Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 structure transition under high pressure
structure transition under high pressureYamanaka, Takamitsu*; Nakamoto, Yuki*; Sakata, Masafumi*; Shimizu, Katsuya*; Hattori, Takanori
Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 51(1), p.4_1 - 4_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Neutron and synchrotron X-ray diffraction and electric conductivity measurements of FeTiO ilmenite were performed under pressures. Ilmenite structure is retained up to 28 GPa. Structure analysis revealed that FeO
ilmenite were performed under pressures. Ilmenite structure is retained up to 28 GPa. Structure analysis revealed that FeO and TiO
and TiO are compressible and less compressible below 8 GPa, respectively. The resistivity is lowest along the Fe-Ti direction that has shortest interatomic distance among all the metal ion pairs. The resistivity in the direction normal to c-axis monotonically decreases with pressure, whereas that along c-axis shows hallow-shape with pressure. Maximum entropy analysis shows that electron configuration of Fe
are compressible and less compressible below 8 GPa, respectively. The resistivity is lowest along the Fe-Ti direction that has shortest interatomic distance among all the metal ion pairs. The resistivity in the direction normal to c-axis monotonically decreases with pressure, whereas that along c-axis shows hallow-shape with pressure. Maximum entropy analysis shows that electron configuration of Fe (3
(3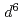 ) is more strongly changed than Ti
) is more strongly changed than Ti (3
(3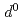 ) under compression. The anisotropic electrical conductivity and non-uniform structure change of Fe-Ti interatomic distance can be explained by the possible spin transition from high-spin state to intermediate-spin state of Fe cation.
) under compression. The anisotropic electrical conductivity and non-uniform structure change of Fe-Ti interatomic distance can be explained by the possible spin transition from high-spin state to intermediate-spin state of Fe cation.
 rays from a neutron-induced
rays from a neutron-induced  -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of  Xe
XeOkudaira, Takuya*; Tani, Yuika*; Endo, Shunsuke; Doskow, J.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kameda, Kento*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Luxnat, M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 107(5), p.054602_1 - 054602_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.16(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 rays in the
rays in the 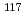 Sn(
Sn( )
)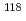 Sn reaction
Sn reactionEndo, Shunsuke; Okudaira, Takuya*; Abe, Ryota*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Oku, Takayuki; Sakai, Kenji; Shima, Tatsushi*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064601_1 - 064601_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:52.69(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 rays from the
rays from the  -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of 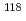 Sn
SnKoga, Jun*; Takada, Shusuke*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Niinomi, Yudai*; Okudaira, Takuya*; et al.
Physical Review C, 105(5), p.054615_1 - 054615_5, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:66.85(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Komuro, Michiyasu; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki; Kokusen, Junya; Shimizu, Osamu; Honda, Junichi; Harada, Katsuya; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Inagawa, Jun
JAEA-Technology 2021-042, 197 Pages, 2022/03
Plutonium Research Building No.1 was constructed in 1960 for the purpose of establishing plutonium handling technology and studying its basic physical properties. Radiochemical research, physicochemical research and analytical chemistry regarding solutions and solid plutonium compounds had been doing for the research program in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). In 1964, the laboratory building was expanded and started the researching plutonium-uranium mixed fuel and reprocessing of plutonium-based fuel, playing an advanced role in plutonium-related research in Japan. Since then, the research target has been expanded to include transplutonium elements, and it has functioned as a basic research facility for actinides. The laboratory is constructed by concrete structure and it has the second floor, equipped with 15 glove boxes and 4 chemical hoods. Plutonium Research Building No.1 was decided as one of the facilities to be decommissioned by Japan Atomic Energy Agency Reform Plan in September 2014. So far, the contamination survey of the radioactive materials in the controlled area, the decontamination of glove boxes, and the consideration of the equipment dismantling procedure have been performed as planned. The radioisotope and nuclear fuel materials used in the facility have been transfer to the other facilities in JAEA. The decommissioning of the facility is proceeding with the goal of completing by decommissioning the radiation controlled area in 2026. In this report, the details of the decommissioning plan and the past achievements are reported with the several data.
Inagawa, Jun; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Takano, Masahide; Akie, Hiroshi; Shimizu, Osamu; Komuro, Michiyasu; Oura, Hirofumi*; Nagai, Isao*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2021-001, 144 Pages, 2021/08
Plutonium Research Building No.1 (Pu1) was qualified as a facility to decommission, and preparatory operations for decommission were worked by the research groups users and the facility managers of Pu1. The operation of transportation of whole nuclear materials in Pu1 to Back-end Cycle Key Element Research Facility (BECKY) completed at Dec. 2020. In the operation included evaluation of criticality safety for changing permission of the license for use nuclear fuel materials in BECKY, cask of the transportation, the registration request of the cask at the institute, the test transportation, formulation of plan for whole nuclear materials transportation, and the main transportation. This report circumstantially shows all of those process to help prospective decommission.
 rays in the
rays in the  La(
La( )
) La
La reaction
reactionOkudaira, Takuya*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; Niinomi, Yudai*; Sakai, Kenji; et al.
Physical Review C, 104(1), p.014601_1 - 014601_6, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:57.13(Physics, Nuclear)Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Hirota, Katsuya*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011116_1 - 011116_6, 2021/03
In neutron fundamental physics, study of correlation term  of a neutron spin
of a neutron spin 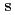 and a target nuclear spin
and a target nuclear spin 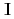 is important because
is important because  term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to
term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to 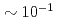 by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study
by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study  term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by
term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by  term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of
term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of  Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change
Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change  of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (
of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (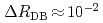 ) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of
) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of  has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained
has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained  in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
Kokusen, Junya; Akasaka, Shingo*; Shimizu, Osamu; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki; Honda, Junichi; Harada, Katsuya; Okamoto, Hisato
JAEA-Technology 2020-011, 70 Pages, 2020/10
The Uranium Enrichment Laboratory in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was constructed in 1972 for the purpose of uranium enrichment research. The smoke emitting accident on 1989 and the fire accident on 1997 had been happened in this facility. The research on uranium enrichment was completed in JFY1998. The decommissioning work was started including the transfer of the nuclear fuel material to the other facility in JFY2012. The decommissioning work was completed in JFY2019 which are consisting of removing the hood, dismantlement of wall and ceiling with contamination caused by fire accident. The releasing the controlled area was performed after the confirmation of any contamination is not remained in the target area. The radioactive waste was generated while decommissioning, burnable and non-flammable are 1.7t and 69.5t respectively. The Laboratory will be used as a general facility for cold experiments.
 He neutron spin filter at J-PARC
He neutron spin filter at J-PARCOkudaira, Takuya; Oku, Takayuki; Ino, Takashi*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakai, Kenji; Hiroi, Kosuke; Takahashi, Shingo*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Endo, Hitoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 977, p.164301_1 - 164301_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:79.13(Instruments & Instrumentation) rays from neutron-induced compound states of
rays from neutron-induced compound states of  La
LaYamamoto, Tomoki*; Okudaira, Takuya; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(6), p.064624_1 - 064624_8, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:73.66(Physics, Nuclear) He
He
 excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron-
excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron- He absorption reaction
He absorption reactionSonnenschein, V.*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kokuryu, Shoma*; Kubo, Wataru*; Suzuki, So*; Tomita, Hideki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Matsushita, Taku*; Wada, Nobuo*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(3), p.033318_1 - 033318_12, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Instruments & Instrumentation) -rays after neutron capture by
-rays after neutron capture by  La for a T-violation search
La for a T-violation searchOkudaira, Takuya; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Haddock, C. C.*; Ito, Ikuya*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Endo, Shunsuke*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Sato, Takumi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 219, p.09001_1 - 09001_6, 2019/12
Parity violating effects enhanced by up to 10 times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n,
times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n, ) reaction was measured with
) reaction was measured with  La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized
La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized  La target and a 70% polarized
La target and a 70% polarized  He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm
He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm cm are needed. Therefore high quality
cm are needed. Therefore high quality  He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n,
He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n, ) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the
) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the  He spin filter will be presented.
He spin filter will be presented.
 He
He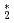 clusters via neutron-
clusters via neutron- He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulence
He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulenceMatsushita, Taku*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Guo, W.*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hirota, Katsuya*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Ito, Daisuke*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 196(1-2), p.275 - 282, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.76(Physics, Applied) rays from neutron-induced compound states of
rays from neutron-induced compound states of  La
LaOkudaira, Takuya*; Takada, Shusuke*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; Nagamoto, Kosuke*; Nakao, Taro*; Okada, Anju*; Sakai, Kenji; et al.
Physical Review C, 97(3), p.034622_1 - 034622_15, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:71.12(Physics, Nuclear) -rays at the ANNRI in the MLF of the J-PARC
-rays at the ANNRI in the MLF of the J-PARCTakada, Shusuke*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Goto, Fumiya*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; Nakao, Taro*; Sakai, Kenji; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; et al.
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 13(2), p.P02018_1 - P02018_21, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:31.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)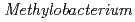 sp. ME121, isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with
sp. ME121, isolated from soil as a mixed single colony with 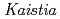 sp. 32K
sp. 32KFujinami, Shun*; Takeda, Kiyoko*; Onodera, Takefumi*; Sato, Katsuya; Shimizu, Tetsu*; Wakabayashi, Yu*; Narumi, Issey*; Nakamura, Akira*; Ito, Masahiro*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 3(5), p.e01005-15_1 - e01005-15_2, 2015/09
Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko*; Tatebe, Yosuke; Tsutsumi, Masahiro; Kawasaki, Katsuya; Kowatari, Munehiko; Yoshizawa, Michio; Shimizu, Shigeru*; Kim, J.-S.*; Lee, J.-G.*; et al.
Proceedings of 4th Asian and Oceanic Congress on Radiation Protection (AOCRP-4) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2015/07

Adachi, Motoyasu; Hirayama, Hiroshi; Shimizu, Rumi; Sato, Katsuya; Narumi, Issey*; Kuroki, Ryota
Protein Science, 23(10), p.1349 - 1358, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:25.51(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Pleiotropic protein promoting DNA repair A (PprA) is a key protein that facilitates the extreme radioresistance of  . To clarify the role of PprA in the radioresistance mechanism, the interaction between recombinant PprA expressed in Escherichia coli with several double-stranded DNAs was investigated. In a gel-shift assay, the band shift of supercoiled pUC19 DNA caused by the binding of PprA showed a bimodal distribution, which was promoted by the addition of 1 mM Mg, Ca, or Sr ions. The dissociation constant of the PprA-supercoiled pUC19 DNA complex, calculated from the relative portions of shifted bands, was 0.6
. To clarify the role of PprA in the radioresistance mechanism, the interaction between recombinant PprA expressed in Escherichia coli with several double-stranded DNAs was investigated. In a gel-shift assay, the band shift of supercoiled pUC19 DNA caused by the binding of PprA showed a bimodal distribution, which was promoted by the addition of 1 mM Mg, Ca, or Sr ions. The dissociation constant of the PprA-supercoiled pUC19 DNA complex, calculated from the relative portions of shifted bands, was 0.6  M with a Hill coefficient of 3.3 in the presence of 1 mM Mg acetate. This indicates that at least 281 PprA molecules are required to saturate a supercoiled pUC19 DNA, which is consistent with the number of bound PprA molecules estimated by the UV absorption of the PprA-pUC19 complex purified by gel filtration. This saturation also suggests linear polymerization of PprA along the dsDNA. On the other hand, the bands of linear dsDNA and nicked circular dsDNA that eventually formed PprA complexes did not saturate, but created larger molecular complexes when the PprA concentration was greater than 1.3
M with a Hill coefficient of 3.3 in the presence of 1 mM Mg acetate. This indicates that at least 281 PprA molecules are required to saturate a supercoiled pUC19 DNA, which is consistent with the number of bound PprA molecules estimated by the UV absorption of the PprA-pUC19 complex purified by gel filtration. This saturation also suggests linear polymerization of PprA along the dsDNA. On the other hand, the bands of linear dsDNA and nicked circular dsDNA that eventually formed PprA complexes did not saturate, but created larger molecular complexes when the PprA concentration was greater than 1.3  M. This result implies that DNA-bound PprA aids association of the termini of damaged DNAs, which is regulated by the concentration of PprA.
M. This result implies that DNA-bound PprA aids association of the termini of damaged DNAs, which is regulated by the concentration of PprA.
Ninomiya, Kazuaki*; Omote, Sayuri*; Sato, Katsuya; Narumi, Issey*; Shimizu, Nobuaki*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 115, 2014/03