Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 I in the Accumulated radioactive water and processing water of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant
I in the Accumulated radioactive water and processing water of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power PlantShimada, Asako; Sakatani, Keiichi; Kameo, Yutaka; Takahashi, Kuniaki
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1137 - 1140, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:42.34(Chemistry, Analytical)Accumulated radioactive water and processing water were sampled from back and forth of the Accumulated radioactive water processing facility (ARWPF) at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) to estimate the radioactivity of the secondary waste such as zeolite and sludge adsorbed radioactive material. Separation method of I from the radioactive materials using solid phase extractant, Anion-SR, was developed, and the concentration of
from the radioactive materials using solid phase extractant, Anion-SR, was developed, and the concentration of  I in the accumulated water and processing water was determined by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry including dynamic reaction cell (DRC-ICP-MS).
I in the accumulated water and processing water was determined by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry including dynamic reaction cell (DRC-ICP-MS).
 I in the contaminated water and tree samples at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station
I in the contaminated water and tree samples at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power StationShimada, Asako; Ozawa, Mayumi; Kameo, Yutaka; Yasumatsu, Takuyo*; Nebashi, Koji*; Niiyama, Takuya; Seki, Shuhei; Kajio, Masatoshi; Takahashi, Kuniaki
Nuclear Back-end and Transmutation Technology for Waste Disposal, p.311 - 317, 2015/00
no abstracts in English
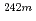 Am in low-level radioactive waste based on extraction chromatography and
Am in low-level radioactive waste based on extraction chromatography and  -ray spectrometry
-ray spectrometryShimada, Asako; Kameo, Yutaka; Takahashi, Kuniaki
Analytical Chemistry, 85(16), p.7726 - 7731, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:20.18(Chemistry, Analytical)A new method for identifying 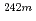 Am in low-level radioactive waste (LLW) using
Am in low-level radioactive waste (LLW) using  -ray spectrometry is proposed. First, Eu, Am, and Cm in a digested solution of simulated LLW were separated from the major components of the digested solution and Pu using transuranium resin. Next, Am and Cm were separated from Eu using tetravalent actinide resin. A
-ray spectrometry is proposed. First, Eu, Am, and Cm in a digested solution of simulated LLW were separated from the major components of the digested solution and Pu using transuranium resin. Next, Am and Cm were separated from Eu using tetravalent actinide resin. A  -ray spectrum of the fraction containing Am and Cm was recorded and the contribution of
-ray spectrum of the fraction containing Am and Cm was recorded and the contribution of  Np, which is a daughter nuclide of
Np, which is a daughter nuclide of  Am, was subtracted to determine the radioactivity of
Am, was subtracted to determine the radioactivity of  Am. The radioactivity of
Am. The radioactivity of 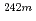 Am determined by
Am determined by  -ray spectrometry agreed with that obtained by analyzing the increase in
-ray spectrometry agreed with that obtained by analyzing the increase in  Cm in the Am fraction just after its separation from Cm with tertiary pyridine resin.
Cm in the Am fraction just after its separation from Cm with tertiary pyridine resin.
Haraga, Tomoko; Kameo, Yutaka; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Shimada, Asako; Tobita, Minoru*; Takahashi, Shigemi*; Takahashi, Kuniaki
JAEA-Data/Code 2012-031, 39 Pages, 2013/02
The Fugen Nuclear Power Station was shut down and decommissioning of the Fugen has been implemented. To calculate the scaling factor of radioactive waste or advance the clearance of dismantled materials, a large number of radioactivity concentration data of dismantled materials have to be accumulated. For these reasons, the simple and rapid radioactivity determination method was applied for metal samples, which were taken from pipes of the Fugen. The present report is summarized analytical procedures and obtained radioactivity data of the Fugen pipe samples.
 I in radioactive liquid waste solidified with bitumen
I in radioactive liquid waste solidified with bitumenKameo, Yutaka; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Shimada, Asako; Takahashi, Kuniaki
Bunseki Kagaku, 61(10), p.845 - 849, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:16.97(Chemistry, Analytical)A simple determination method was developed to measure  I in low level radioactive liquid waste solidified with bitumen. A simulated bituminized product sample was cut to 0.02 g pieces, subsequently these pieces and sodium carbonate were heated in an electric furnace. This procedure could well decompose the bituminized sample without volatilizing
I in low level radioactive liquid waste solidified with bitumen. A simulated bituminized product sample was cut to 0.02 g pieces, subsequently these pieces and sodium carbonate were heated in an electric furnace. This procedure could well decompose the bituminized sample without volatilizing  I. Sixty to seventy percent of
I. Sixty to seventy percent of  I was recovered by a solid phase extraction disk from a solution containing the decomposed sample. A dynamic reaction cell inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer was applied to measure
I was recovered by a solid phase extraction disk from a solution containing the decomposed sample. A dynamic reaction cell inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer was applied to measure  I, and as a result, detection limit of
I, and as a result, detection limit of  I was reduced to by a factor of about 6 comparing with conventional ICP-MS measurement. Determined radioactivity concentration for the simulated bituminized sample containing
I was reduced to by a factor of about 6 comparing with conventional ICP-MS measurement. Determined radioactivity concentration for the simulated bituminized sample containing  I was good agreement with expected value within 6% error.
I was good agreement with expected value within 6% error.
Kameo, Yutaka; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Haraga, Tomoko; Shimada, Asako; Katayama, Atsushi; Nakashima, Mikio*; Takahashi, Kuniaki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 10(3), p.216 - 225, 2011/09
Analytical methods have been developed for simple and rapid determination of radioactive nuclides, which are selected as important nuclides for safety assessment of disposal of wastes generated from research facilities. We advanced the development of a high-efficiency non-destructive measurement technique for  -ray emitting nuclides, simple and rapid methods for pretreatment of hard-to dissolve samples and subsequent radiochemical separations, and rapid determination methods for long-lived nuclides. In order to establish a system to analyze the important nuclides in various kinds of samples, actual radioactive wastes such as concentrated liquid waste, activated concrete, and metal pipes, were analyzed by the present method. The results showed that the present method was well suited for a rapid and simple determination of low-level radioactive wastes generated from research facilities.
-ray emitting nuclides, simple and rapid methods for pretreatment of hard-to dissolve samples and subsequent radiochemical separations, and rapid determination methods for long-lived nuclides. In order to establish a system to analyze the important nuclides in various kinds of samples, actual radioactive wastes such as concentrated liquid waste, activated concrete, and metal pipes, were analyzed by the present method. The results showed that the present method was well suited for a rapid and simple determination of low-level radioactive wastes generated from research facilities.
Kameo, Yutaka; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Shimada, Asako; Tobita, Minoru*; Takahashi, Shigemi*; Takahashi, Kuniaki
JAEA-Data/Code 2010-028, 32 Pages, 2011/02
The Fugen Nuclear Power Station was shut down and decommissioning of the Fugen has been implemented. To calculate the scaling factor of radioactive waste or advance the clearance of dismantled materials, a large number of radioactivity concentration data of dismantled materials have to be accumulated. For these reasons, the simple and rapid radioactivity determination method was applied for metal samples, which were taken from pipes of the Fugen. The present report is summarized analytical procedures and obtained radioactivity data of the Fugen pipe samples.
Shimada, Asako; Haraga, Tomoko; Hoshi, Akiko; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio; Takahashi, Kuniaki
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 286(3), p.765 - 770, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:39.00(Chemistry, Analytical)Ishimori, Kenichiro; Haraga, Tomoko; Shimada, Asako; Kameo, Yutaka; Takahashi, Kuniaki
JAEA-Technology 2010-016, 54 Pages, 2010/08
Simple and rapid analytical methods for radionuclides in low-level radioactive waste have been developed by the present authors. The methods were applied to simulated solidified products and actual metal wastes to confirm their usefulness. The results were summarized as analytical guide lines. In the present work, cement solidified products and ash wastes were analyzed followed by the analytical guide lines and subjects were picked up and improved for the application of the analytical guide lines to these wastes. Pulverization and homogenization methods for ash wastes were improved to prevent a contamination since the radioactivity concentrations of the ash wastes were relatively high. Pre-treatment method was altered for the ash wastes and cement solidified products taking account for their high composition of Ca. Newly, an analytical method was also developed to measure  I with a dynamic reaction cell inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer. In the analytical test based on the guide lines,
I with a dynamic reaction cell inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer. In the analytical test based on the guide lines,  -ray emitting nuclides,
-ray emitting nuclides,  CoCo and
CoCo and  CoCs, were measured to estimate the radioactivity of the other alpha and
CoCs, were measured to estimate the radioactivity of the other alpha and  -ray emitting nuclides. The radionuclides assumed detectable,
-ray emitting nuclides. The radionuclides assumed detectable,  H,
H, C,
C, Cl,
Cl, Ni,
Ni, Sr, and
Sr, and  -ray emitting nuclides, were analyzed with the analytical guide lines and their applicability for ash wastes and cement solidified products were confirmed.
-ray emitting nuclides, were analyzed with the analytical guide lines and their applicability for ash wastes and cement solidified products were confirmed.
Shimada, Kuniaki*; Abe, Kenichi*; Fujii, Mitsuru*; Tanada, Masuaki*
JNC TJ7400 2004-019, 203 Pages, 2004/03
A borehole that is drilling in high-level nuclear waste site uses for long period between investigation stage and monitoring stage after closing the repository and it is necessary to carry out the sealing of it finally.
Shimada, Asako; Kameo, Yutaka; Takahashi, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ikeda, Koki; Shimada, Kuniaki*; Osato, Kazumi*
no journal, ,
A borehole that is drilled in high-level nuclear waste site uses for long period between investigation stage and monitoring stage after closing the repository and it is necessary to carry out the sealing of it finally. If the borehole sealing is not complete, the borehole may act as a passage of groundwater flow and performance of the natural barrier that is most important element for intercepting high-level radioactive waste may be influenced by this passage. In this report, we searched and evaluated regarding the recent technology to solve these problems, the problem regarding the relevant technology was abstracted, and the technical development procedure to solve the problem was examined.
Shimada, Asako; Haraga, Tomoko; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio; Takahashi, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
As a rapid and simple analytical method for alpha nuclides in metal waste of which surface was contaminated by radionuclides, extraction chromatography using TRU resin for analysis of Pu and Am and UTEVA resin for analysis of Th and U is evaluated. The metal waste contained lots of Fe. Trivalent iron interfere the adsorption of trivalent actinides on TRU resin. Therefore, trivalent iron was reduced bivalent with excess amount of ascorbic acid. Since F interfere the adsorption of Th on UTEVA resin, Al
interfere the adsorption of Th on UTEVA resin, Al was generally added into the sample solution to mask F
was generally added into the sample solution to mask F . Since Fe
. Since Fe also can mask F
also can mask F , addition of Al
, addition of Al was deleted. The developed schemes were examined with dissolved solution of stainless steel and good recovery of Th, U, Pu, and Am was obtained. Therefore, contaminated metal waste was analyzed using the scheme.
was deleted. The developed schemes were examined with dissolved solution of stainless steel and good recovery of Th, U, Pu, and Am was obtained. Therefore, contaminated metal waste was analyzed using the scheme.
Shimada, Asako; Kameo, Yutaka; Takahashi, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
Neptunium separation procedure was added into reported separation scheme of Pu and Am to construct analytical scheme of Pu, Np, and Am using one extraction chromatographic column. Based on the result, Pu, Np, and Am in ash of inflammable waste and cement solidified waste were analyzed. Plutonium and Am were determined accurately and more than 80% of recoveries were obtained. Although a few % of Pu and Am were detected in Np fraction, they did not influence the determination of Np. Uranium was considered to exist in the Np fraction. However, U(VI) was not co-precipitated with samarium fluoride. Because  source was prepared by co-precipitation with samarium fluoride, determination of
source was prepared by co-precipitation with samarium fluoride, determination of  Np was not influenced by
Np was not influenced by  U. It was found that Pu, Np, and Am could be separated by one extraction chromatographic column.
U. It was found that Pu, Np, and Am could be separated by one extraction chromatographic column.
Shimada, Asako; Takahashi, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimada, Asako; Nash, K.*; Kameo, Yutaka; Takahashi, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimada, Asako; Haraga, Tomoko; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio; Takahashi, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
Extraction chromatography technique was applied to analysis of alpha nuclides stuck on surface of stainless steel. Firstly, the surface of stainless steel was dissolved with mixed acid (nitric acid: hydrochloric acid: water = 1:1:4), and then Th and U or Pu and Am were spiked. These solutions were introduced into UTEVA or TRU resins and alpha nuclides were separated. All of the experimented nuclides were recovered in the expected fractions and these recovery percents were over 80%. These methods were applied to analysis of alpha nuclides in pipings of cooling system of Fugen power plant, Advanced Thermal Reactor.