Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Aoki, Takeshi; Shimizu, Atsushi; Ishii, Katsunori; Morita, Keisuke; Mizuta, Naoki; Kurahayashi, Kaoru; Yasuda, Takanori; Noguchi, Hiroki; Nomoto, Yasunobu; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 220, p.111503_1 - 111503_7, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0Aiming to establish coupling technologies between a high temperature gas cooled reactor and a hydrogen production plant, JAEA has initiated the HTTR Heat Application Test Project and is conducting the safety design and the safety analysis for the licensing of the HTTR Heat Application Test Facility. The present study proposed a relative evaluation methodology for the demarcation of applicable laws and design standards for the nuclear hydrogen production system and applied it to the HTTR Heat Application Test Facility. The evaluation results showed that a candidate applying the High Pressure Gas Safety Act to the Heat Application Test Facility (hydrogen production plant) and design standards established under the High Pressure Gas Safety Act to the steam reformer did not show the lowest category in any of the metrics, and was proposed as the most superior demarcation option for the HTTR Heat Application Test Facility.
 rays in the
rays in the  La(
La(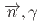 )
) La reaction
La reactionOkuizumi, Mao*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; et al.
Physical Review C, 111(3), p.034611_1 - 034611_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Iwami, Satone*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Mitsuyasu, Yusuke*; Ono, Kenta*; Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sekine, Tsutomu*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; Chiba, Mirei*; et al.
KEK Proceedings 2024-6, p.91 - 95, 2024/12
We aim to improve the detection limit of the ESR dosimetry method. In this study, the saturation behavior of each radical was investigated by varying the microwave power during ESR measurement. Based on the difference in spin relaxation time between carbonate radicals and native radicals, it is expected that the signal-to-noise ratio improves and the detection limit can be lowered when the microwave power is increased to 4.0 mW.
Yamashita, Takuma*; Iwami, Satone*; Mitsuyasu, Yusuke*; Ono, Kenta*; Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Sekine, Tsutomu*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; Chiba, Mirei*; et al.
KEK Proceedings 2024-6, p.85 - 90, 2024/12
To clarify the radiation effects of the accident at the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi NPP on living organisms, it is important to accurately estimate the dose to each individual. We have developed a multi-component analysis program using random number optimization to extract only the components derived from carbonate radicals from the ESR spectra.
Morita, Keisuke; Aoki, Takeshi; Shimizu, Atsushi; Sato, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 31st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE31) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2024/11
Aoki, Takeshi; Hasegawa, Takeshi; Kurahayashi, Kaoru; Nomoto, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Atsushi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Sakaba, Nariaki
Proceedings of 11th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2024), 6 Pages, 2024/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is planning to perform a test named HTTR heat application test coupling HTTR (High temperature engineering test reactor) and a hydrogen production plant. The present study reports results of the safety design and safety analysis for HTTR heat application test facility. As a safety design, safety classification of structures, systems, and components was defined in the test facility based on their safety functions. As a preliminary safety analysis, a thermal-hydraulic analysis was performed with RELAP5 code. The safety analysis revealed that newly identified events for HTTR heat application test facility except for the rupture of heat transfer tube of steam generator was enveloped by the licensing basis events in conventional HTTR. The preliminary analysis proved that the safety criteria is satisfied in the candidate of licensing basis event.
Endo, Shunsuke; Abe, Ryota*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Ino, Takashi*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kawamura, Shiori*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kobayashi, Ryuju*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 60(8), p.166_1 - 166_10, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:78.45(Physics, Nuclear)Nagatsuka, Kentaro; Noguchi, Hiroki; Nagasumi, Satoru; Nomoto, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Atsushi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Sakaba, Nariaki
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 425, p.113338_1 - 113338_11, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:93.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)HTGR has a potential to contribute to decarbonization of hard-to-abate industries by supplying a large amount of hydrogen and high temperature heat or steam without carbon dioxide emission. JAEA has been conducting R&Ds for HTGR technologies with High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR). This paper shows that HTTR's tests including the loss of core cooing test as a joint the OECD/NEA international research project and a HTTR heat application test plan which demonstrate hydrogen production by coupling the HTTR with a hydrogen production test facility. Additionally, aiming for operation start from the latter half of 2030s, the basic design of the HTGR demonstration reactor has been shown. The Japan's HTGR technology capabilities established by the HTTR project will be fully utilized for the construction of HTGR demonstration reactor.
 -odd/
-odd/ -odd interactions on the 0.75 eV
-odd interactions on the 0.75 eV  -wave resonance in
-wave resonance in 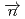 +
+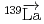 forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beam
forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beamNakabe, Rintaro*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Gudkov, V.*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kambara, Wataru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.L041602_1 - L041602_4, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.17(Physics, Nuclear) -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of 
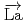 +
+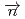
Okudaira, Takuya*; Nakabe, Rintaro*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Gudkov, V.*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kambara, Wataru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.044606_1 - 044606_9, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:78.45(Physics, Nuclear)Kido, Eiji*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Kobayashi, Nobuyuki*; Nagataki, Shigehiro*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Tamii, Atsushi*; Utsuno, Yutaka
Astroparticle Physics, 152, p.102866_1 - 102866_12, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.14(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Ishii, Katsunori; Morita, Keisuke; Noguchi, Hiroki; Aoki, Takeshi; Mizuta, Naoki; Hasegawa, Takeshi; Nagatsuka, Kentaro; Nomoto, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Atsushi; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
Dai-27-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2023/09
Tamii, Atsushi*; Pellegri, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 59(9), p.208_1 - 208_21, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:76.15(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Mitsuyasu, Yusuke*; Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Sekine, Tsutomu*; Yamashita, Takuma*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; Chiba, Mirei*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(14), p.1620 - 1625, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.62(Environmental Sciences)We have been conducting dose assessments for Japanese macaques captured in Fukushima to reveal radiobiological effects on the low-dose expose animals. To accurately determine the external exposure dose, it is desirable to examine the analysis of the CO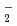 radical intensity. We examined ESR spectra of teeth of 10 macaques captured in Fukushima by two spectrum-decomposition algorithms.
radical intensity. We examined ESR spectra of teeth of 10 macaques captured in Fukushima by two spectrum-decomposition algorithms.
 rays from a neutron-induced
rays from a neutron-induced  -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of  Xe
XeOkudaira, Takuya*; Tani, Yuika*; Endo, Shunsuke; Doskow, J.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kameda, Kento*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Luxnat, M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 107(5), p.054602_1 - 054602_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:76.15(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Mizuta, Naoki; Morita, Keisuke; Aoki, Takeshi; Okita, Shoichiro; Ishii, Katsunori; Kurahayashi, Kaoru; Yasuda, Takanori; Tanaka, Masato; Isaka, Kazuyoshi; Noguchi, Hiroki; et al.
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/05
Aoki, Takeshi; Shimizu, Atsushi; Noguchi, Hiroki; Kurahayashi, Kaoru; Yasuda, Takanori; Nomoto, Yasunobu; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Sato, Hiroyuki; Sakaba, Nariaki
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
The safety design philosophy is developed for the HTTR (High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor) heat application test facility connecting high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) and the hydrogen production plant. The philosophy was proposed to apply proven conventional chemical plant standards to the hydrogen production facility for ensuring public safety against anticipated disasters caused by high pressure and combustible gases. The present study also proposed the safety design philosophy to meet specific safety requirements identified to the nuclear facilities with coupling to the hydrogen production facility such as measures to ensure a capability of normal operation of the nuclear facility against a fire and/or explosion of leaked combustible material, and fluctuation of amount of heat removal occurred in the hydrogen production plant. The safety design philosophy will be utilized to establish its basic and detailed designs of the HTTR-heat application test facility.
Ishii, Katsunori; Aoki, Takeshi; Isaka, Kazuyoshi; Noguchi, Hiroki; Shimizu, Atsushi; Sato, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
Nomoto, Yasunobu; Mizuta, Naoki; Morita, Keisuke; Aoki, Takeshi; Okita, Shoichiro; Ishii, Katsunori; Kurahayashi, Kaoru; Yasuda, Takanori; Tanaka, Masato; Isaka, Kazuyoshi; et al.
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/05
 Ta(n,
Ta(n, )
)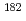 Ta reaction
Ta reactionKawamura, Shiori*; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Nakamura, Shoji; Okudaira, Takuya*; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2023-001, p.115 - 120, 2023/02
no abstracts in English