Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kusano, Kanya*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Ishii, Mamoru*; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Akiyoshi, Hideharu*; Asai, Ayumi*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Goto, Tadanori*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.159_1 - 159_29, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:39.36(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The PSTEP is a nationwide research collaboration in Japan and was conducted from April 2015 to March 2020, supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. It has made a significant progress in space weather research and operational forecasts, publishing over 500 refereed journal papers and organizing four international symposiums, various workshops and seminars, and summer school for graduate students at Rikubetsu in 2017. This paper is a summary report of the PSTEP and describes the major research achievements it produced.
 He neutron spin filter at J-PARC
He neutron spin filter at J-PARCOkudaira, Takuya; Oku, Takayuki; Ino, Takashi*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakai, Kenji; Hiroi, Kosuke; Takahashi, Shingo*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Endo, Hitoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 977, p.164301_1 - 164301_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:89.09(Instruments & Instrumentation)Sugimoto, Masahiro*; Kosugi, Keizo*; Katayama, Kota*; Ii, Hideki*; Takagi, Akira*; Endo, Sakaru*; Shimizu, Hitoshi*; Tsubouchi, Hirokazu*; Kizu, Kaname; Yoshida, Kiyoshi
Proceedings of 24th International Cryogenic Engineering Conference (ICEC 24) and International Cryogenic Materials Conference 2012 (ICMC 2012) (CD-ROM), p.799 - 802, 2012/05
We have successfully manufactured all superconducting cables for CS and EF coils of JT-60SA. The low temperature performance of superconducting wires satisfied the specifications under sufficiently low deviations and high production yields. Ni-plated strands of EF cables having the larger sliding friction between strands than that of Cr-plated strands of CS cable caused difficulties on the cabling without any defects. Consequently, the newly developed cabling techniques with the original inspection apparatus significantly enhanced the manufacturability and were effective for guarantee of the quality.
Mishima, Kenji*; Ino, Takashi*; Sakai, Kenji; Shinohara, Takenao; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ikeda, Kazuaki*; Sato, Hiromi*; Otake, Yoshie*; Omori, Hitoshi*; Muto, Suguru*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600, p.342 - 345, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:87.48(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new beamline for a fundamental physics experiment is under construction at BL05 port in the Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF) at Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), this beamline is designed using novel techniques of neutron optics and it is termed "Neutron Optics and Physics". The beam from the moderator is deflected by multi-channel supermirrors and split into three branches for individual experiments. In this study, we have optimized the design of the beam optics and shields using the Monte Carlo simulation package PHITS. The neutron fluxes of beams are expected to be 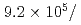 cm
cm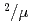 str
str s
s MW,
MW, 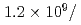 cm
cm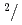 s
s MW,
MW, 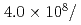 cm
cm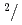 s
s MW, with polarization of 99.8%.
MW, with polarization of 99.8%.
 N(n,
N(n, )
) N reaction as a
N reaction as a  -ray intensity standard up to 11 MeV
-ray intensity standard up to 11 MeVMiyazaki, Itaru*; Sakane, Hitoshi*; Takayama, Hirokazu*; Kasaishi, Masafumi*; Tojo, Akinori*; Furuta, Masataka*; Hayashi, Hiroaki*; Suematsu, Osamu*; Narasaki, Hiromichi*; Shimizu, Toshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(6), p.481 - 486, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)The intensities of the prompt  rays from the
rays from the  N(n,
N(n, )
) N reaction have been precisely measured. As the samples, a liquid nitrogen target and a deuterated melamine (C
N reaction have been precisely measured. As the samples, a liquid nitrogen target and a deuterated melamine (C D
D N
N ) were used. The previous values widely used as intensity standards agreed with those obtained in this study within 4-5% in the 2-11 MeV region, however, showed a monotonous decrease with the increase of
) were used. The previous values widely used as intensity standards agreed with those obtained in this study within 4-5% in the 2-11 MeV region, however, showed a monotonous decrease with the increase of  -ray energy.
-ray energy.
Maekawa, Keisuke; Sawada, Atsushi; Ota, Kunio; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Kunimaru, Takanori; Funaki, Hironori; Hama, Katsuhiro; Takeuchi, Shinji; Amano, Kenji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-011, 8 Pages, 2007/03
In the current programme for research and development on the technical aspects of geological disposal, it is of significance to establish techniques for evaluating solute transport with a direct link to surface-based investigations through the processes of data interpretation, modelling and parameter designation within the immediate five years following the H17 Project. This report presents a basic approach to promoting multidisciplinary research activities involving field investigations and relevant solute transport analysis.
Miyamoto, Yoichi; Umeki, Hiroyuki; Osawa, Hideaki; Naito, Morimasa; Nakano, Katsushi; Makino, Hitoshi; Shimizu, Kazuhiko; Seo, Toshihiro
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 38(6), p.505 - 534, 2006/08
Ensuring sufficient supplies of clean, economic and acceptable energy is a critical global challenge for the 21st century. There seems little alternative to a greatly expanded role for nuclear power, but implementation of this option will depend on ensuring that all resulting wastes can be disposed of safely. Although there is a consensus on the fundamental feasibility of such disposal by experts in the field, concepts have to be developed to make them more practical to implement and, in particular, more acceptable to key stakeholders. By considering global trends and using illustrative examples from Japan, key areas for future R&D are identified and potential areas where the synergies of international collaboration would be beneficial are highlighted.
Miyazaki, Itaru*; Shimizu, Toshiaki*; Shibata, Michihiro*; Kawade, Kiyoshi*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Nakamura, Shoji; Sakane, Hitoshi; Harada, Hideo
JNC TY8400 2005-002, 40 Pages, 2005/06
Accurate cross section data for the neutron capture of long-lived fission products (LLFP) are needed for developing a nuclear transmutation technology which reduces radioactive wastes by transmuting nuclides that have half-lives of as long as a few million years to other nuclides that have much shorter half-lives. There are some nuclides, whose cross sections cannot be measured in activation method. Utilization of prompt gamma-rays is expected to solve this problem. The aim of present study was twofold: (i) to measure emission probabilities of the high energy gamma-ray, up to 10MeV, emitted from  N(
N( )
) N reaction, which are usually used as standards, in order to improve their accuracies and (ii) to develop a measurement method for neutron capture cross sections by using prompt gamma-rays. Emission probabilities of principal prompt gamma-rays from
N reaction, which are usually used as standards, in order to improve their accuracies and (ii) to develop a measurement method for neutron capture cross sections by using prompt gamma-rays. Emission probabilities of principal prompt gamma-rays from  N(
N( )
) N reaction were determined with 0.2-0.9% errors. For ten nuclides,
N reaction were determined with 0.2-0.9% errors. For ten nuclides,  Na,
Na,  Al,
Al, 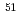 V,
V,  Mn,
Mn,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Cu,
Cu, 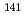 Pr,
Pr,  W, and
W, and  Au capture cross sections were measured by using prompt gamma-rays and gamma-rays following b-decay. By comparing both cross section values, it was found that emission probabilities of prompt gamma-rays reported in the literatures were systematically larger than those inferred from the cross sections that were determined in activation methods. The cross section of a
Au capture cross sections were measured by using prompt gamma-rays and gamma-rays following b-decay. By comparing both cross section values, it was found that emission probabilities of prompt gamma-rays reported in the literatures were systematically larger than those inferred from the cross sections that were determined in activation methods. The cross section of a 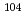 Pd(
Pd( )
)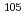 Pd reaction at thermal energy was measured. Considering transmutation of the nuclide, the cross section of
Pd reaction at thermal energy was measured. Considering transmutation of the nuclide, the cross section of 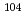 Pd(
Pd( ), which is an isotope of palladium, is also necessary. A lower limit of the cross section was determined with 6% accuracy. Additionally, a method of estimating an upper limit was examined by noting similarity of nuclear structures to the neighboring nuclides. It was estimated that the observed lower limit of emission probabilities correspond to 79% of the cross section.
), which is an isotope of palladium, is also necessary. A lower limit of the cross section was determined with 6% accuracy. Additionally, a method of estimating an upper limit was examined by noting similarity of nuclear structures to the neighboring nuclides. It was estimated that the observed lower limit of emission probabilities correspond to 79% of the cross section.
Tsutagi, Koichi; Shimizu, Ryo; Sugiyama, Takayuki; Nakazawa, Y.; Tanaka, Hitoshi; Watahiki, Masaru; Muto, Hideyo
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (21), p.33 - 40, 2003/00
This report describes the outline of the measurement system of HALW storage tank and a measurement situation, and a thickness measurement result.
Nakano, Masanao; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Shimizu, Takehiko; ; Morita, Shigemitsu; Katagiri, Hiromi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 243(2), p.319 - 322, 2002/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.98(Chemistry, Analytical)None
Oku, Takayuki*; ; ; Yamagata, Yutaka*; Omori, Hitoshi*; Adachi, Tomohiro*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; ; Hirota, T.*; Iwasa, Hirokatsu*; et al.
JAERI-Conf 2001-002, p.537 - 541, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
; ; Shimizu, Kazuhiko; Miyahara, Kaname; ; Hasegawa, Hiroshi; Makino, Hitoshi
JNC TN1410 2000-004, 462 Pages, 2000/04
It was demonstrated in Supporting Report 1, based on extensive investigations and literature surveys, that stable geological environments exist in Japan that are suitable for geological disposal of HLW. The characteristics of these geological environments have been summarized to provide a basis for the H12 design study and safety assessment. Examples of repository designs have been developed and presented in Supporting Report 2. In this Supporting Report, a robust safety assessment methodology has been developed, focusing on the barrier functions of the engineered barrier system (EBS) and the near-field host rock within tens of meters of the repository. Moreover, this methodology has been applied to assess the safety of the geological disposal system defined in Supporting Reports 1 and 2. This Supporting Report consists of the following nine Chapters. Chapter I presents the objectives of H12 safety assessment, Chapter II summarized the AEC Guidelines and safety assessment procedures, I
; ; Shimizu, Kazuhiko; Miyahara, Kaname; ; Hasegawa, Hiroshi; Makino, Hitoshi
JNC TN1410 2000-003, 714 Pages, 2000/04
This report provides a summary of the results of studies on design and engineering technology for a deep geological repository for vitrified high-level radioactive waste (HLW) that have been conducted by the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC). The Japanese multibarrier system is illustrated in Figure 1. The purpose of this H12 Supporting Report 2 is to address the objectives and issues on repository design and engineering that are described in a report published in 1997 by the Advisory Committee on Nuclear Fuel Cycle Backend Policy of the Atomic Energy Commission of Japan, entitled "Guidelines on Research and Development Relating to the Geological Disposal of High-Level Radioactive Waste in Japan" (the "AEC Guidelines"). For H12, the specific objectives are: to propose design requirements for a safe, reliable engineered barrier system (EBS) and disposal facility and, to show that the EBS and disposal facility can be reasonably constructed using currently available engine
; ; Shimizu, Kazuhiko; Miyahara, Kaname; ; Hasegawa, Hiroshi; Makino, Hitoshi
JNC TN1410 2000-001, 395 Pages, 2000/04
(Background) As outlined in the overall program for high-level waste (HLW) management in Japan, defined by the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC), HLW separated from spent nuclear fuel during reprocessing will be immobilized in a glass matrix and stored for a period of 30 to 50 years to allow cooling; it will then be disposed of in a stable deep geological formation. An organization with responsibility for implementing HLW disposal will be established around the year 2000; this will be followed by site selection and characterization, demonstration of disposal technology, establishment of the necessary regulatory infrastructure, relevant licensing applications and repository construction. The aim is to start repository operation by the 2030s, but no later than the mid 2040s. The aim of current R&D activities, in which the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) takes the leading role, is to provide a scientific and technical basis for geological disposal of HLW in Japan and to promo
; ; Shimizu, Kazuhiko; Miyahara, Kaname; ; Hasegawa, Hiroshi; Makino, Hitoshi
JNC TN1400 99-023, 529 Pages, 1999/11
None
; ; Shimizu, Kazuhiko; Miyahara, Kaname; ; Hasegawa, Hiroshi; Makino, Hitoshi
JNC TN1400 99-022, 704 Pages, 1999/11
None
; ; Shimizu, Kazuhiko; Miyahara, Kaname; ; Hasegawa, Hiroshi; Makino, Hitoshi
JNC TN1400 99-013, 415 Pages, 1999/05
The Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC), successor to the Power Reactor and Nuclear Fuel Development Corporation (PNC) as of 1st October 1998, has prepared a second progress report (entitled H12) on research and development for geological disposal of high-level waste (HLW) in Japan. H12, which documents progress made since the publication of the first progress report (H3) in 1992, will be presented to the Japanese Government for their review by the year 2000. The purpose of the work was specified in a, report published in April 1997 by the Advisory Committee on Nuclear Fuel Cycle Backend Policy of the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) entitled "Guidelines on Research and Development Relating to Geological Disposal of High-Level Radioactive Waste in Japan" (AEC Guidelines). The primary objective of H12, as specified in the AEC Guidelines, is to present an outline of the technical reliability of geological disposal in Japan. It should also provide input for the siting and regula
; ; Shimizu, Kazuhiko; Miyahara, Kaname; ; Hasegawa, Hiroshi; Makino, Hitoshi
JNC TN1400 99-012, 586 Pages, 1999/05
The Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC), successor to the Power Reactor and Nuclear Fuel Development Corporation (PNC) as of 1st October 1998, has prepared a second progress report (entitled H12) on research and development for geological disposal of high-level waste (HLW) in Japan. H12, which documents progress made since the publication of the first progress report (H3) in 1992, will be presented to the Japanese Government for their review by the year 2000. The purpose of the work was specified in a report published in April 1997 by the Advisory Committee on Nuclear Fuel Cycle Backend Policy of the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) entitled "Guidelines on Research and Development Relating to Geological Disposal of High-Level Radioactive Waste in Japan" (AEC Guidelines). The primary objective of H12, as specified in the AEC Guidelines, is to present an outline of the technical reliability of geological disposal in Japan. It should also provide input for the siting and regulat
; ; Shimizu, Kazuhiko; Miyahara, Kaname; ; Hasegawa, Hiroshi; Makino, Hitoshi
JNC TN1400 99-010, 423 Pages, 1999/05
The Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC), successor to the Power Reactor and Nuclear Fuel Development Corporation (PNC) as of 1st October 1998, has prepared a second progress report (entitled H12) on research and development for geological disposal of high-level waste (HLW) in Japan. H12, which documents progress made since the publication of the first progress report (H3) in 1992, will be presented to the Japanese Government for their review by the year 2000. The purpose of the work was specified in a report published in April 1997 by the Advisory Committee on Nuclear Fuel Cycle Backend Policy of the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) entitled "Guidelines on Research and Development Relating to Geological Disposal of High-Level Radioactive Waste in Japan" (hereafter the AEC Guidelines). The primary objective of H12, as specified in the AEC Guidelines, is to present an outline of the technical reliability of geological disposal in Japan. It should also provide input for the siti
; ; Shimizu, Kazuhiko; Miyahara, Kaname; ; Hasegawa, Hiroshi; Makino, Hitoshi
JNC TN1400 99-009, 505 Pages, 1999/04
None