Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hirano, Koichiro; Ito, Takashi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Shinto, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012077_1 - 012077_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:69.74(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have upgraded a 3-MeV linac at J-PARC. The ion source is same as the J-PARC linac's, and the old 30-mA RFQ is replaced by a spare 50-mA RFQ, therefore, the beam energy is 3 MeV and the nominal beam current is 50 mA. The main purpose of this system is to test the spare RFQ, but also used for testing of various components required in order to keep the stable operation of the J-PARC accelerator. The accelerator has been already commissioned, and measurement programs have been started. In this paper, present status of this 3-MeV linac is presented.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Asano, Hiroyuki*; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirano, Koichiro; Ishiyama, Tatsuya; Ito, Takashi; Kawane, Yusuke; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Meigo, Shinichiro; Miura, Akihiko; et al.
Proceedings of 28th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2016) (Internet), p.298 - 300, 2017/05
We have constructed a linac for development of various accelerator components at J-PARC. The ion source is same as the J-PARC linac's, and the RFQ is a used one in the J-PARC linac. The beam energy is 3 MeV and nominal beam current is 30 mA. The accelerator has been already commissioned, and the first development program, laser-charge-exchange experiment for the transmutation experimental facility, has been started. In this paper, present status of this 3-MeV linac is presented.
Hirano, Koichiro; Asano, Hiroyuki; Ishiyama, Tatsuya; Ito, Takashi; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Oguri, Hidetomo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kawane, Yusuke; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Sato, Yoshikatsu; et al.
Proceedings of 13th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.310 - 313, 2016/11
We have used a beam scraper with the incident angle of 65deg to reduce the beam power deposition density in the MEBT between a 324 MHz RFQ and a 50-MeV DTL of the J-PARC linac. The 65 scraper was irradiated by the H
scraper was irradiated by the H beam up to particle number of 1.47E22. We observed a lot of surface projections with several hundred micrometers high in the beam irradiation damage on the scraper by using the laser microscope. In order to study the limits of scrapers, we constructed a new 3 MeV linac at J-PARC. We will conduct the scraper irradiation test at the end of this year.
beam up to particle number of 1.47E22. We observed a lot of surface projections with several hundred micrometers high in the beam irradiation damage on the scraper by using the laser microscope. In order to study the limits of scrapers, we constructed a new 3 MeV linac at J-PARC. We will conduct the scraper irradiation test at the end of this year.
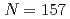 nucleus
nucleus  No
NoAsai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sakama, Minoru*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ichikawa, Takatoshi*; Ishii, Yasuo; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Ishii, Tetsuro; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
Physical Review C, 87(1), p.014332_1 - 014332_6, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.87(Physics, Nuclear)The spin-parity and neutron configuration of the ground state of  No have been identified through
No have been identified through  -decay spectroscopy. The
-decay spectroscopy. The  No is the nucleus with the largest neutron number whose spin-parities and single-particle configurations have ever been identified. The neutron 9/2
No is the nucleus with the largest neutron number whose spin-parities and single-particle configurations have ever been identified. The neutron 9/2 [615] configuration was assigned to the ground state of
[615] configuration was assigned to the ground state of  No as well as to the 231.4 keV level in
No as well as to the 231.4 keV level in  Fm. This allowed us to establish energy spacings and order of the neutron single-particle orbitals in such heaviest nuclear region. The appearance of the 9/2
Fm. This allowed us to establish energy spacings and order of the neutron single-particle orbitals in such heaviest nuclear region. The appearance of the 9/2 [615] ground state at
[615] ground state at  =157 implies that the order of the neutron orbitals between the
=157 implies that the order of the neutron orbitals between the  =152 and 162 deformed shell gaps should change considerably with increasing neutron number.
=152 and 162 deformed shell gaps should change considerably with increasing neutron number.
Fukumoto, Naoyuki*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Nagata, Masayoshi*; Uyama, Tadao*; Shibata, Takatoshi; Kashiwa, Yoshitoshi; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Kusama, Yoshinori; JFT-2M Group
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(23-24), p.2849 - 2857, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:55.89(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kamiya, Kensaku; Shinohara, Koji; Bakhtiari, M.*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kurita, Genichi; Takechi, Manabu; Kasai, Satoshi; Sato, Masayasu; Kawashima, Hisato; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(11), p.966 - 971, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:46.92(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Shinohara, Koji; Sato, Masayasu; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Isei, Nobuaki; Tani, Takashi; Kikuchi, Kazuo; Shibata, Takatoshi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.187 - 196, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)In JFT-2M, the toroidal field ripple was reduced by ferritic insert. Two kinds of ripple reduction were carried out. In the first case, ferritic steel was installed between toroidal field coil and vacuum vessel, just under toroidal field coil, outside vacuum vessel. In the second one, ferritic steel was installed inside vacuum vessel covering almost whole inside wall. The ripple was successfully reduced in the both cases. The temperature increment on the first wall measured by infrared TV was also reduced. A new version of OFMC code was also developed to analyze fast ion behavior in the complex structure of the toroidal field. The TF ripple reduction with ferritic insert in JFT-2M is summarized in this article.
Kawashima, Hisato; Sengoku, Seio; Uehara, Kazuya; Tamai, Hiroshi; Shoji, Teruaki*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Shibata, Takatoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Kusama, Yoshinori; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.168 - 186, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experimental efforts on JFT-2M have been devoted to understand SOL/Divertor plasmas and to investigate power and particle controllability. Open divertor configuration was used for the first decade of JFT-2M started in 1984. We found out the SOL/Divertor plasma properties such as in/out asymmetry, heat and particle diffusivities, and SOL current at ELMs. Handling of power and particle was demonstrated by active control methods such as local pumping, edge ergodization, divertor biasing, and edge heating. For improvement of power and particle control capability of divertor, it was modified to closed configuration in 1995, which demonstrated the baffling effects with narrower divertor throat. Dense and cold divertor state (n
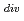 = 4
= 4 10
10 m
m and T
and T
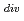 = 4 eV), compatible with the improved confinement modes (e.g. H-mode), was realized by strong gas puffing. Being related with the core confinement at H-mode, the edge plasma fluctuations were identified by an electrostatic probe. These are reviewed in this paper.
= 4 eV), compatible with the improved confinement modes (e.g. H-mode), was realized by strong gas puffing. Being related with the core confinement at H-mode, the edge plasma fluctuations were identified by an electrostatic probe. These are reviewed in this paper.
Ogawa, Hiroaki; Ogawa, Toshihide; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kawashima, Hisato; Kasai, Satoshi*; Kashiwa, Yoshitoshi; Hasegawa, Koichi; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Shibata, Takatoshi; Miura, Yukitoshi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.209 - 224, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Hoshino, Katsumichi; Yamamoto, Takumi; Tamai, Hiroshi; Oasa, Kazumi; Kawashima, Hisato; Miura, Yukitoshi; Ogawa, Toshihide; Shoji, Teruaki*; Shibata, Takatoshi; Kikuchi, Kazuo; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.139 - 167, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)The main results obtained by the various heating and current drive systems, external coil system and divertor bias system are reviewed from the viewpoint of the advanced active control of the tokamak plasma. Also, the features of each system are described. The contribution of the JFT-2M in these areas are summarized.
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro*; Kimura, Haruyuki; Kusama, Yoshinori; Sato, Masayasu; Kawashima, Hisato; Kamiya, Kensaku; Shinohara, Koji; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Uehara, Kazuya; Kurita, Genichi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.197 - 208, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Shibata, Takatoshi; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Sato, Masayasu; Kimura, Haruyuki; Okano, Fuminori; Kawashima, Hisato; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Shinohara, Koji; JFT-2M Group; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 49(2), p.241 - 248, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)JFT-2M has been modified three times in the Advanced Material Tokamak Experiment (AMTEX) program to investigate compatibility of the low activation ferritic steel F82H with tokamak plasmas as a structural material for future reactors. The ferritic steel plate/wall was installed inside and/or outside of the vacuum vessel to reduce the ripple of toroidal magnetic field step by step through three modifications. This paper focuses on engineering aspects in these modifications; electromagnetic analysis to find a suitable way for fixing these plates, installation procedure to keep small tolerance, a three-dimensional magnetic field measurement device used to obtain information of the actual shape of the vacuum vessel used as a installation standard surface. To keep a good surface condition of the ferritic steel plate/wall that rusts easily, careful treatment was executed before the installation. To reduce oxygen impurities further, a boronization system with tri-methyl boron, which is safe and easy to operate, was developed.
Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Okano, Fuminori; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Shibata, Takatoshi
JAERI-Tech 2005-061, 11 Pages, 2005/09
Ferritic steel plates were installed in the JFT-2M vacuum vessel to conduct "the Advanced Material Tokamak Experiments (AMTEX)". A coating device with tri-methyl-bron(TMB)was developed to coat the ferritic steel surface with boron, since the ferritic steel is easy to rust and also has a property to absorb much impurity in the surface. The TMB gas used in the device was diluted with helium gas to 1% for ensuring workers themselves against the toxicity of the TMB. The uniformity and stability of the coated layer have been confirmed through sample tests with a microscope, whose samples had been set in the tokamak vacuum vessel. The coating thickness measured with X-ray photoelectron emission spectroscopy was roughly 130nm. In the plasma experiments after the boron coating, radiation loss in the plasma decreased to 1/3, and oxygen impurity also decreased to 1/10 compared to without the boron coating.
Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kimura, Haruyuki; Sato, Masayasu; Shibata, Takatoshi; Okano, Fuminori; Suzuki, Sadaaki
JAERI-Tech 2005-060, 16 Pages, 2005/09
The low activation ferritic steel is one of the candidate for structural material of a demo-reactor. However, it was afraid that the plasma confinement and stability might degrade due to the error field by the ferromagnetic property of the ferritic material. So, on JFT-2M tokamak Advanced Material Tokamak EXperiment program (AMTEX) has been carried out to investigate about the conformity with the plasma and ferritic steel. AMTEX was performed by introducing low activation ferritic plates (FPs) step by step. At the third stage, the FPs were installed to cover almost whole inside wall (FIW) of the vacuum vessel (VV) as a simulation of the blanket wall.In this experiment the accurate measurement of the distribution of the magnetic fields strength was required before and after the installation of the FIW.Therefore, the device for 3D-measurement of the magnetic field profile along the toroidal direction was developed.
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Shinohara, Koji; Kamiya, Kensaku; Kawashima, Hisato; Sato, Masayasu; Kurita, Genichi; Bakhtiari, M.; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Kasai, Satoshi; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(1), p.721 - 725, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.09(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Kimura, Haruyuki; Kawashima, Hisato; Sato, Masayasu; Kamiya, Kensaku; Shinohara, Koji; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Bakhtiari, M.; Kasai, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(10), p.1288 - 1293, 2003/10
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:72.81(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Sato, Masayasu; Kawashima, Hisato; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kimura, Haruyuki; Okano, Fuminori; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Komata, Masao; Sawahata, Masayuki; Shinohara, Koji; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 313-316, p.177 - 181, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:52.41(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Sato, Masayasu; Kawashima, Hisato; Isei, Nobuaki; Kimura, Haruyuki; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Miyachi, Kengo; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Shibata, Takatoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 307-311(Part2), p.1386 - 1390, 2002/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:66.70(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Isei, Nobuaki; Kawashima, Hisato; Sato, Masayasu; Kimura, Haruyuki; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Miura, Yukitoshi; Ogawa, Toshihide; Shibata, Takatoshi; Akiyama, Takashi*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 78(5), p.455 - 461, 2002/05
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Takatoshi; Akiyama, Takashi*; Isei, Nobuaki; Kawashima, Hisato; Kimura, Haruyuki; Miyachi, Kengo; Okano, Fuminori; Sato, Masayasu; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 19th IEEE/NPSS Symposium on Fusion Engineering (SOFE), p.360 - 363, 2002/00
no abstracts in English