Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Amano, Tsukasa; Shibata, Ryodai; Sato, Yoshiharu; Yamazaki, Katsuyuki; Shiromo, Hideo; Nakamura, Hironobu
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Annual Meeting 2023 (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/05
In Japan, about 10 years have passed since the law obligated nuclear operators to develop and maintain a nuclear security culture. During this period, the global nuclear situation has changed significantly, and it is becoming important to maintain a stance that emphasizes compliance with regulations and nuclear security culture. In JAEA, the policy of legal compliance and developing nuclear security culture is determined by the president of JAEA. For legal compliance and developing nuclear security culture, many activities are carried out based on that policy. Finally, these activities are evaluated and improved it every year. Case study is the one of activities that can obtain skills for legal compliance and developing nuclear security culture, such as sensitivity of nuclear security risks, correct understanding of the laws. The procedure for the case study was created with reference to a method called KY-Training which is often applied to safety training program in Japan. KY-Training is a training that participants (groups) can reach the conclusion how to respond to cases through four questions. Firstly, participants are given illustrations and descriptions which has potential of nuclear security risks. Then, participants make discussion according to four questions. Consequently, participants can effectively become aware of nuclear security risks. In the 2022 case study, we prepared 23 cases so that they can select choose freely according to role of participants such as in charge of nuclear security, guards, general employees. Finally, participants are asked to fill a questionnaire to evaluate effectiveness of case study. The result of questionnaires indicated that the case study was able to lead to improvement sensitivity of nuclear security risks and correct understanding of the laws. Overall, case study results suggested that JAEA's efforts were implying sufficiently to develop and maintain a nuclear security culture.
Amano, Tsukasa; Sato, Yoshiharu; Shibata, Ryodai; Yamazaki, Katsuyuki; Shiromo, Hideo; Nakamura, Hironobu
Dai-43-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/11
About ten years have passed since the introduction of nuclear security compliance and security culture development activities. While there have been changes in domestic and international situations, it is essential for nuclear security that the entire organization maintains an attitude that emphasizes compliance with laws and regulations and nuclear security. JAEA has been effectively implementing various activities with evaluation and improvement. Especially, e-learning which combines education and awareness, case studies, and internal audits are considered effective in maintaining nuclear security compliance and security culture development activities.
Shibata, Ryodai; Yamazaki, Katsuyuki; Yamada, Hiroyuki; Miyaji, Noriko; Nakamura, Hironobu
Dai-42-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2021/11
Physical protection systems (PPS) operated for security in nuclear facilities uses computer-controlled systems. If malicious peoples change program or install computer virus to PPS, they are invalidated. Due to insufficient surveillance etc., and then unauthorized removal and sabotage may be caused. This paper introduces efforts of necessary procurement and quality managements etc., for decreasing there affect, and their details.
Fukaya, Masaaki*; Noda, Masaru*; Hata, Koji*; Takeda, Nobufumi*; Akiyoshi, Kenji*; Ishizeki, Yoshikazu*; Kaneda, Tsutomu*; Sato, Shin*; Shibata, Chihoko*; Ueda, Tadashi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2014-019, 495 Pages, 2014/08
The researches on engineering technology in the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) plan consists of (1) research on engineering technology deep underground, and (2) research on engineering technology as a basis of geological disposal. The former research is mainly aimed in this study, which is categorized in (a) development of design and construction planning technologies, (b) development of construction technologies, (c) development of countermeasure technologies, and (d) development of technologies for security. In this study, the researches on engineering technology are being conducted in these four categories by using data measured during construction as a part of the second phase of the MIU plan.
Osakabe, Kazuya; Onizawa, Kunio; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Suzuki, Masahide
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 6(2), p.161 - 171, 2007/06
As a part of the materials aging degradation and structural integrity research for LWR components, the probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL has been developed in JAEA. This code evaluates the conditional probabilities of crack initiation and fracture of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) under transient conditions such as pressurized thermal shock (PTS). A standardized analysis method is proposed on the basis of the development of PASCAL ver.2 and results of sensitivity analyses. Graphical user interface (GUI) including the standardized analysis method as default settings and values has been also developed for PASCAL ver.2. A case study showed that non-destructive examination with good performance had a more significant effect on the probability of failure than non-destructive examinations repeated with low performance.
Osakabe, Kazuya; Onizawa, Kunio; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Suzuki, Masahide
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 6(2), p.172 - 182, 2007/06
Fifty-five nuclear power plants of light water reactors (LWRs) in Japan including seven plants which have already reached a 30-year operation have been operated as of September 2006. The probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) method has been recently highlighted to rationally incorporate the uncertainties arising from the material properties, defect distribution, inspection quality and so on, unlike the conventional deterministic method. As a part of the materials aging degradation and structural integrity research for LWR components, the PFM analysis code PASCAL has been developed in JAEA. This code evaluates the conditional probabilities of crack initiation and fracture of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) under transient conditions such as pressurized thermal shock (PTS). Sensitivity analyses for pre-service and in-service inspections have been performed according to JSME S NA1-2004 and the correlation between the results by deterministic analysis according to the JEAC 4206-2004 and probabilistic analysis based on PFM for the integrity of RPV under PTS has also been described.
Osakabe, Kazuya; Kato, Daisuke*; Onizawa, Kunio; Shibata, Katsuyuki
JAEA-Data/Code 2006-020, 371 Pages, 2006/09
As a part of the aging structural integrity research for LWR components, the probabilistic fracture mechanics analysis code PASCAL has been developed in JAEA. This code evaluates the conditional probabilities of crack initiation and fracture of a reactor pressure vessel under transient conditions such as pressurized thermal shock. PASCAL Ver.1 has functions of optimized sampling in stratified Monte Carlo simulation and so on. Since then, under the contract between the Ministry of Economy, Trading and Industry of Japan and JAEA, we have continued to develop and introduce new functions into PASCAL Ver.2 such as the evaluation method for an embedded crack and others. A generalized analysis method is proposed based on the development of PASCAL Ver.2 and results of sensitivity analyses. Graphical user interface including a generalized method as default values has been also developed for PASCAL Ver.2. This report provides the user's manual and theoretical background of PASCAL Ver.2.
Shibata, Katsuyuki; Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide; Li, Y.*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2006 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfuarensu Koen Rombunshu, p.395 - 396, 2006/08
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Katsuyuki; Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide; Li, Y.*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2006 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfuarensu Koen Rombunshu, p.397 - 398, 2006/08
no abstracts in English
Osakabe, Kazuya; Onizawa, Kunio; Shibata, Katsuyuki
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-3-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.75 - 78, 2006/07
no abstracts in English
Onizawa, Kunio; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Osakabe, Kazuya; Tanaka, Kazuhisa
Proceedings of 2006 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Division Conference (PVP 2006)/International Council on Pressure Vessel Technology (ICPVT-11) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2006/07
Probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL (PFM Analysis of Structural Components in Aging LWR) has been developed at JAEA to evaluate the conditional failure probability of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) containing a flaw under transient conditions such as pressurized thermal shock (PTS). Some functions of PASCAL have been improved such as Monte Carlo method, probability of crack detection (POD) by inspection and the GUI. Using the improved PASCAL, case studies on some parameters for some typical PTS transients have been performed. When the crack existence probability for the Marshall- and PNNL-type distributions is considered, the failure probability could be the same order of magnitude. The effect of chemical composition of vessel material was studied through the comparison of conditional failure probabilities for some transients. The effect of POD by inspection was also compared and evaluated in terms of inspection time.
Shibata, Katsuyuki; Onizawa, Kunio; Tanaka, Kazuhisa; Suzuki, Masahide
Proceedings of 2006 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Division Conference (PVP 2006)/International Council on Pressure Vessel Technology (ICPVT-11) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2006/07
no abstracts in English
Onizawa, Kunio; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Suzuki, Masahide
Proceedings of 6th International Conference on the Integrity of Nuclear Components, p.230 - 238, 2006/04
The probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) method has been recently highlighted to rationally incorporate the uncertainties arising from the material properties, defect distribution, inspection quality and so on, unlike the conventional deterministic method. We are developing analytical codes for PFM analysis of RPV and piping under design base loading conditions such as transient loading and seismic loading. In JAEA, the PFM codes called as PASCAL (PFM Analysis of Structural Components in Aging LWRs) series have been developed. For reactor pressure vessel (RPV), PASCAL code has been developed which can evaluate the conditional probabilities of crack initiation and fracture under transient conditions such as pressurized thermal shock (PTS) considering neutron irradiation embrittlement of the material in the beltline region. For piping, considering aging degradation and seismic stress calculated with seismic hazard, piping reliability analysis codes have been developed. PASCAL-SC and PASCAL-EC analyze failure probability of piping under operational and seismic stresses considering stress corrosion cracking and flow accelerated corrosion, respectively. The outlines and some results of these computer codes are described.
Tsutsumi, Hideaki*; Sugino, Hideharu*; Onizawa, Kunio; Mori, Kazunari*; Yamada, Hiroyuki*; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Ebisawa, Katsumi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2006-004, 167 Pages, 2006/03
EBISA (Equipment Base Isolation System Analysis) code evaluates the effectiveness of seismic isolation for the important components in the seismic safety, and consists of the three codes, probabilistic seismic hazard code (SHEAT), seismic dynamic response analysis code (RESP) and seismic failure probability and frequency evaluation code. In these codes, RESP code is used for the calculation of the dynamic response behavior of a nuclear component with seismic isolation devices. This report describes the overall explanation of EBISA, and user's guide of RESP code including the analysis function, input manual and sample problem.
Ito, Hiroto; Kato, Daisuke*; Onizawa, Kunio; Shibata, Katsuyuki
JAEA-Data/Code 2006-001, 33 Pages, 2006/02
As a part of the aging and structural integrity research for LWR components, new probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL-EC (PFM Analysis of Structural Components in Aging LWR - Erosion/-Corrosion) has been developed. This code evaluates the failure probability of an aged piping with a wall thinning by Monte Carlo method. PASCAL-EC treats the wall thinning due to erosion/corrosion or flow accelerated corrosion (FAC) in piping. The development of this code has been aimed to improve the accuracy and reliability of analysis by introducing new analysis methodologies and algorithms considering the recent developments in the structural mechanics and aging researches. This report provides the user's manual and theoretical background of PASCAL-EC.
Shibata, Katsuyuki*; Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide; Li, Y.*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2005 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfarensu Koen Rombunshu, p.299 - 300, 2005/11
no abstracts in English
Ito, Hiroto*; Onizawa, Kunio; Shibata, Katsuyuki*
JAERI-Data/Code 2005-007, 118 Pages, 2005/09
As a part of the aging and structual integrity research for LWR components, new PFM (Probabilistic Fracture Mechanics) codes PASCAL-SC and PASCAL-EQ have been developed. These codes evaluate the failure probability of an aged welded joint by Monte Carlo method. PASCAL-SC treats Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) in piping, while PASCAL-EQ takes fatigue crack growth by seismic load into account. The development of these codes has been aimed to improve the accuracy and reliability of analysis by introducing new analysis and methodologies and algorithms considering the recent development in the fracture machanics methodologies and computer performance. The crack growth by an irregular stress due to seismic load in detail is considered in these codes. They also involves recent stress intensity factors and fracture criteria. In addition, a user's friendly operation of a GUI (Graphical User Interface) which generates input data, supports calculations and plots results is introduced. This report provides the user's manual and theoretical background of these codes.
Onizawa, Kunio; Shibata, Katsuyuki*; Suzuki, Masahide
Proceedings of 2005 ASME/JSME Pressure Vessels and Piping Division Conference (PVP 2005), 12 Pages, 2005/07
Under a transient loading like pressurized thermal shock (PTS), the stress discontinuity near the interface between cladding and base metal of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) is caused by the difference in their thermal expansion factors. So the stress intensity factor (SIF) of a surface crack which the deepest point exceeds the interface should be calculated by taking account of the stress discontinuity. Many SIF calculations are performed in Monte Carlo simulation of the probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis. To avoid the time consuming process from the SIF calculation in the PFM analysis, the non-dimensional SIF coefficients corresponding to the stress distributions in the cladding and base metal were developed. The non-dimensional SIF coefficients database were obtained from 3D FEM analyses. The SIF value at the surface was determined by linear extrapolation of SIF value near the surface. Using the SIF coefficients database, the SIF values at both surface and deepest points of a surface crack can be evaluated precisely and in a reasonable time.
Shibata, Katsuyuki; Onizawa, Kunio; Li, Y.*; Kato, Daisuke*
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 81(9), p.749 - 756, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.63(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)The paper describes the procedure to evaluate the ductile crack extension, where an increase in fracture resistance by a ductile crack extension is considered. Two standard 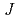 -resistance curves are prepared for applying the elasto-plastic fracture criterion. Case studies concerning the effect of elasto-plastic fracture criterion were carried out using a severe PTS transient. The introduction of the elasto-plastic fracture criterion significantly contributes to remove the over-conservatism in applying the linear elastic fracture criterion. It was also found that the algorithm of the re-evaluation of crack tip characterization also has a significant effect on the failure probability.
-resistance curves are prepared for applying the elasto-plastic fracture criterion. Case studies concerning the effect of elasto-plastic fracture criterion were carried out using a severe PTS transient. The introduction of the elasto-plastic fracture criterion significantly contributes to remove the over-conservatism in applying the linear elastic fracture criterion. It was also found that the algorithm of the re-evaluation of crack tip characterization also has a significant effect on the failure probability.
Onizawa, Kunio; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Kato, Daisuke*; Li, Y.*
JSME International Journal, Series A, 47(3), p.486 - 493, 2004/07
The probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL has been developed in JAERI. This code can evaluate the conditional probabilities of crack initiation and fracture of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) under transient conditions such as pressurized thermal shock (PTS). Based on the temperature and stress distributions in the vessel wall for four PTS sequences in a typical 3-loop PWR, parametric PFM analyses are performed using PASCAL on the variables such as pre-service inspection model, crack geometry, fracture toughness curve and irradiation embrittlement prediction equation. The results showed that the good perfomance inspection model had a significant effect on the fracture probability and reduced it by more than 3 orders of magnitude. The fracture probability calculated by the fracture toughness estimation method in Japan was about 2 orders of magnitude lower than that by the USA method. It was found that the treatment of a semi-elliptical crack in PASCAL reduced the conservatism in a conventional method that it is transformed into an infinite length crack.