by consideration of absorption correction and diffraction in individual thickness of quartz cell.
O buffer. The elastic intensity profiles of the buffer in a low Q region were identical between both quartz cell and Al cell (A1070). In a high Q region, however, the profiles were different caused by the first sharp diffraction peak of quartz glass. For this region the data should be analyzed by consideration of absorption correction and diffraction in individual thickness of quartz cell.
Gonzal z, M. A.*; Borodin, O.*; Kofu, Maiko; Shibata, Kaoru; Yamada, Takeshi*; Yamamuro, Osamu*; Xu, K.*; Price, D. L.*; Saboungi, M.-L.*
z, M. A.*; Borodin, O.*; Kofu, Maiko; Shibata, Kaoru; Yamada, Takeshi*; Yamamuro, Osamu*; Xu, K.*; Price, D. L.*; Saboungi, M.-L.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 11(17), p.7279 - 7284, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:80.73(Chemistry, Physical)Fujiwara, Satoru*; Matsuo, Tatsuhito*; Sugimoto, Yasunobu*; Shibata, Kaoru
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 10(23), p.7505 - 7509, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:17.43(Chemistry, Physical)Characterization of the dynamics of disordered polypeptide chains is required to elucidate the behavior of intrinsically disordered proteins and proteins under non-native states related to the folding process. Here we develop a method using quasielastic neutron scattering, combined with small-angle X-ray scattering and dynamic light scattering, to evaluate segmental motions of proteins as well as diffusion of the entire molecules and local side-chain motions. We apply this method to RNase A under the unfolded and molten-globule (MG) states. The diffusion coefficients arising from the segmental motions are evaluated and found to be different between the unfolded and MG states. The values obtained here are consistent with those obtained using the fluorescence-based techniques. These results demonstrate not only feasibility of this method but also usefulness to characterize the behavior of proteins under various disordered states.
 -synuclein related to propensity to amyloid fibril formation
-synuclein related to propensity to amyloid fibril formationFujiwara, Satoru*; Kono, Fumiaki*; Matsuo, Tatsuhito*; Sugimoto, Yasunobu*; Matsumoto, Tomoharu*; Narita, Tetsuhiro*; Shibata, Kaoru
Journal of Molecular Biology, 431(17), p.3229 - 3245, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:49.25(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology) -synuclein (
-synuclein ( Syn) is an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) with unknown function.
Syn) is an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) with unknown function.  Syn is known to form amyloid fibrils, which are implicated with the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies. Elucidating the mechanism of fibril formation of
Syn is known to form amyloid fibrils, which are implicated with the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies. Elucidating the mechanism of fibril formation of  Syn is therefore important for understanding the mechanism of the pathogenesis of these diseases. Here, using the quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) techniques, we investigated the dynamic and structural properties of
Syn is therefore important for understanding the mechanism of the pathogenesis of these diseases. Here, using the quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) techniques, we investigated the dynamic and structural properties of  Syn. These results imply that fibril formation of
Syn. These results imply that fibril formation of  Syn requires not only the enhanced local motions but also the segmental motions such that the proper inter-molecular interactions are possible.
Syn requires not only the enhanced local motions but also the segmental motions such that the proper inter-molecular interactions are possible.
Okuchi, Takuo*; Tomioka, Naotaka*; Purevjav, N.*; Shibata, Kaoru
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 51, p.1564 - 1570, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.03(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)It is demonstrated that quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS) is a novel and effective method to analyse atomic scale hydrogen transport processes occurring within a mineral crystal lattice. The method was previously characterized as sensitive for analysing the transport frequency and distance of highly diffusive hydrogen atoms or water molecules in condensed matter. Here are shown the results of its application to analyse the transport of much slower hydrogen atoms which are bonded into a crystal lattice as hydroxyls. Two types of hydrogen transport process were observed in brucite, Mg(OH) : a jump within a single two-dimensional layer of the hydrogen lattice and a jump into the next nearest layer of it. These transport processes observed within the prototypical structure of brucite have direct implications for hydrogen transport phenomena occurring within various types of oxides and minerals having layered structures.
: a jump within a single two-dimensional layer of the hydrogen lattice and a jump into the next nearest layer of it. These transport processes observed within the prototypical structure of brucite have direct implications for hydrogen transport phenomena occurring within various types of oxides and minerals having layered structures.
Yoshida, Koji*; Inoue, Takuya*; Torigoe, Motokatsu*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Yamaguchi, Toshio*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 149(12), p.124502_1 - 124502_10, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:14.97(Chemistry, Physical)Differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray diffraction, and quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) measurements of aqueous glycine solutions confined in mesoporous silica (MCM-41) were performed at different glycine concentrations, pH, and loading ratio (= mass of glycine solution / mass of dry MCM-41) in the temperature range from 305 to 180 K to discuss the confinement effect on the thermal behavior, the structure, and the dynamic properties of the solutions.
Nemoto, Fumiya*; Kofu, Maiko; Nagao, Michihiro*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Takata, Shinichi; Suzuki, Junichi*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Ueki, Takeshi*; Kitazawa, Yuzo*; et al.
Journal of Chemical Physics, 149(5), p.054502_1 - 054502_11, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:74.13(Chemistry, Physical)Abe, Hiroshi*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 264, p.54 - 57, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:56.66(Chemistry, Physical)Shudo, Yasuyuki*; Izumi, Atsushi*; Hagita, Katsumi*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Shibayama, Mitsuhiro*
Macromolecules, 51(16), p.6334 - 6343, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:45.92(Polymer Science)Fukushima, Yoshiaki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Tamura, Kenji*; Shibata, Kaoru
Applied Clay Science, 155, p.15 - 19, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:16.76(Chemistry, Physical)Dynamics of a fluoromica (ME100) cation exchanged for dioctadecyl dimethyl ammonium ion (DODA )/ polypropylene composite was analyzed by quasi elastic neutron scattering (QENS), besides XRD and DSC. The QENS spectra for the DODA-ME100 at low Q=2.75 nm
)/ polypropylene composite was analyzed by quasi elastic neutron scattering (QENS), besides XRD and DSC. The QENS spectra for the DODA-ME100 at low Q=2.75 nm were not changed even at temperature higher than 445 K, the melting point of DODA
were not changed even at temperature higher than 445 K, the melting point of DODA . The results suggested the long range (
. The results suggested the long range ( 2 nm) molecular motions in interlayer space are restricted due to the rigid silicate layers and the strong electrostatic interaction between DODA
2 nm) molecular motions in interlayer space are restricted due to the rigid silicate layers and the strong electrostatic interaction between DODA and the ME100. Elastic intensity scan results suggested that a little amount of motion of the polymer chains in the composite was also restricted in the molten state at 445 K. The QENS is expected to be one of the useful tools for studying the composite materials.
and the ME100. Elastic intensity scan results suggested that a little amount of motion of the polymer chains in the composite was also restricted in the molten state at 445 K. The QENS is expected to be one of the useful tools for studying the composite materials.
Li, B.; Wang, H.*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Zhang, Q.*; Feygenson, M.*; Yu, H. L.*; Wu, D.*; Ohara, Koji*; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Shibata, Kaoru; et al.
Nature Materials, 17(3), p.226 - 230, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:161 Percentile:97.18(Chemistry, Physical)Shibata, Kaoru
Hamon, 28(1), p.26 - 28, 2018/02
We briefly introduce the pedigree of the backscattering neutron spectrometer and the specification of DNA; a time-of-flight (TOF) type near-backscattering spectrometer (n-BSS), with Si crystal analyzers which was constructed at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC).
Shamoto, Shinichi; Ito, Takashi; Onishi, Hiroaki; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Matsuura, Masato*; Akatsu, Mitsuhiro*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Nakao, Akiko*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; et al.
Physical Review B, 97(5), p.054429_1 - 054429_9, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:64.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nuclear and magnetic structure and full magnon dispersions of yttrium iron garnet Y Fe
Fe O
O have been studied by neutron scattering. The lowest-energy dispersion below 14 meV exhibits a quadratic dispersion as expected from ferromagnetic magnons. The imaginary part of
have been studied by neutron scattering. The lowest-energy dispersion below 14 meV exhibits a quadratic dispersion as expected from ferromagnetic magnons. The imaginary part of  -integrated dynamical spin susceptibility
-integrated dynamical spin susceptibility  "(
"( ) exhibits a square-root energy-dependence in the low energies. The magnon density of state is estimated from the
) exhibits a square-root energy-dependence in the low energies. The magnon density of state is estimated from the  "(
"( ) obtained on an absolute scale. The value is consistent with a single chirality mode for the magnon branch expected theoretically.
) obtained on an absolute scale. The value is consistent with a single chirality mode for the magnon branch expected theoretically.
Inoue, Rintaro*; Kanaya, Toshiji*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Fukao, Koji*
Physical Review E, 97(1), p.012501_1 - 012501_6, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.50(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In this study, we investigate the  process of a polystyrene thin film using inelastic neutron scattering (INS), dielectric relaxation spectroscopy (DRS), and thermal expansion spectroscopy (TES). The DRS and TES measurements exhibited a decrease in glass transition temperature (
process of a polystyrene thin film using inelastic neutron scattering (INS), dielectric relaxation spectroscopy (DRS), and thermal expansion spectroscopy (TES). The DRS and TES measurements exhibited a decrease in glass transition temperature (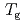 ) with film thickness. On the other hand, an increase in
) with film thickness. On the other hand, an increase in 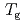 was observed in INS studies. In order to interpret this contradiction, we investigated the temperature dependence of the peak frequency (
was observed in INS studies. In order to interpret this contradiction, we investigated the temperature dependence of the peak frequency (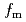 ) of the
) of the  process probed by DRS and TES. The experiments revealed an increase in the peak frequency (
process probed by DRS and TES. The experiments revealed an increase in the peak frequency (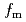 ) with decreasing film thickness in the frequency region. This observation is consistent with the observed decrease in
) with decreasing film thickness in the frequency region. This observation is consistent with the observed decrease in 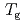 with thickness. The discrepancy between INS and DRS or TES descriptions of the
with thickness. The discrepancy between INS and DRS or TES descriptions of the  process is likely to be attributed to a decrease in the apparent activation energy with film thickness and reduced mobility, due to the impenetrable wall effect.
process is likely to be attributed to a decrease in the apparent activation energy with film thickness and reduced mobility, due to the impenetrable wall effect.
Nakajima, Kenji; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Ito, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Endo, Hitoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Gong, W.*; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(3), p.9_1 - 9_59, 2017/12
The neutron instruments suite, installed at the spallation neutron source of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), is reviewed. MLF has 23 neutron beam ports and 21 instruments are in operation for user programs or are under commissioning. A unique and challenging instrumental suite in MLF has been realized via combination of a high-performance neutron source, optimized for neutron scattering, and unique instruments using cutting-edge technologies. All instruments are/will serve in world-leading investigations in a broad range of fields, from fundamental physics to industrial applications. In this review, overviews, characteristic features, and typical applications of the individual instruments are mentioned.