Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
秋田 祐介; 石坂 宏*; 中山 真義*; 島田 明彦; 北村 智; 長谷 純宏; 鳴海 一成; 田中 淳
Journal of Horticultural Science & Biotechnology, 85(5), p.437 - 443, 2010/09
シクラメンの花色合成遺伝子に関する解析のために、紫色の花を有するシクラメン野生種( ,gra6)とその白花変異体(gra50)を用いて、花色成分とその合成にかかわる遺伝子群の比較解析を行った。gra6の花の色素は、アントシアニンのマルビジン3,5ジグルコシドであった。一方、gra50の花ではアントシアニンが確認されず、その前駆物質であるフラボノールの蓄積が確認された。花色合成にかかわる酵素遺伝子群をgra6より単離し、その発現をgra6とgra50で解析したところ、二つのdihydroflavonol-4-reductase(DFR)遺伝子(
,gra6)とその白花変異体(gra50)を用いて、花色成分とその合成にかかわる遺伝子群の比較解析を行った。gra6の花の色素は、アントシアニンのマルビジン3,5ジグルコシドであった。一方、gra50の花ではアントシアニンが確認されず、その前駆物質であるフラボノールの蓄積が確認された。花色合成にかかわる酵素遺伝子群をgra6より単離し、その発現をgra6とgra50で解析したところ、二つのdihydroflavonol-4-reductase(DFR)遺伝子(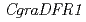 ,
, 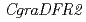 )のうち、
)のうち、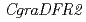 の発現がgra50で減少していた。
の発現がgra50で減少していた。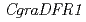 を含む他の遺伝子群には大差がみられなかったことから、
を含む他の遺伝子群には大差がみられなかったことから、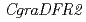 が
が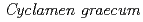 における花色に重要であり、その発現抑制によってアントシアニンの合成が進まず、白花に変異したと考えられた。
における花色に重要であり、その発現抑制によってアントシアニンの合成が進まず、白花に変異したと考えられた。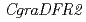 の発現が減少した理由として、遺伝子発現にかかわるプロモーター領域の変異が大きな候補として挙げられた。本研究は、シクラメン花色合成に関する選抜マーカーとして
の発現が減少した理由として、遺伝子発現にかかわるプロモーター領域の変異が大きな候補として挙げられた。本研究は、シクラメン花色合成に関する選抜マーカーとして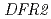 遺伝子が一つの候補であることを示した。
遺伝子が一つの候補であることを示した。
 sp. nov., isolated from the stratosphere
sp. nov., isolated from the stratosphereYang, Y.*; 伊藤 隆*; 横堀 伸一*; 島田 治男*; 板橋 志保*; 佐藤 勝也; 大庭 寛史*; 鳴海 一成; 山岸 明彦*
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 60, p.776 - 779, 2010/04
被引用回数:26 パーセンタイル:50.57(Microbiology)A pink pigmented, non-motile, coccoid bacterial strain, ST0316, was isolated from dust samples collected from the stratosphere in Japan. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that it belonged to the genus  . DNA G+C content, desiccation tolerance, and resistance to
. DNA G+C content, desiccation tolerance, and resistance to  -rays and UV radiation supported the affiliation of strain ST0316 to the genus
-rays and UV radiation supported the affiliation of strain ST0316 to the genus  . Strain ST0316 diverged from recognized species of the genus
. Strain ST0316 diverged from recognized species of the genus  , showing less than 93% similarity values to its closest relatives
, showing less than 93% similarity values to its closest relatives  ,
,  ,
,  and
and  . We propose a new species of the genus
. We propose a new species of the genus  ,
,  sp. nov.
sp. nov.
 sp. nov., isolated from the high atmosphere
sp. nov., isolated from the high atmosphereYang, Y.*; 伊藤 隆*; 横堀 伸一*; 板橋 志保*; 島田 治男*; 佐藤 勝也; 大庭 寛史; 鳴海 一成; 山岸 明彦*
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 59, p.1862 - 1866, 2009/00
被引用回数:32 パーセンタイル:56.58(Microbiology)日本の高度大気圏で収集した塵から、橙色の色素を持ち運動性のない球菌TR0125株が分離された。16S rRNA遺伝子をもとにした系統解析によってこの菌はデイノコッカス属細菌であることが示された。強い乾燥耐性,UV耐性, 線耐性及び高いGC含量は、この菌株がデイノコッカス属細菌であることを支持している。TR0125株は、デイノコッカス・アパチェンシスの標準菌株の16S rRNA遺伝子配列と最も高い類似性(95.7%)をもち、系統解析の結果は、TR0125株が、デイノコッカス・ジオサーマリス以上に、デイノコッカス・アパチェンシスと進化的に離れていることを示しており、このことは、TR0125株がこれら2種のデイノコッカス属細菌に属するものではないことを表している。他にも、TR0125株と上記2種のデイノコッカス属細菌の標準菌株との間には、幾つかの表現型に違いがあった。よって、われわれは今回分離した菌株に適合するものとして、新種デイノコッカス・アエリウスという名前を提案する。
線耐性及び高いGC含量は、この菌株がデイノコッカス属細菌であることを支持している。TR0125株は、デイノコッカス・アパチェンシスの標準菌株の16S rRNA遺伝子配列と最も高い類似性(95.7%)をもち、系統解析の結果は、TR0125株が、デイノコッカス・ジオサーマリス以上に、デイノコッカス・アパチェンシスと進化的に離れていることを示しており、このことは、TR0125株がこれら2種のデイノコッカス属細菌に属するものではないことを表している。他にも、TR0125株と上記2種のデイノコッカス属細菌の標準菌株との間には、幾つかの表現型に違いがあった。よって、われわれは今回分離した菌株に適合するものとして、新種デイノコッカス・アエリウスという名前を提案する。
近藤 昌也; 中村 秀夫; 安濃田 良成; 最首 貞典*; 小幡 宏幸*; 島田 ルミ*; 川村 慎一*
Proceedings of 10th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 10) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2002/00
横型熱交換器を用いた静的格納容器冷却系(PCCS)が検討されている。横型熱交換器の伝熱特性評価のため、水平単一U字伝熱管を用いた実験を行った。実験の結果、伝熱管入口端付近の環状流の局所熱伝達率を既存のモデルが過小評価する傾向があることがわかった。また、同時に行った可視化実験(伝熱管の一部区間に可視窓を取り付け、高速度ビデオを用いて行った)から、環状流の液膜表面に多数の巻波が存在することを確認した。そこで、巻波が液膜を撹拌、伝熱を促進するとの仮定の下に、局所熱伝達率を巻波の時間あたりの通過頻度に対して整理したところ、両者の間には強い相関関係があることを見出し、仮定を裏付けた。さらに、この相関関係を基に、液膜の通過頻度を考慮した、水平管内環状流凝縮熱伝達率を与えるモデルを提案した。
新井 健司*; 栗田 智久*; 中丸 幹英*; 藤木 保伸*; 中村 秀夫; 近藤 昌也; 小幡 宏幸*; 島田 ルミ*; 山口 献*
Proceedings of 10th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 10) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2002/00
次世代型BWR格納容器の過圧破損を防ぐ静的格納容器冷却系(PCCS)横型熱交換器の総合性能の確認を目的として、13年度から大型モデル試験を行っている。この大型モデル試験の開始に先立ち、TRACコードの3次元炉心モジュールに改造を施した多次元二相流コードを用いてPCCS熱交換器2次側のボイド率分布及び1次側の熱交換器伝熱管間の流量配分を求めた。この結果、除熱性能と圧力損失の双方で要求性能を満たすこと、膜沸騰が生じないこと、上部管束と下部管束との間からかなりの2次側冷却水の流入があること,除熱管間の流量配分が各管の除熱量に依存することなどを予測した。
秋田 祐介; 石坂 宏*; 島田 明彦; 中山 真義*; 北村 智; 長谷 純宏; 田中 淳; 鳴海 一成
no journal, ,
シクラメンの花色とその生合成に関する遺伝子群との関連を調べるために、紫色の花色を有するシクラメン野生種(C. graecum, 2n=4x=84)とその花色が白色である変異体を用いて、それぞれの花弁における色素分析とアントシアニン生合成に関与する遺伝子群の比較解析を行った。HPLCの結果、野生種(gra6)のアントシアニンはマルビジン-3,5-ジグルコシド(Mv3,5dG)であった。一方、白色変異体(gra50)ではアントシアニンがほとんど確認されず、フラボノールが、gra6と比較すると増加していた。このgra50における花弁の色素減少の原因因子を探るため、gra6よりアントシアニン合成関連遺伝子群の単離を試みた。その結果、フラボノール合成以降に関与する酵素遺伝子のホモログとして、フラボノイド3'5'-水酸化酵素を1種類(CgF3'5'H),ジヒドロフラボノール4-還元酵素を2種類(CgDFR1, CgDFR2),アントシアニジン合成酵素を1種類(CgANS)それぞれ単離した。それぞれの遺伝子の発現を解析したところ、CgF3'5'H, CgDFR1, CgANSの発現は、gra6, gra50のスリップでともに強い発現がみられ、2種間で大差がなかった。一方、CgDFR2の発現はgra6で強く確認されたが、gra50ではその発現は極端に減少していた。
 and its white-flowered mutant
and its white-flowered mutant秋田 祐介; 石坂 宏*; 中山 真義*; 島田 明彦; 北村 智; 長谷 純宏; 田中 淳; 鳴海 一成
no journal, ,
To reveal the relationship between floral pigmentation and flavonoid biosynthesis genes in cyclamen ( species), we analyzed flower pigments from wild-type cyclamen (
species), we analyzed flower pigments from wild-type cyclamen ( ) and its white-flowered mutant. Analysis with high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) showed that major anthocyanins of the wild-type petal were malvidin 3,5-diglucosides. The white-flowered mutant possessed smaller amount of anthocyanins but higher amount of flavonols than the wild-type, suggesting the change of metabolic flow by disruption of anthocyanin biosynthesis. By degenerate-PCR with total RNAs from wild-type petals, we isolated some flavonoid biosynthesis gene. RT-PCR using a specific primer set for each gene demonstrated that the expression of
) and its white-flowered mutant. Analysis with high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) showed that major anthocyanins of the wild-type petal were malvidin 3,5-diglucosides. The white-flowered mutant possessed smaller amount of anthocyanins but higher amount of flavonols than the wild-type, suggesting the change of metabolic flow by disruption of anthocyanin biosynthesis. By degenerate-PCR with total RNAs from wild-type petals, we isolated some flavonoid biosynthesis gene. RT-PCR using a specific primer set for each gene demonstrated that the expression of 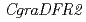 decreased in white-flowered mutant compared with wild-type, whereas the expressions of other genes did not appear to differ greatly. The genomic construction of
decreased in white-flowered mutant compared with wild-type, whereas the expressions of other genes did not appear to differ greatly. The genomic construction of 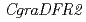 was not different between wild-type and white-flowered mutant, inferring that reduced expression of
was not different between wild-type and white-flowered mutant, inferring that reduced expression of 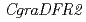 correlates with white-flowered mutation. These results suggest that
correlates with white-flowered mutation. These results suggest that 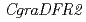 is involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway in
is involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway in 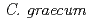 , and the white-flowered mutation could be caused by transcriptional regulation of
, and the white-flowered mutation could be caused by transcriptional regulation of 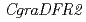 gene.
gene.
横堀 伸一*; Yang, Y.*; 杉野 朋弘*; 河口 優子*; 板橋 志保*; 藤崎 健太*; 伏見 英彦*; 長谷川 直*; 橋本 博文*; 林 宣宏*; et al.
no journal, ,
We isolated two novel species of the genus  , one from top of troposphere (
, one from top of troposphere (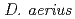 ) and the other from bottom of stratosphere (
) and the other from bottom of stratosphere (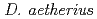 ). Can these newly isolated bacterial species and strains survive harsher environment such as space environment and/or other astronomical objects such as Mars? To address these questions, we have analyzed the survival of these microbial species and strains under the extreme conditions. Environment at high altitude is extreme for microorganisms not only because of high UV radiation, but also other stresses such as extreme dryness. To clarify how dryness affects to the survivability of microorganisms, we examined the effects of desiccation and high humidity on survival and DNA double strand breaks (DSB) of
). Can these newly isolated bacterial species and strains survive harsher environment such as space environment and/or other astronomical objects such as Mars? To address these questions, we have analyzed the survival of these microbial species and strains under the extreme conditions. Environment at high altitude is extreme for microorganisms not only because of high UV radiation, but also other stresses such as extreme dryness. To clarify how dryness affects to the survivability of microorganisms, we examined the effects of desiccation and high humidity on survival and DNA double strand breaks (DSB) of  ,
,  and spores of
and spores of 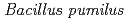 . They exhibited different survival rates and DSB patterns under desiccation and high humidity. Higher survival and less DSB occurred at lower temperatures. Spores of
. They exhibited different survival rates and DSB patterns under desiccation and high humidity. Higher survival and less DSB occurred at lower temperatures. Spores of  showed the highest survivability at each condition. Survivability of
showed the highest survivability at each condition. Survivability of  at desiccation condition is higher than that at the humid condition, although survivability of
at desiccation condition is higher than that at the humid condition, although survivability of  at desiccation condition is lower than that at the humid condition. We also tested the effects of various factors on survivability of
at desiccation condition is lower than that at the humid condition. We also tested the effects of various factors on survivability of  spp. Together with tests under desiccation condition, these test results suggested that
spp. Together with tests under desiccation condition, these test results suggested that  spp. which we tested can survive in space for years.
spp. which we tested can survive in space for years.
 における
における 遺伝子の遺伝子破壊解析
遺伝子の遺伝子破壊解析島田 岳*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
 は、至適生育温度が通常30
は、至適生育温度が通常30 Cである
Cである 属細菌においては例外的に、至適生育温度が45から50
属細菌においては例外的に、至適生育温度が45から50 Cの中等度好熱菌である。本研究では、
Cの中等度好熱菌である。本研究では、 の
の 遺伝子を薬剤耐性マーカーとすげ替えた形の
遺伝子を薬剤耐性マーカーとすげ替えた形の 遺伝子欠失株を作製するとともに、
遺伝子欠失株を作製するとともに、 遺伝子を発現させたプラスミドDNAを遺伝子欠失株に導入して
遺伝子を発現させたプラスミドDNAを遺伝子欠失株に導入して 遺伝子相補株を作製した。また、これらの株を用いて、各種変異原(
遺伝子相補株を作製した。また、これらの株を用いて、各種変異原( 線, UV, マイトマイシンC, ブレオマイシン, 過酸化水素など)に対する耐性を野生株と比較することで
線, UV, マイトマイシンC, ブレオマイシン, 過酸化水素など)に対する耐性を野生株と比較することで における
における 遺伝子の機能を調査した。その結果、欠失株は野生株と比べて生存率が低下し、相補株では耐性が野生株と同等にまで復帰するという結果が得られた。このことから、
遺伝子の機能を調査した。その結果、欠失株は野生株と比べて生存率が低下し、相補株では耐性が野生株と同等にまで復帰するという結果が得られた。このことから、 遺伝子は
遺伝子は においても変異原耐性に関与しており、
においても変異原耐性に関与しており、 が関与するDNA修復機構は他の
が関与するDNA修復機構は他の 属細菌に広く保存されていることが示唆された。
属細菌に広く保存されていることが示唆された。
 における
における 遺伝子破壊解析
遺伝子破壊解析島田 岳*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
 は、至適生育温度が45から50
は、至適生育温度が45から50 Cの中等度好熱菌である。本研究では、
Cの中等度好熱菌である。本研究では、 の
の 遺伝子欠失株を作製するとともに、
遺伝子欠失株を作製するとともに、 遺伝子を発現させたプラスミドDNAを遺伝子欠失株に導入して
遺伝子を発現させたプラスミドDNAを遺伝子欠失株に導入して 遺伝子相補株を作製した。また、これらの株を用いて、各種変異原(
遺伝子相補株を作製した。また、これらの株を用いて、各種変異原( 線, UV, マイトマイシンC, ブレオマイシン, 過酸化水素など)に対する耐性を野生株と比較することで
線, UV, マイトマイシンC, ブレオマイシン, 過酸化水素など)に対する耐性を野生株と比較することで における
における 遺伝子の機能を調査した。その結果、欠失株は野生株と比べて生存率が低下し、相補株では耐性が野生株と同等にまで復帰するという結果が得られた。このことから、
遺伝子の機能を調査した。その結果、欠失株は野生株と比べて生存率が低下し、相補株では耐性が野生株と同等にまで復帰するという結果が得られた。このことから、 遺伝子は
遺伝子は においても変異原耐性に関与しており、
においても変異原耐性に関与しており、 が関与するDNA修復機構は他の
が関与するDNA修復機構は他の 属細菌に広く保存されていることが示唆された。
属細菌に広く保存されていることが示唆された。
藁科 友朗*; 佐藤 朝子*; Shagimardanova, E.*; 丸山 茂徳*; 森 宙史*; 鳴海 一成*; Gusev, O.*; 斎藤 元文*; 眞田 幸尚; 佐々木 祥人; et al.
no journal, ,
原子炉内の大量の放射性物質は、福島第一原子力発電所(1F)の廃止措置を妨げている。この研究の目的は、(1)1F周囲の環境を分析して原子炉内の滞留水に存在する可能性のある微生物を調査すること、(2)微生物腐食の原因となる細菌を特定することの2つである。環境サンプルは、1Fに関連する3つの場所、敷地境界南の土壌、海岸から3km離れた表層海水、および福海底土壌から得られた。16S rRNAアンプリコンシーケンシングの結果、土壌サンプルから少なくとも17の門が確認された。最も豊富な門はアシドバクテリアとプロテオバクテリアであり、門レベルでの群集構造は、福島の低放射能の土壌からのものと類似していた。海水には、少なくとも9つの門が確認された。プロテオバクテリアとシアノバクテリアが最も豊富である。門レベルでの群構造も日立港沖の結果と類比していた。さらに、シュードモナスなどの腐食誘起細菌とディノコッカスなどの耐放射線性細菌が、土壌と海水の両方で発見された。ただし、腐食誘起細菌の相対的存在量は、全体量の1%未満である。原子炉内は還元雰囲気,嫌気性,暗所であるため、微生物群の分布も変化することが予想される。