Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Obara, Satoshi*; Kobayashi, Ryoei*; Yagi, Shuichi*; Toyama, Yuko*; Kutluk, G.*; Osawa, Tetsutaro*; Ogura, Koichi; Shibata, Takemasa; Azuma, Yoshiro*; Nagata, Tetsuo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 269(3), p.263 - 271, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)A crossed photon-atom beam apparatus has been constructed for absolute measurement of total photoionization cross sections of isolated and neutral metallic atoms. Using this apparatus, measurements on Ba and Eu atoms have been made at their 4d giant resonance regions 110-140 eV and 140-180 eV, respectively. The target atom density was determined using the deposition rate on a quartz crystal sensor and the average velocity of the atoms obtained by a time-of-flight method combined with a pulsed electron gun. The number of photons was determined with use of a double ion chamber. The comparison of the measured cross-section values with previous experimental and theoretical results is reasonable, indicating that the crossed photon-atom beam method is fairly promising technique.
Shibata, Takemasa; Ogura, Koichi
JAEA-Research 2008-124, 12 Pages, 2009/03
The metastable states' population of neodymium atoms produced by electron beam heating was measured with the laser induced fluorescence method. The atomic excitation temperature derived from the metastable state distribution decreased to about 1500K with increasing deposition rate. This atomic excitation temperature is about three times higher than that of gadolinium atoms produced by electron beam heating. Near the evaporation surface the collisional relaxation of neodymium and gadolinium atoms occurs through inelastic collisions between fine structures. The gadolinium and neodymium atoms have ten valence electrons of 4f 5d6s
5d6s and six valence electrons of 4f
and six valence electrons of 4f 6s
6s , respectively. The orbital radius of 5d electron is relatively larger than that of 4f electron. Low collisional relaxation of neodymium is considered to be due to small orbital radius of 4f electron and no existence of 5d electron.
, respectively. The orbital radius of 5d electron is relatively larger than that of 4f electron. Low collisional relaxation of neodymium is considered to be due to small orbital radius of 4f electron and no existence of 5d electron.
Shibata, Takemasa; Tamura, Koji; Ogura, Koichi
JAEA-Research 2008-076, 13 Pages, 2008/10
Cross sections of symmetric charge transfer are calculated for ytterbium, lutetium and samarium. Symmetric charge transfer of lanthanoide elements in most cases has two main reaction paths, that is, resonant and non-resonant paths due to open 4f shells inside 6s electrons. At low impact energy, charge transfer cross sections are small because only resonant path is possible. On the other hand, the charge transfer of ytterbium, lutetium and samarium has only resonant path. Therefore the charge transfer cross sections of these atoms decrease monotonically with the impact energy. The cross sections of ytterbium and samarium are 203 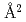 and 224
and 224 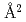 at the impact energy of 1 eV/amu, respectively. These values are larger than the cross sections of many lantanoid elements such as dysprosium. The cross section of lutetium is 65
at the impact energy of 1 eV/amu, respectively. These values are larger than the cross sections of many lantanoid elements such as dysprosium. The cross section of lutetium is 65 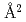 at the impact energy of 1 eV/amu. This value is small due to d-electron transfer.
at the impact energy of 1 eV/amu. This value is small due to d-electron transfer.
Shibata, Takemasa
Gendai Shakai To Kagaku Gijutsu, p.75 - 101, 2008/03
The modern society uses a large quantity of energy of a one-10,000th of radiant energy given the earth from the sun. The present fossil energy consumption continues only in around 100 from dozens of years. The consumption of the fossil energy causes global warming. There is a problem to renewable energy and the atomic energy which can solve these in various ways. For future energy use, economy and politics are important, too.
Wang, H.*; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Miyabe, Masabumi; Shibata, Takemasa; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Iimura, Hideki
Applied Physics B, 81(8), p.1127 - 1133, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:34.33(Optics)Laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy has been employed to characterize the plume produced in nanosecond laser ablation of metallic neodymium. The kinetic-energy distributions of the neutral and ionized atoms in the plume under both vacuum and gas environments have been investigated. The population distribution of metastable levels in the ablated atoms was also derived. The results show some metastable states are more heavily populated than predicted by a Boltzman-type distribution. These investigations provide preliminary data for the design of a new type of resonance photo-ionization laser ion source as well as for hign-resolution laser spectroscopy of refractory elements.
Takayanagi, Tomohiro*; Ikehata, Takashi*; Mase, Hiroshi*; Oba, Hironori; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Research 2005-024, 14 Pages, 2005/09
A weakly ionized plasma contained in the gadolinium atomic beam produced by electron beam heating was passed led to a magnetic field of 0
 1.5kG between iron cores. When the magnetic field was applied, the instability appeared in the ion saturation current. With increasing the magnetic field, the ions detected by the ion collectors decreased and no ions were detected at all. The magnetic field intensity at which the plasma does not flow and ions are not detected does not depend on plasma ion density. At this magnetic field, Larmor radius of ions are two times wider than plasma width. In addition, it is found that the plasma contained in the atomic beam can be removed by the magnetic field.
1.5kG between iron cores. When the magnetic field was applied, the instability appeared in the ion saturation current. With increasing the magnetic field, the ions detected by the ion collectors decreased and no ions were detected at all. The magnetic field intensity at which the plasma does not flow and ions are not detected does not depend on plasma ion density. At this magnetic field, Larmor radius of ions are two times wider than plasma width. In addition, it is found that the plasma contained in the atomic beam can be removed by the magnetic field.
Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Conf 2004-014, 212 Pages, 2004/12
no abstracts in English
Wang, H.*; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Miyabe, Masabumi; Shibata, Takemasa; Iimura, Hideki
Review of Scientific Instruments, 75(10), p.3775 - 3776, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.10(Instruments & Instrumentation)Laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy has been employed to characterize a plume produced in nanosecond laser ablation of metallic neodymium. Kinetic energy distributions of ions and neutrals in the plume were investigated as functions of processing parameters such as laser fluence and ambient gas pressure. Population distributions of metastable levels in the ablated atoms were also measured. These investigations provide useful data for the design of a new types of resonance photo-ionization ion source and also for high-resolution laser spectroscopy.
Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Conf 2003-021, 551 Pages, 2004/02
no abstracts in English
 La,
La,  La and
La and 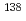 La by collinear laser spectroscopy
La by collinear laser spectroscopyIimura, Hideki; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Shibata, Takemasa; Shinohara, Nobuo; Ishida, Yoshihisa*; Horiguchi, Takayoshi*; Schuessler, H. A.*
Physical Review C, 68(5), p.054328_1 - 054328_7, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:57.41(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Si by infrared multiple photon decomposition of Si
Si by infrared multiple photon decomposition of Si F
F
Yokoyama, Atsushi; Oba, Hironori; Shibata, Takemasa; Kawanishi, Shunichi*; Sugimoto, Shunichi*; Ishii, Takeshi*; Oya, Akio*; Miyamoto, Yoshiki*; Isomura, Shohei*; Arai, Shigeyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(4), p.457 - 462, 2002/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Oba, Hironori; Ogura, Koichi; Nishimura, Akihiko; Tamura, Koji; Shibata, Takemasa
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 39(9A), p.5347 - 5351, 2000/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.08(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Oba, Hironori; Nishimura, Akihiko; Ogura, Koichi; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Research 2000-033, 17 Pages, 2000/08
no abstracts in English
Oba, Hironori; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Research 2000-032, 17 Pages, 2000/08
no abstracts in English
Oba, Hironori; Nishimura, Akihiko; Ogura, Koichi; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Research 2000-030, 17 Pages, 2000/08
no abstracts in English
Tamura, Koji; Oba, Hironori; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Research 99-064, p.12 - 0, 1999/12
no abstracts in English
Adachi, Hajime; Tamura, Koji; Ogura, Koichi; Shibata, Takemasa
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 38(12A), p.6887 - 6889, 1999/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:28.09(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Tamura, Koji; Adachi, Hajime*; Ogura, Koichi; Oba, Hironori; Shibata, Takemasa
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 38(11), p.6512 - 6516, 1999/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:50.49(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Tamura, Koji; Oba, Hironori; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Tech 99-050, 8 Pages, 1999/07
no abstracts in English
Oba, Hironori; Ogura, Koichi; Nishimura, Akihiko; Tamura, Koji; Shibata, Takemasa
JAERI-Research 99-043, 17 Pages, 1999/07
no abstracts in English