Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shibata, Yoshihide; Isayama, Akihiko; Matsunaga, Go; Kawano, Yasunori; Miyamoto, Seiji*; Lukash, V.*; Khayrutdinov, R.*; JT-60 Team
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 9(Sp.2), p.3402084_1 - 3402084_5, 2014/06
We performed the disruption simulation using DINA code to investigate the effect of the electron temperature  on the plasma current decay after the initial phase of current quench (CQ). In this calculation, we used the measured
on the plasma current decay after the initial phase of current quench (CQ). In this calculation, we used the measured  profile during the initial phase of CQ. After the initial phase of CQ, we assumed that the
profile during the initial phase of CQ. After the initial phase of CQ, we assumed that the  profile does not change in time and used the value at the end of the initial phase of current quench because
profile does not change in time and used the value at the end of the initial phase of current quench because  profile could not be measured after the initial phase of CQ. From the simulation results, it was found that the time evolution of plasma current calculated by DINA was similar to experimental one in this calculation. However, the time evolution of
profile could not be measured after the initial phase of CQ. From the simulation results, it was found that the time evolution of plasma current calculated by DINA was similar to experimental one in this calculation. However, the time evolution of  profile in this calculation was different from the measured
profile in this calculation was different from the measured  profile because Te after first mini-collapse rapidly decreased until the value below a measurement limit (less than 0.1 keV). Moreover, the time evolution of poloidal cross-section S calculated by DINA code was rapidly decreased although the experimental one was gradually decreased. The plasma current decay during the disruption is determined by various parameters,
profile because Te after first mini-collapse rapidly decreased until the value below a measurement limit (less than 0.1 keV). Moreover, the time evolution of poloidal cross-section S calculated by DINA code was rapidly decreased although the experimental one was gradually decreased. The plasma current decay during the disruption is determined by various parameters, 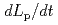 ,
,  and S. It is necessary to evaluate the effect of
and S. It is necessary to evaluate the effect of  profile on the plasma current decay after the initial phase of CQ by using various assumed
profile on the plasma current decay after the initial phase of CQ by using various assumed  model and DINA code.
model and DINA code.
Ueta, Shohei; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Aihara, Jun; Fujita, Ichiro*; Ohashi, Jun*; Nagaishi, Yoshihide*; Muto, Takenori*; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Sakaba, Nariaki
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 271, p.309 - 313, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new concept of the high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) is proposed as a challenge to assure no event sequences to the harmful release of radioactive materials even when the design extension conditions (DECs) occur by deterministic approach based on the inherent safety features of the HTGR. The air/water ingress accident, one of the DECs for the HTGR, is prevented by additional measures (e.g. facility for suppression to air ingress). With regard to the core design, it is important to prevent recriticality accidents by keeping the geometry of the fuel rod which consists of the graphite sleeve, fuel compact and SiC-TRISO (TRIstructural-ISOtropic) coated fuel particle, and by improving the oxidation resistance of the graphite when air/water ingress accidents occur. Therefore, it is planned to develop the oxidation-resistant graphite, which is coated with gradient SiC layer. It is also planned that the experimental identification of the condition to form the stable oxide layer (SiO ) for SiC layer on the oxidation-resistant graphite and on the SiC-TRISO fuel. This paper describes the R&D plan for un-irradiation and irradiation test under simulating air/water ingress accident condition to develop oxidation-resistant graphite and to investigate the oxidation behavior of SiC coated fuel particle.
) for SiC layer on the oxidation-resistant graphite and on the SiC-TRISO fuel. This paper describes the R&D plan for un-irradiation and irradiation test under simulating air/water ingress accident condition to develop oxidation-resistant graphite and to investigate the oxidation behavior of SiC coated fuel particle.
Shibata, Yoshihide; Isayama, Akihiko; Miyamoto, Seiji*; Kawakami, Sho*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Matsunaga, Go; Kawano, Yasunori; Lukash, V.*; Khayrutdinov, R.*; JT-60 Team
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 56(4), p.045008_1 - 045008_8, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.96(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In JT-60U disruption, the plasma current decay during the initial phase of current quench has been calculated by a disruption simulation code (DINA) using the measured electron temperature  profile. In the case of fast plasma current decay,
profile. In the case of fast plasma current decay,  has a peaked profile just after thermal quench and the
has a peaked profile just after thermal quench and the  profile doesn't change significantly during the initial phase of current quench. On the other hand, in the case of the slow plasma current decay, the
profile doesn't change significantly during the initial phase of current quench. On the other hand, in the case of the slow plasma current decay, the  profile is border just after the thermal quench, and the
profile is border just after the thermal quench, and the  profile shrinks. The results of DINA simulation show that plasma internal inductance
profile shrinks. The results of DINA simulation show that plasma internal inductance 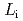 increases during the initial phase of current quench, while plasma external inductance
increases during the initial phase of current quench, while plasma external inductance 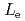 does not change in time. The increase of
does not change in time. The increase of 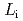 is caused by current diffusion toward the core plasma due to the decrease of
is caused by current diffusion toward the core plasma due to the decrease of  in intermediate and edge regions. It is suggested that an additional heating in the plasma periphery region has the effect of slowing down plasma current decay.
in intermediate and edge regions. It is suggested that an additional heating in the plasma periphery region has the effect of slowing down plasma current decay.
Kawakami, Sho*; Shibata, Yoshihide; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Isayama, Akihiko; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Kawano, Yasunori; Okamoto, Masaaki*
Physics of Plasmas, 20(11), p.112507_1 - 112507_6, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.40(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)According to an early work on the behavior of the plasma current decay in the JT-60U disruptive discharges caused by the radiative collapse with a massive neon-gas-puff, the increase of the internal inductance mainly determined the current decay time of plasma current during the initial phase of current quench. To investigate what determines the increase of the internal inductance, we focus attention on the relationship between the electron temperature (or the resistivity) profile and the time evolution of the current density profile, and carry out numerical calculations. As a result, we find the reason of the increase of the internal inductance: The current density profile at the start of the current quench is broader than an expected current density profile in the steady state, which is determined by the temperature (or resistivity) profile. The current density profile evolves into peaked one and the internal inductance is increasing.
Ueta, Shohei; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Aihara, Jun; Fujita, Ichiro*; Ohashi, Jun*; Nagaishi, Yoshihide*; Muto, Takenori*; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Sakaba, Nariaki
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
A new concept of the High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR), so-called the Naturally Safe HTGR, is proposed as a challenge to assure no event sequences to the harmful release of radioactive materials even when the design extension conditions such as the air/water ingress accidents occur by deterministic approach based on the inherent safety features of the HTGR. For the Naturally Safe HTGR it is important to prevent recriticality accidents by keeping the geometry of the fuel rod which consists of the graphite sleeve, fuel compact and SiC-TRISO coated fuel particle, and by improving the oxidation resistance of the graphite when air/water ingress accidents occur. This paper describes the R&D plan for un-irradiation and irradiation test under simulating air/water ingress accident condition to develop oxidation-resistant graphite and to investigate the oxidation behavior of SiC coated fuel particle.
Shibata, Yoshihide*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Okamoto, Masaaki*; Isayama, Akihiko; Kurihara, Kenichi; Oyama, Naoyuki; Nakano, Tomohide; Kawano, Yasunori; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 6, p.1302136_1 - 1302136_4, 2011/10
no abstracts in English
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.53(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
Shibata, Yoshihide*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Okamoto, Masaaki*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Isayama, Akihiko; Kurihara, Kenichi; Nakano, Tomohide; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kawano, Yasunori; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 50(2), p.025015_1 - 025015_7, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:52.48(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Shibata, Yoshihide; Isayama, Akihiko; Matsunaga, Go; Kawano, Yasunori; Miyamoto, Seiji*; Lukash, V. E.*; Khayrutdinov, R.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Kiyomasa; Hara, Yujiro*; Shibata, Yoshihide; Shimada, Yoshihiro*; Nakamura, Yuji*; Isayama, Akihiko; Miyamoto, Seiji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Yoshihide*; Shiraishi, Junya; Matsunaga, Go; Sakakibara, Satoru*; Isayama, Akihiko; Kawano, Yasunori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Yoshihide; Matsunaga, Go; Sakakibara, Satoru*; Kawano, Yasunori; Isayama, Akihiko; Watanabe, Kiyomasa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Np isomer and its decay properties
Np isomer and its decay propertiesAsai, Masato; Suekawa, Yoshihide*; Higashi, Masato*; Kamada, Hiroki*; Tobe, Teruhisa*; Andreyev, A. N.; Hirose, Kentaro; Ito, Yuta; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; et al.
no journal, ,
A new isomer 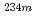 Np with a half-life of
Np with a half-life of  9 min has been discovered. It was produced in the reaction of
9 min has been discovered. It was produced in the reaction of  U target with
U target with  Li beam at JAEA tandem accelerator, and was identified through characteristic X-ray measurement and mass separation with an on-line isotope separator (ISOL). Gamma-ray singles, gamma-gamma coincidence, and internal-conversion electron measurements were performed. It was revealed that the
Li beam at JAEA tandem accelerator, and was identified through characteristic X-ray measurement and mass separation with an on-line isotope separator (ISOL). Gamma-ray singles, gamma-gamma coincidence, and internal-conversion electron measurements were performed. It was revealed that the 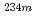 Np decays mostly through an isomeric E4 transition followed by an M1 transition, and that the spin-parity of the
Np decays mostly through an isomeric E4 transition followed by an M1 transition, and that the spin-parity of the 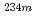 Np should be 5
Np should be 5 . The results are introduced in detail, and the nuclear structure of the
. The results are introduced in detail, and the nuclear structure of the 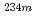 Np are discussed.
Np are discussed.
 Np isomer
Np isomerAsai, Masato; Suekawa, Yoshihide*; Higashi, Masato*; Kamada, Hiroki*; Tobe, Teruhisa*; Andreyev, A. N.; Hirose, Kentaro; Ito, Yuta; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; et al.
no journal, ,
We have carried out experiments to study nuclear structure of the new isomer 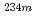 Np which we discovered recently. The
Np which we discovered recently. The 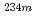 Np was produced in the reaction of
Np was produced in the reaction of  U target with
U target with  Li beam at JAEA tandem accelerator, and was mass-separated with an on-line isotope separator (ISOL). The half-life was determined accurately through LX-ray measurements. The
Li beam at JAEA tandem accelerator, and was mass-separated with an on-line isotope separator (ISOL). The half-life was determined accurately through LX-ray measurements. The  transition emitted by following the isomeric transition was successfully observed through LX-
transition emitted by following the isomeric transition was successfully observed through LX- coincidence measurements. Moreover, the multipolarities of the
coincidence measurements. Moreover, the multipolarities of the  transitions were determined with internal-conversion electron measurements. On the basis of these experimental results, We have clarified excitation energy, spin-parity, and nuclear structure of
transitions were determined with internal-conversion electron measurements. On the basis of these experimental results, We have clarified excitation energy, spin-parity, and nuclear structure of 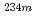 Np.
Np.

 disruptive discharges in JT-60U
disruptive discharges in JT-60UShibata, Yoshihide*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Okamoto, Masaaki*; Isayama, Akihiko; Kurihara, Kenichi; Oyama, Naoyuki; Nakano, Tomohide; Kawano, Yasunori; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
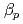 disruptive discharges of JT-60U
disruptive discharges of JT-60UShibata, Yoshihide*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Okamoto, Masaaki*; Isayama, Akihiko; Kurihara, Kenichi; Oyama, Naoyuki; Nakano, Tomohide; Kawano, Yasunori; Sugihara, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
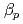 plasma discharges of JT-60U
plasma discharges of JT-60UShibata, Yoshihide*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Okamoto, Masaaki*; Isayama, Akihiko; Kurihara, Kenichi; Oyama, Naoyuki; Nakano, Tomohide; Kawano, Yasunori; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kawakami, Sho*; Shibata, Yoshihide*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Kajita, Shin*; Okamoto, Masaaki*; Isayama, Akihiko; Sugihara, Masayoshi*; Kawano, Yasunori; Lukash, V. E.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Yoshihide*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Ono, Noriyasu*; Okamoto, Masaaki*; Isayama, Akihiko; Kawano, Yasunori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English