Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimada, Mikio*; Tokumiya, Takumi*; Miyake, Tomoko*; Tsukada, Kaima*; Kanzaki, Norie; Yanagihara, Hiromi*; Kobayashi, Junya*; Matsumoto, Yoshihisa*
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 64(2), p.345 - 351, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.01(Biology)Kameo, Yutaka; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Haraga, Tomoko; Shimada, Asako; Katayama, Atsushi; Nakashima, Mikio*; Takahashi, Kuniaki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 10(3), p.216 - 225, 2011/09
Analytical methods have been developed for simple and rapid determination of radioactive nuclides, which are selected as important nuclides for safety assessment of disposal of wastes generated from research facilities. We advanced the development of a high-efficiency non-destructive measurement technique for  -ray emitting nuclides, simple and rapid methods for pretreatment of hard-to dissolve samples and subsequent radiochemical separations, and rapid determination methods for long-lived nuclides. In order to establish a system to analyze the important nuclides in various kinds of samples, actual radioactive wastes such as concentrated liquid waste, activated concrete, and metal pipes, were analyzed by the present method. The results showed that the present method was well suited for a rapid and simple determination of low-level radioactive wastes generated from research facilities.
-ray emitting nuclides, simple and rapid methods for pretreatment of hard-to dissolve samples and subsequent radiochemical separations, and rapid determination methods for long-lived nuclides. In order to establish a system to analyze the important nuclides in various kinds of samples, actual radioactive wastes such as concentrated liquid waste, activated concrete, and metal pipes, were analyzed by the present method. The results showed that the present method was well suited for a rapid and simple determination of low-level radioactive wastes generated from research facilities.
Shimada, Asako; Haraga, Tomoko; Hoshi, Akiko; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio; Takahashi, Kuniaki
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 286(3), p.765 - 770, 2010/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.12(Chemistry, Analytical)Kameo, Yutaka; Shimada, Asako; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Haraga, Tomoko; Katayama, Atsushi; Hoshi, Akiko; Nakashima, Mikio
JAEA-Technology 2009-051, 81 Pages, 2009/10
Simple and rapid determination methods were developed for an evaluation of important nuclides, U, and Th in wastes generated from research facilities at Nuclear Science Research Institute and Oarai Research and Development Center. The present methods were assumed to apply to solidified products made from miscellaneous wastes by plasma melting at the Advanced Volume Reduction Facilities. In order to reduce costs of radiochemical analysis and to establish a routine analytical system, counting efficiency of non-destructive  -ray measurements was improved, and times for pretreatment of solidified product samples and subsequent radiochemical separations were shortened. In addition to this, rapid and high sensitive detection methods were developed for a determination of long-lived nuclides. The present paper describes guidelines for the determination of radionuclides in the low-level radioactive wastes by using the present simple and rapid methods.
-ray measurements was improved, and times for pretreatment of solidified product samples and subsequent radiochemical separations were shortened. In addition to this, rapid and high sensitive detection methods were developed for a determination of long-lived nuclides. The present paper describes guidelines for the determination of radionuclides in the low-level radioactive wastes by using the present simple and rapid methods.
Ioki, Kimihiro*; Barabash, V.*; Cordier, J.*; Enoeda, Mikio; Federici, G.*; Kim, B. C.*; Mazul, I.*; Merola, M.*; Morimoto, Masaaki*; Nakahira, Masataka*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(7-9), p.787 - 794, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper presents recent results of ITER activities on Vacuum Vessel (VV), blanket, limiter, and divertor. Major results can be summarized as follows. (1) The VV design is being developed in more details considering manufacturing and assembly methods, and cost. Incorporating manufacturing studies being performed in cooperation with parties, the regular VV sector design has been nearly finalized. (2) The procurement allocation of blanket modules among 6 parties was fixed and the blanket module design has progressed in cooperation with parties. Fabrication of mock-ups for prequalification testing is under way and the tests will be performed in 2007-2008. (3) The divertor activities have progressed with the aim of launching the procurement according to the ITER project schedule.
Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Shimada, Mikio*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Matsumura, Sho*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.235 - 238, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:65.77(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated the microstructure change and atomic disordering process in magnesium aluminate spinel, MgO  Al
Al O
O with
with  =1.1 and 2.4, irradiated with swift heavy ions of 200-MeV Xe
=1.1 and 2.4, irradiated with swift heavy ions of 200-MeV Xe and 350-MeV Au
and 350-MeV Au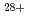 . Transmission electron microscopy techniques of bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) imaging, as well as high angular resolution electron channeling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS) are employed in quantitative analysis of irradiation-induced structural change. Ion tracks show columnar dark contrast of 4-7 nm in diameter at the incident surface in BF images. Strong strain contrast often arises among plural ion tracks formed closely. Clear lattice fringes are observed in HR images even inside the ion tracks. It indicates that the spinel crystals are not amorphized but partially disordered along the ion tracks. Quantitative HARECXS analysis shows that cation disordering progresses with ion fluence. It is revealed that the disordered regions are extended over 12
. Transmission electron microscopy techniques of bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) imaging, as well as high angular resolution electron channeling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS) are employed in quantitative analysis of irradiation-induced structural change. Ion tracks show columnar dark contrast of 4-7 nm in diameter at the incident surface in BF images. Strong strain contrast often arises among plural ion tracks formed closely. Clear lattice fringes are observed in HR images even inside the ion tracks. It indicates that the spinel crystals are not amorphized but partially disordered along the ion tracks. Quantitative HARECXS analysis shows that cation disordering progresses with ion fluence. It is revealed that the disordered regions are extended over 12 2 nm in diameter along the ion tracks.
2 nm in diameter along the ion tracks.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Matsukawa, Makoto; Kurita, Genichi; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Urata, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Yushi; Kizu, Kaname; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Kudo, Yusuke; et al.
Plasma Science and Technology, 6(1), p.2141 - 2150, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.49(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The dominant issue for the the modification program of JT-60 (JT-60SC) is to demonstrate the steady state reactor relevant plasma operation. Physics design on plasma parameters, operation scenarios, and the plasma control method are investigated for the achievement of high- . Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
. Engineering design and the R&D on the superconducting magnet coils, radiation shield, and vacuum vessel are performed. Recent progress in such physics and technology developments is presented.
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Chujo, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
no abstracts in English
Ishida, Shinichi; Abe, Katsunori*; Ando, Akira*; Cho, T.*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Goto, Seiichi*; Hanada, Kazuaki*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Hino, Tomoaki*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 43(7), p.606 - 613, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:69.03(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Shimada, Asako; Haraga, Tomoko; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio; Takahashi, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
Extraction chromatography technique was applied to analysis of alpha nuclides stuck on surface of stainless steel. Firstly, the surface of stainless steel was dissolved with mixed acid (nitric acid: hydrochloric acid: water = 1:1:4), and then Th and U or Pu and Am were spiked. These solutions were introduced into UTEVA or TRU resins and alpha nuclides were separated. All of the experimented nuclides were recovered in the expected fractions and these recovery percents were over 80%. These methods were applied to analysis of alpha nuclides in pipings of cooling system of Fugen power plant, Advanced Thermal Reactor.
Shimada, Asako; Haraga, Tomoko; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio; Takahashi, Kuniaki
no journal, ,
As a rapid and simple analytical method for alpha nuclides in metal waste of which surface was contaminated by radionuclides, extraction chromatography using TRU resin for analysis of Pu and Am and UTEVA resin for analysis of Th and U is evaluated. The metal waste contained lots of Fe. Trivalent iron interfere the adsorption of trivalent actinides on TRU resin. Therefore, trivalent iron was reduced bivalent with excess amount of ascorbic acid. Since F interfere the adsorption of Th on UTEVA resin, Al
interfere the adsorption of Th on UTEVA resin, Al was generally added into the sample solution to mask F
was generally added into the sample solution to mask F . Since Fe
. Since Fe also can mask F
also can mask F , addition of Al
, addition of Al was deleted. The developed schemes were examined with dissolved solution of stainless steel and good recovery of Th, U, Pu, and Am was obtained. Therefore, contaminated metal waste was analyzed using the scheme.
was deleted. The developed schemes were examined with dissolved solution of stainless steel and good recovery of Th, U, Pu, and Am was obtained. Therefore, contaminated metal waste was analyzed using the scheme.
Kanzaki, Norie; Shimada, Mikio*; Yanagihara, Hiromi*
no journal, ,
After ionizing radiation exposure, several types of DNA damage occur in mammalian cells. Several studies have been reported that the mutation type depends on the radiation type and the cell type. Thus, it is important to characterize the type of mutation caused by irradiation for understanding of the biological effects of radiation. This study is a foundational investigation of construction of data analysis method dedicated to characteristics extraction of mutations. Two datasets were hypothetically made by reference to previous researches. The data was composed of eight items, namely two types of transition, four types of transversion, insertion, and deletion. The datasets were first analyzed by Self-Organizing Maps. We categorized and predicted the characteristics of mutations. This result was compared with those of other multivariate analysis methods. The data with similar mutation patterns was closely located on the output map, indicating the variation of mutations given by different radiation types.
Shimada, Mikio*; Tsukada, Kaima*; Miyake, Tomoko*; Kanzaki, Norie; Yanagihara, Hiromi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihisa*
no journal, ,
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are generated by transduction of reprogramming transcriptional factors. iPSCs have multipotency to differentiate all organs and expected for the application of regenerative medicine. However, it is reported that cancer risk of iPSCs, because of expression of reprogramming factors increased DNA damage. It is important to analysis DNA damage response of iPSCs to prevent chromosomal abnormality and tumor formation. In this study, we attempted to elucidate the molecular mechanism of maintenance of genome stability in iPSCs. RNA-seq analysis by the next generation sequencer showed increased expression of genome maintenance genes such as DNA repair, cell cycle checkpoint and apoptosis. Interestingly, expression level of these genes was decreased after differentiation to the neural stem cells. Furthermore, colony formation assay showed high sensitivity and apoptosis activity to the IR exposure in iPSCs. These results suggested that instead of DNA repair, increasing of apoptosis activity maintain cell population having accurate genome DNA. These molecular insight have important implication for safety medical application of iPSCs.
Shimada, Mikio*; Kanzaki, Norie; Yanagihara, Hiromi*; Miyake, Tomoko*; Matsumoto, Yoshihisa*
no journal, ,
Although mutation frequency depends on organ cell types and differentiation level, it is not fully understood that organ cell types dependent mutation frequency in human cells. In this study, we aimed to establish measurement system of radiation dependent mutation frequency for analyze radiation effect to the human body. For this purpose, we derived four different organ cells such as neural cells, skin keratinocytes, heart muscle cells and blood cells from hiPSCs. Further, using artificial intelligence technology and machine leaning method, we w analyzed differences of mutation frequency during samples.