Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
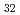 (Al, Zn)
(Al, Zn)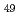 Approximant crystal; Influence of chemical disorder
Approximant crystal; Influence of chemical disorderShimizu, Kazuyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Akamaru, Satoshi*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Abe, Rion*; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Wang, Y.*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 265, p.116730_1 - 116730_7, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Ebihara, Kenichi; Fujihara, Hiro*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Toda, Hiroyuki*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 136, p.751 - 756, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0It has been experimentally reported that adding tin (Sn) to high-strength aluminum-zinc-magnesium (Al-Zn-Mg) alloys effectively suppresses hydrogen (H) embrittlement, which may be attributed to H absorption by the second-phase particles of Sn. To verify this fact, a simulation of H entry into the Sn phase in Al was performed using a model based on the reaction-diffusion equation that incorporates the solid solution energy of H evaluated by first-principles calculations. The results showed that the H solid solution site concentration of the second-phase particles must be at least five times higher than that of the Al phase for H absorption by the Sn second-phase particles to suppress H embrittlement. Therefore, the actual H embrittlement suppression effect of Sn second-phase particles is limited, and other factors may influence the suppression of H embrittlement in the experiment.
Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 109, p.1421 - 1436, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:93.94(Chemistry, Physical)Our preceding investigation revealed that multiple hydrogen traps at coherent interfaces of MgZn precipitates initiated spontaneous interface decohesion, causing hydrogen-induced quasicleavage cracking in Al-Zn-Mg alloys. Herein, we performed a quantitative and systematic investigation to discern the mechanisms by which hydrogen trapped at coherent/semi-coherent interfaces of precipitates could influence macroscopic hydrogen embrittlement by modulating the coherent interface of MgZn
precipitates initiated spontaneous interface decohesion, causing hydrogen-induced quasicleavage cracking in Al-Zn-Mg alloys. Herein, we performed a quantitative and systematic investigation to discern the mechanisms by which hydrogen trapped at coherent/semi-coherent interfaces of precipitates could influence macroscopic hydrogen embrittlement by modulating the coherent interface of MgZn through aging. To explore this hydrogen embrittlement phenomenon based on hydrogen trapping at the precipitate interface, we determined the hydrogen trapping energy of the semi-coherent MgZn
through aging. To explore this hydrogen embrittlement phenomenon based on hydrogen trapping at the precipitate interface, we determined the hydrogen trapping energy of the semi-coherent MgZn interface via first-principles calculations (0.56 eV/atom). Hydrogen partitioning of all hydrogen trapping sites, including vacancies, grain boundaries, and coherent and semi-coherent MgZn
interface via first-principles calculations (0.56 eV/atom). Hydrogen partitioning of all hydrogen trapping sites, including vacancies, grain boundaries, and coherent and semi-coherent MgZn interfaces, revealed that in overaged alloys, over 90% of the hydrogen was sequestered at semi-coherent interfaces. Owing to the inherent characteristics of the MgZn
interfaces, revealed that in overaged alloys, over 90% of the hydrogen was sequestered at semi-coherent interfaces. Owing to the inherent characteristics of the MgZn interface, the hydrogen sequestered at the semi-coherent interface decreased the interfacial cohesive energy, causing semispontaneous decohesion of the interface and quasicleavage fracture in the Al-Zn-Mg alloys. These results implied that intergranular fracture was not directly induced by hydrogen trapped at grain boundaries but rather by the decohesion of precipitate interfaces along grain boundaries.
interface, the hydrogen sequestered at the semi-coherent interface decreased the interfacial cohesive energy, causing semispontaneous decohesion of the interface and quasicleavage fracture in the Al-Zn-Mg alloys. These results implied that intergranular fracture was not directly induced by hydrogen trapped at grain boundaries but rather by the decohesion of precipitate interfaces along grain boundaries.
Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Akamaru, Satoshi*; Lee, S.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Higemoto, Wataru; et al.
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 95, p.292 - 299, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.55(Chemistry, Physical)Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments were conducted on Al-0.06%Mn, Al-0.06%Cr, Al-0.02%Fe, and Al-0.02%Ni alloys (at.%) across the temperature ranging from 5 to 300 K. The temperature-dependent variations of the dipole field widths ( ) elucidated four distinct peaks for the prepared alloys. Atomic configurations of the muon trapping sites corresponding to the observed
) elucidated four distinct peaks for the prepared alloys. Atomic configurations of the muon trapping sites corresponding to the observed  peaks below 200 K were meticulously characterized utilizing first-principles calculations for the trapping energies of hydrogen in proximity to a solute and solute-vacancy pair. This comprehensive analysis facilitated the establishment of a linear correlation between the muon
peaks below 200 K were meticulously characterized utilizing first-principles calculations for the trapping energies of hydrogen in proximity to a solute and solute-vacancy pair. This comprehensive analysis facilitated the establishment of a linear correlation between the muon  peak temperature and the hydrogen trapping energy. However, significant deviations from this linear relationship were observed for the fourth
peak temperature and the hydrogen trapping energy. However, significant deviations from this linear relationship were observed for the fourth  peaks above 200 K in Al-Mn, Al-Cr, Al-Fe, and Al-Ni alloys. This discrepancy can be interpreted by considering the disparate distribution functions of muon and hydrogen within the tetrahedral site, wherein two of the four Al atoms are substituted by the solute element and vacancy (solute-vacancy pair).
peaks above 200 K in Al-Mn, Al-Cr, Al-Fe, and Al-Ni alloys. This discrepancy can be interpreted by considering the disparate distribution functions of muon and hydrogen within the tetrahedral site, wherein two of the four Al atoms are substituted by the solute element and vacancy (solute-vacancy pair).
 -phase in Al-Mg-Si alloys during aging treatment
-phase in Al-Mg-Si alloys during aging treatmentAhmed, A.*; Uttarasak, K.*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 988, p.174234_1 - 174234_9, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:95.29(Chemistry, Physical)This study aims to clarify the growth process of the -phase in Al-Mg-Si alloys from the point of view of morphology evolution. For this research, the
-phase in Al-Mg-Si alloys from the point of view of morphology evolution. For this research, the  -phase orientation relationship, shape, growth process, misfit value, and interfacial condition between the
-phase orientation relationship, shape, growth process, misfit value, and interfacial condition between the  -phase and Al matrix were investigated using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), focus ion beam (FIB), and optical microscope (OM). Results include the identification of {111}
-phase and Al matrix were investigated using high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), focus ion beam (FIB), and optical microscope (OM). Results include the identification of {111}  facets at the edges of the
facets at the edges of the  -phase, as well as the proposal of two new three-dimensional shapes for the
-phase, as well as the proposal of two new three-dimensional shapes for the  -phase. We purposed the morphology evolution during the growth process of Mg
-phase. We purposed the morphology evolution during the growth process of Mg Si crystal and calculated the misfit to understand the unstable (111)
Si crystal and calculated the misfit to understand the unstable (111) facet has a higher misfit value as compared to the (001)
facet has a higher misfit value as compared to the (001) and (011)
and (011) facets. Our observations provide how they influence the behavior of Mg
facets. Our observations provide how they influence the behavior of Mg Si crystals.
Si crystals.
 Mn
MnShimizu, Kazuyuki*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Akamaru, Satoshi*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Tsuru, Tomohito; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 245, p.116051_1 - 116051_6, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.76(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Hydrogen at the mass ppm level causes hydrogen embrittlement in metallic materials, but it is extremely difficult to experimentally elucidate the hydrogen trapping sites. We have taken advantage of the fact that positive muons can act as light isotopes of hydrogen to study the trapping state of hydrogen in matter. Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments and the density functional theory (DFT) calculations for hydrogen trapping energy are carried out for Al Mn. The DFT calculations for hydrogen in Al
Mn. The DFT calculations for hydrogen in Al Mn have found four possible trapping sites in which the hydrogen trapping energies are 0.168 (site 1), 0.312 (site 2), 0.364 (site 3), and 0.495 (site 4) in the unit of eV/atom. Temperature variations of the deduced dipole field width (
Mn have found four possible trapping sites in which the hydrogen trapping energies are 0.168 (site 1), 0.312 (site 2), 0.364 (site 3), and 0.495 (site 4) in the unit of eV/atom. Temperature variations of the deduced dipole field width ( ) indicated step-like changes at temperatures, 94, 193, and 236 K. Considering their site densities, the observed
) indicated step-like changes at temperatures, 94, 193, and 236 K. Considering their site densities, the observed  change temperatures are interpreted by trapping muons at sites 1, 3, and 4.
change temperatures are interpreted by trapping muons at sites 1, 3, and 4.
Fujihara, Hiro*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Kobayashi, Masakazu*; Mayama, Tsuyoshi*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Masayuki*
International Journal of Plasticity, 174, p.103897_1 - 103897_22, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:93.27(Engineering, Mechanical)Hydrogen(H) embrittlement in high-strength aluminum(Al) alloys is a crucial problem. H accumulation at the interface of precipitates in Al alloy is considered to cause embrittlement. However, there is no quantitative knowledge regarding the interaction between H distribution and stress field near cracks. In this study, using a multi-modal three-dimensional image-based simulation combining the crystal plasticity finite element method and H diffusion analysis, we tried to capture the stress distribution near the crack, its influence on the H distribution, and the probability of crack initiation in the experimental condition. As a result, it was found that grain boundary cracks transition to quasi-cleavage cracks in the region where the cohesive energy of the semi-coherent interface of MgZn precipitates decreases due to H accumulation near the tip. We believe the present simulation method successfully bridges nanoscale delamination and macroscale brittle fracture.
precipitates decreases due to H accumulation near the tip. We believe the present simulation method successfully bridges nanoscale delamination and macroscale brittle fracture.
Linh, B. D.*; Corsi, A.*; Gillibert, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(3), p.034312_1 - 034312_15, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Tang, J.*; Wang, Y.*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 239, p.115804_1 - 115804_5, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:80.41(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behaviors induced by the combination of external and internal hydrogen (H) in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy were systematically investigated via in situ 3D characterization techniques. SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy could initiate and propagate in the potential crack region where the H concentration exceeded a critical value, in which the nanoscopic H-induced decohesion of  -MgZn
-MgZn precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Nishijima, Masahiko*; Kamada, Yasuhiro*
Corrosion, 79(8), p.818 - 830, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:52.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)7xxx aluminum alloys are representative high-strength aluminum alloys; however, mechanical property degradation due to hydrogen hinders further strengthening. We propose the dispersion of Mn-based second-phase particles as a novel technique for preventing 7xxx aluminum alloy hydrogen embrittlement. In this study, the deformation and fracture behaviors of high hydrogen 7xxx alloys containing 0.0% Mn and 0.6% Mn are observed in situ using synchrotron radiation X-ray tomography. The obtained macroscopic hydrogen embrittlement is quantitatively analyzed based on hydrogen partitioning in alloys. Adding 0.6% Mn, generating second-phase particles with high hydrogen trapping abilities, significantly suppresses hydrogen-induced quasicleavage fracture.
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:95.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:67.28(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
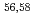 Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Chazono, Yoshiki*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:89.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Gamma decays were observed in  Ca and
Ca and  Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from
Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from 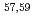 Sc. For
Sc. For  Ca, a
Ca, a  ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for
ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for  Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the
Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the 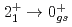 decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for
decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for 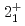 level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the
level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the 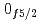 and
and 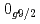 orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic
orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic  Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to
Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to  Ca or even beyond.
Ca or even beyond.
 muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculations
muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculationsTsuru, Tomohito; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Lee, S.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 54(6), p.2374 - 2383, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:23.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Although hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of high-strength Al alloys is recognized as a critical issue in the practical use of Al alloys, identifying the hydrogen trapping or distribution has been challenging. In the present study, an effective approach based on experiment and simulation is proposed to explore the potential trap sites in Al alloys. Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments were carried out for Al-0.5%Mg, Al-0.2%Cu, Al-0.15%Ti, Al-0.011%Ti, Al-0.28%V, and Al-0.015%V (at.%) in the temperature range from 5 to 300 K. The temperature variations of the dipole field widths have revealed three peaks for Al-0.5%Mg, four peaks for Al-0.2%Cu, three peaks for Al-0.011%Ti and Al-0.015%V. Atomic configurations of the muon trapping sites corresponding to the observed  peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon
peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon  peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
 100 MeV/nucleon
100 MeV/nucleonPohl, T.*; Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Lee, J.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_8, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:87.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report on the first proton-induced single proton- and neutron-removal reactions from the neutron deficient  O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at
O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at  100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
 Ca; Spectroscopy of
Ca; Spectroscopy of  K,
K,  Ca, and
Ca, and  Ca
CaKoiwai, Takuma*; Wimmer, K.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; Holt, J. D.*; Miyagi, Takayuki*; Navr til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 827, p.136953_1 - 136953_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:71.48(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
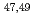 Cl isotopes
Cl isotopesLinh, B. D.*; Corsi, A.*; Gillibert, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Barbieri, C.*; Chen, S.*; Chung, L. X.*; Duguet, T.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 104(4), p.044331_1 - 044331_16, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:74.33(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Yoshinaka, Kazuyuki; Shimizu, Kazuyuki; Sugiyama, Takayuki
JAEA-Review 2021-008, 112 Pages, 2021/07
We had drastically been improving quality assurance system for Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP), through applying new regulatory requirements, giving up ISO certification from FY2012 to 2019. In revising QA system, it is obviously necessary to satisfy the regulatory requirements, but it is important to continuously improve the QA system considering effectiveness to safety performance based on earlier experiences. In this report, the background of QA system revision, interpretation and thinking way of conformation and application to new regulation and "Application Guide to Quality Assurance Code for Safety in Nuclear Power Plants (JEAC 4111)" to TRP, issues considered. And matters that require attention for future QA activities are described. Key points are "in work processes planning, relationship with other sections and responsibility boundaries should be clearly defined with such as flow chart", "to manage decision-making processes is important, including input information, judgment criteria and so on", "concerning process monitoring and measurement, not only focusing on scheduling but also viewpoints toward conditions of facilities/systems, conformance to regulatory requirements and process improvement are necessary", and "in documentation, matching for existing system, clear relation to other fundamental documents are necessary".
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:95.90(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,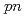 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
 = 32 shell closure below calcium; Low-lying structure of
= 32 shell closure below calcium; Low-lying structure of  Ar
ArCort s, M. L.*; Rodriguez, W.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Holt, J. D.*; Men
s, M. L.*; Rodriguez, W.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Holt, J. D.*; Men ndez, J.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Schwenk, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Simonis, J.*; et al.
ndez, J.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Schwenk, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Simonis, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(6), p.064320_1 - 064320_9, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:75.82(Physics, Nuclear)Low-lying excited states in the  = 32 isotope
= 32 isotope  Ar were investigated by in-beam
Ar were investigated by in-beam  -ray spectroscopy following proton- and neutron-knockout, multinucleon removal, and proton inelastic scattering at the RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory. The energies of the two previously reported transitions have been confirmed, and five additional states are presented for the first time, including a candidate for a 3
-ray spectroscopy following proton- and neutron-knockout, multinucleon removal, and proton inelastic scattering at the RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory. The energies of the two previously reported transitions have been confirmed, and five additional states are presented for the first time, including a candidate for a 3 state. The level scheme built using
state. The level scheme built using 
 coincidences was compared to shell-model calculations in the
coincidences was compared to shell-model calculations in the 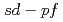 model space and to
model space and to  predictions based on chiral two- and three-nucleon interactions. Theoretical proton- and neutron-knockout cross sections suggest that two of the new transitions correspond to 2
predictions based on chiral two- and three-nucleon interactions. Theoretical proton- and neutron-knockout cross sections suggest that two of the new transitions correspond to 2 states, while the previously proposed 4
states, while the previously proposed 4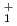 state could also correspond to a 2
state could also correspond to a 2 state.
state.