Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targets
Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targetsSun, X. H.*; Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Ahn, D. S.*; Aikawa, Masayuki*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; Kawakami, Shunsuke*; Koyama, Shumpei*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(6), p.064623_1 - 064623_12, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:54.17(Physics, Nuclear)The spallation and fragmentation reactions of  Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
 Sc and development of the
Sc and development of the 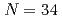 subshell closure
subshell closureSteppenbeck, D.*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Aoi, Nori*; Doornenbal, P.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Wang, H.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Go, Shintaro*; Holt, J. D.*; Lee, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 96(6), p.064310_1 - 064310_10, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:79.83(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 decay of unbound neutron-hole states in
decay of unbound neutron-hole states in  Sn
SnVaquero, V.*; Jungclaus, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Wimmer, K.*; Gargano, A.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Chen, S.*; N cher, E.*; Sahin, E.*; Shiga, Yoshiaki*; et al.
cher, E.*; Sahin, E.*; Shiga, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 118(20), p.202502_1 - 202502_5, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:75.67(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Ar and the
Ar and the  =32 subshell closure
=32 subshell closureSteppenbeck, D.*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Aoi, Nori*; Doornenbal, P.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Wang, H.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Baba, Hidetada*; Go, Shintaro*; Lee, J.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 114(25), p.252501_1 - 252501_6, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:88.13(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The neutron-rich nucleus  Ar is produced by the fragmentation reactions of
Ar is produced by the fragmentation reactions of  Ca,
Ca,  Sc, and
Sc, and  Ti at the RIBF facility in RIKEN, and its deexcited
Ti at the RIBF facility in RIKEN, and its deexcited  rays are observed for the first time. The first
rays are observed for the first time. The first 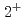 level in
level in  Ar is identified to lie at 1178(18)keV from the most intense
Ar is identified to lie at 1178(18)keV from the most intense  -ray spectra. This experimental data, together with the systematics of the
-ray spectra. This experimental data, together with the systematics of the 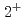 levels for surrounding nuclei, is analyzed with large-scale shell-model calculations. Consequently, the
levels for surrounding nuclei, is analyzed with large-scale shell-model calculations. Consequently, the 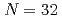 sub-shell gap in
sub-shell gap in  Ar is equivalent to that of
Ar is equivalent to that of  Ca, thus making the
Ca, thus making the 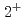 level in
level in  Ar higher than that of
Ar higher than that of  Ar. The shell-model calculation also predicts that the
Ar. The shell-model calculation also predicts that the  sub-shell gap enhances in going from Ca to Ar, which will be verified by forthcoming experiments for
sub-shell gap enhances in going from Ca to Ar, which will be verified by forthcoming experiments for  Ar.
Ar.
Vela, S.*; Mota, F.*; Deumal, M.*; Suizu, Rie*; Shuku, Yoshiaki*; Mizuno, Asato*; Awaga, Kunio*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Novoa, J.*; Ribas-Arino, J.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 5, p.4411_1 - 4411_9, 2014/07
Recent years have witnessed a growing interest in the use of organic radicals as building blocks for bistable materials, i.e. materials that exist in two inter-exchangeable phases under identical thermodynamic conditions. The neutral radical TTTA is a prominent dithiazolyl-based compound because of its spin transition with a hysterisis nature near the room temperature. From ab initio molecular dynamics simulations, it has been evident that this phase transition is driven by the pair exchange dynamics of molecular stacking units accompanied by a significant gain of vibrational entropy.
 Ca
CaSteppenbeck, D.*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Aoi, Nori*; Doornenbal, P.*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Wang, H.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Go, Shintaro*; Homma, Michio*; et al.
Nature, 502(7470), p.207 - 210, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:333 Percentile:99.77(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English