Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sr in cattle bone and tooth samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
Sr in cattle bone and tooth samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryKoarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Aoki, Jo; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kino, Yasushi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; et al.
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 36(8), p.1678 - 1682, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:55.72(Chemistry, Analytical)Rapid analysis of  Sr in bone and tooth samples of cattle were achieved by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) coupled with mass shift and solid phase extraction techniques. Limit of detection (LOD) in the ICP-MS measurement of 0.1 g samples was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. Analytical time of the ICP-MS method was reduced from 20 days to 11 hours, compared with the radiometric method. Therefore, the ICP-MS method can be rapid and useful procedure of
Sr in bone and tooth samples of cattle were achieved by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) coupled with mass shift and solid phase extraction techniques. Limit of detection (LOD) in the ICP-MS measurement of 0.1 g samples was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. Analytical time of the ICP-MS method was reduced from 20 days to 11 hours, compared with the radiometric method. Therefore, the ICP-MS method can be rapid and useful procedure of  Sr in small bone and tooth samples derived from terrestrial animals.
Sr in small bone and tooth samples derived from terrestrial animals.
Takahashi, Atsushi*; Chiba, Mirei*; Tanahara, Akira*; Aida, Jun*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; Murakami, Shinobu*; Koarai, Kazuma; Ono, Takumi*; Oka, Toshitaka; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.10355_1 - 10355_11, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.49(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Takeda, Tetsuaki*; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aihara, Jun; Aoki, Takeshi; Fujiwara, Yusuke; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ho, H. Q.; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Imai, Yoshiyuki; et al.
High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.5, 464 Pages, 2021/02
As a general overview of the research and development of a High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) in JAEA, this book describes the achievements by the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) on the designs, key component technologies such as fuel, reactor internals, high temperature components, etc., and operational experience such as rise-to-power tests, high temperature operation at 950 C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
C, safety demonstration tests, etc. In addition, based on the knowledge of the HTTR, the development of designs and component technologies such as high performance fuel, helium gas turbine and hydrogen production by IS process for commercial HTGRs are described. These results are very useful for the future development of HTGRs. This book is published as one of a series of technical books on fossil fuel and nuclear energy systems by the Power Energy Systems Division of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers.
Shimizu, Yusei*; Miyake, Atsushi*; Maurya, A.*; Honda, Fuminori*; Nakamura, Ai*; Sato, Yoshiki*; Li, D.*; Homma, Yoshiya*; Yokoyama, Makoto*; Tokunaga, Yo; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(13), p.134411_1 - 134411_11, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts applied by determination of passing-through time of plume using noble gas counts
I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts applied by determination of passing-through time of plume using noble gas countsYamada, Junya; Hashimoto, Makoto; Seya, Natsumi; Haba, Risa; Muto, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Takehiko; Takasaki, Koji; Yokoyama, Sumi*; Shimo, Michikuni*
Hoken Butsuri, 52(1), p.5 - 12, 2017/03
The purpose of this study is to improve a quick method for estimation of  I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts in case that a nuclear disaster occurs. In this method,
I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts in case that a nuclear disaster occurs. In this method,  I concentrations were estimated by multiplying
I concentrations were estimated by multiplying  I count rates of cloud-shine measured with NaI (Tl) detector by concentration conversion factor. A previous study suggested that it was difficult to determine passing-through time of plume from temporal change of
I count rates of cloud-shine measured with NaI (Tl) detector by concentration conversion factor. A previous study suggested that it was difficult to determine passing-through time of plume from temporal change of  I count rates or dose rate. Our study applies the method for estimating passing-through time of plume from temporal change of noble gas counts. The
I count rates or dose rate. Our study applies the method for estimating passing-through time of plume from temporal change of noble gas counts. The  I concentrations in the air at Oarai center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency resulting from the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant were estimated by proposal technique. The result of comparison of this method with sampling method for
I concentrations in the air at Oarai center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency resulting from the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant were estimated by proposal technique. The result of comparison of this method with sampling method for  I concentrations in the air were within factor 3.
I concentrations in the air were within factor 3.
Ono, Masato; Shimizu, Atsushi; Kondo, Makoto; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Shinohara, Masanori; Tochio, Daisuke; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Takada, Shoji; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 2(4), p.044502_1 - 044502_4, 2016/10
In the loss of forced core cooling test using High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), the forced cooling of reactor core is stopped without inserting control rods into the core and cooling by Vessel Cooling System (VCS) to verify safety evaluation codes to investigate the inherent safety of HTGR be secured by natural phenomena to make it possible to design a severe accident free reactor. The VCS passively removes the retained residual heat and the decay heat from the core via the reactor pressure vessel by natural convection and thermal radiation. In the test, the local temperature was supposed to exceed the limit from the viewpoint of long-term use at the uncovered water cooling tube by thermal reflectors in the VCS, although the safety of reactor is kept. Through a cold test, which was carried out by non-nuclear heat input from gas circulators with stopping water flow in the VCS, the local higher temperature position was specified although the temperature was sufficiently lower than the maximum allowable working temperature, and natural circulation of water had insufficient cooling effect on the temperature of water cooling tube below 1 C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
 I concentrations in the air from pulse-height distribution observed by NaI(Tl) detector in monitoring posts
I concentrations in the air from pulse-height distribution observed by NaI(Tl) detector in monitoring postsYamada, Junya; Hashimoto, Makoto; Seya, Natsumi; Haba, Risa; Muto, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Takehiko; Takasaki, Koji; Yokoyama, Sumi*; Shimo, Michikuni*
Radioisotopes, 65(10), p.403 - 408, 2016/10
The purpose of this study is to develop a quick method for estimation of  I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts. In this method,
I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts. In this method,  I concentrations were estimated by multiplying
I concentrations were estimated by multiplying  I count rates at the full-energy peak measured with a NaI(Tl) detector by a concentration conversion factor. The concentration conversion factor for monitoring posts in JAEA Oarai Center was calculated with an EGS5 Monte Carlo code. As a result, the concentration conversion factor for an infinite-air-source was 25.7 Bq/m
I count rates at the full-energy peak measured with a NaI(Tl) detector by a concentration conversion factor. The concentration conversion factor for monitoring posts in JAEA Oarai Center was calculated with an EGS5 Monte Carlo code. As a result, the concentration conversion factor for an infinite-air-source was 25.7 Bq/m /cps.
/cps.
Takada, Shoji; Shimizu, Atsushi; Kondo, Makoto; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Shinohara, Masanori; Seki, Tomokazu; Tochio, Daisuke; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2015/05
In the loss of forced core cooling test using High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), the forced cooling of reactor core is stopped without inserting control rods into the core and cooling by Vessel Cooling System (VCS) to demonstrate the inherent safety of HTGR be secured by natural phenomena to make it possible to design a severe accident free reactor. In the test, the local temperature was supposed to exceed the limit from the viewpoint of long-term use at the uncovered water cooling tube by thermal reflectors in the VCS, although the safety of reactor is kept. The local higher temperature position was specified although the temperature was sufficiently lower than the maximum allowable working temperature, and natural circulation of water had insufficient cooling effect on the temperature of water cooling tube below 1 C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
C. Then, a new safe and secured procedure for the loss of forced core cooling test was established, which will be carried out soon after the restart of HTTR.
Hoshino, Kazuo; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Tokunaga, Shinsuke; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Someya, Yoji; Nakamura, Makoto; Uto, Hiroyasu; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Tobita, Kenji
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 9(Sp.2), p.3403070_1 - 3403070_8, 2014/06
no abstracts in English
Seya, Natsumi; Hashimoto, Makoto; Nemoto, Koji*; Shimizu, Takehiko; Takasaki, Koji
Hoken Butsuri, 49(1), p.29 - 38, 2014/03
Evaluation of annual average of radionuclide concentration in surface air obtained from atmospheric dispersion factor is intended to determine a public dose as a primary source for the safety analysis of nuclear facilities in normal operation. Oarai Research and Development Center (ORDC) of the JAEA have used fixed 5-year meteorological statistics for derivation of atmospheric dispersion factors as average conditions. To show that the meteorological statistics for any 5-year period could be used as representative data for evaluation of average conditions, annual average (1-year average) and 5-year average of evaluated radionuclide concentrations derived from the meteorological data observed from 1991 to 2010 at ORDC were analyzed. The fluctuations of evaluated radionuclide concentrations of any 5-year averages were smaller than those of 1-year averages during 20 years, and any 5-year averages contained no rejections by the F-test (5% significance level). It means that any 5-year averages of radionuclide concentration evaluations are well representative for the safety analysis under normal condition in ORDC.
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Shinya, Kichiro*; Tobita, Kenji; Hoshino, Kazuo; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Uto, Hiroyasu; Someya, Yoji; Nakamura, Makoto; Ono, Noriyasu*; Kobayashi, Masahiro*; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 63(1T), p.70 - 75, 2013/05
no abstracts in English
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Shinya, Kichiro*; Tobita, Kenji; Hoshino, Kazuo; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Uto, Hiroyasu; Someya, Yoji; Nakamura, Makoto; Ono, Noriyasu*; Kobayashi, Masahiro*; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 63(1T), p.70 - 75, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:72.14(Nuclear Science & Technology)Design study of poloidal field coil (PFC) locations and current distribution for the advanced divertor in the Demo tokamak reactor was presented. Concept of the super-X divertor (SXD) for Demo reactor has an outer divertor leg longer than the conventional divertor, and it extends outboard to increase both the target wetted area and connection length to the outer target (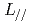 ). Equilibrium calculation code, TOSCA, was developed by introducing two parameters, i.e. super-X null radius (
). Equilibrium calculation code, TOSCA, was developed by introducing two parameters, i.e. super-X null radius (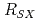 ) and a ratio of the poloidal flux at the super-X null to that at the separatrix (
) and a ratio of the poloidal flux at the super-X null to that at the separatrix (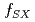 ). Some SXD magnetic configurations with minimal number of PFCs located outside toroidal field coil (TFC) were Demonstrated. Locations of the divertor target were also investigated. It was found that the flux expansion can be increased up to 4-10 depending on the target location and
). Some SXD magnetic configurations with minimal number of PFCs located outside toroidal field coil (TFC) were Demonstrated. Locations of the divertor target were also investigated. It was found that the flux expansion can be increased up to 4-10 depending on the target location and 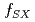 , and that SXD has an advantage to increase
, and that SXD has an advantage to increase 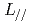 with
with 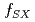 . Thus, the divertor plasma temperature is expected to decrease at the same upstream plasma density. On the other hand, large currents for the divertor PFCs were necessary. Other arrangements of PFCs such as (1) larger
. Thus, the divertor plasma temperature is expected to decrease at the same upstream plasma density. On the other hand, large currents for the divertor PFCs were necessary. Other arrangements of PFCs such as (1) larger 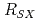 and (2) inside TFC, can reduce the PFC currents.
and (2) inside TFC, can reduce the PFC currents.
Satoh, Daiki; Maeda, Yoshikazu*; Tameshige, Yuji*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Shibata, Tokushi*; Endo, Akira; Tsuda, Shuichi; Sasaki, Makoto*; Maekawa, Motokazu*; Shimizu, Yasuhiro*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 49(11), p.1097 - 1109, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:71.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)At the Fukui Prefectural Hospital Proton Therapy Center, neutron doses behind concrete shields and at maze have been measured by using radiation monitors, DARWIN, Wendi-2, a rem meter, and solid state nuclear track detectors. The measured data were compared with the estimations by analytical models and Monte Carlo code PHITS. The analytical model with the parameters employed in shielding design of the facility gave considerably larger estimates than the measured data. This means that the facility was designed with an enough safety margin. The calculation results of PHITS were less than those of the analytical model, and were about 3 times larger than the measured data. From the view point of a safety policy with conservative estimation for shielding design, Monte Carlo simulation is a better tool for estimating radiation safety at accelerator-based proton treatment facilities.
Ueda, Yoshio*; Oya, Kaoru*; Ashikawa, Naoko*; Ito, Atsushi*; Ono, Tadayoshi*; Kato, Daiji*; Kawashima, Hisato; Kawamura, Gakushi*; Kenmotsu, Takahiro*; Saito, Seiki*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 88(9), p.484 - 502, 2012/09
no abstracts in English
Hoshino, Kazuo; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Nakamura, Makoto; Tobita, Kenji
Contributions to Plasma Physics, 52(5-6), p.550 - 554, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:67.76(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The power handling in the divertor is one of the most important issues for fusion tokamak reactor design. In this study, the effect of the divertor leg length on the power handling in the SlimCS DEMO reactor is investigated for future divertor design. The SONIC simulation shows enhancement of recycling in the outer divertor region due to effects of the long divertor leg and deep V-shaped corner. As a result, the ion and electron temperature at the outer divertor significantly decreases. In addition, peak of the Ar impurity radiation, which is located close to the outer divertor target in the standard divertor geometry, moves upstream. The former decreases the heat load to the outer divertor due to the ion conduction and convection, and the latter reduces the heat load due to the impurity radiation. The peak of the total heat load on the outer divertor decreases by about 30%.

Matsuoka, Takahiro*; Fujihisa, Hiroshi*; Hirao, Naohisa*; Oishi, Yasuo*; Mitsui, Takaya; Masuda, Ryo; Seto, Makoto*; Yoda, Yoshitaka*; Shimizu, Katsuya*; Machida, Akihiko; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 107(2), p.025501_1 - 025501_4, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:77.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Europium-hydride EuH exposed to high-pressure H
exposed to high-pressure H conditions has been found to exhibit structural and valence changes,
conditions has been found to exhibit structural and valence changes, 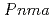 (
( =2, divalent)
=2, divalent) 
 63/
63/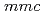 (
( =2, 7.2-8.7 GPa)
=2, 7.2-8.7 GPa) 
 4/
4/ (
(
 2, 8.7-9.7 GPa)
2, 8.7-9.7 GPa) 
 4/
4/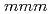 (
(
 2, 9.7 GPa-, trivalent). Having trivalent character and distorted cubic fcc structure, the
2, 9.7 GPa-, trivalent). Having trivalent character and distorted cubic fcc structure, the  4/
4/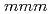 structure is the
structure is the  -phase which has been commonly observed for other rare-earth metal hydrides. Our study clearly demonstrates that EuH
-phase which has been commonly observed for other rare-earth metal hydrides. Our study clearly demonstrates that EuH is no longer an "irregular" member of the rare earth metal hydrides.
is no longer an "irregular" member of the rare earth metal hydrides.

 radical cations
radical cationsShimizu, Yuta*; Inagaki, Makoto*; Kumada, Takayuki; Kumagai, Jun*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 132(24), p.244503_1 - 244503_8, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)We performed electron spin resonance studies of trapped electrons and H
 radical cations produced by radiolysis of solid para-H
radical cations produced by radiolysis of solid para-H , para-H
, para-H -ortho-D
-ortho-D , and para-H
, and para-H -HD mixtures. Yields of both trapped electrons, and H
-HD mixtures. Yields of both trapped electrons, and H
 radical cations, and its isotopic analogues increased with increasing the concentration of ortho-D
radical cations, and its isotopic analogues increased with increasing the concentration of ortho-D and HD concentrations in solid para-H
and HD concentrations in solid para-H . We have concluded that electrons were found trapped nearby an ortho-D
. We have concluded that electrons were found trapped nearby an ortho-D or an HD in solid para-H
or an HD in solid para-H due to a the long-range charge-induced dipole and charge-induced quadrupole interactions between an electrons and an isotopic hydrogen molecules.
due to a the long-range charge-induced dipole and charge-induced quadrupole interactions between an electrons and an isotopic hydrogen molecules.
Saito, Kenji; Shimizu, Atsushi; Hirato, Yoji; Kondo, Makoto; Kawamata, Takanori; Nemoto, Masumi; Motegi, Toshihiro
JAEA-Technology 2009-015, 52 Pages, 2009/05
As In-core temperature monitoring system, Type N thermocouples arranged at hot plenum block measures the primary coolant temperature at each hot plenum block in order to monitor the condition of the reactor core during the reactor operation. Type N thermocouples should have a long lifetime with high reliability under the high temperature environment of about 1000 C, because they are used in HTTR reactor pressure vessel. This report shows that the characteristic change of Type N thermocouples was confirmed from operation and maintenance data of current HTTR.
C, because they are used in HTTR reactor pressure vessel. This report shows that the characteristic change of Type N thermocouples was confirmed from operation and maintenance data of current HTTR.
Kawashima, Hisato; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Takizuka, Tomonori; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Sakurai, Shinji; Matsukawa, Makoto; Fujita, Takaaki
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(10-12), p.1643 - 1647, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:74.54(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ishida, Takekazu*; Matsushima, Yoshiaki*; Shimizu, Makoto*; Hayashi, Masahiko*; Ebisawa, Hiromichi*; Sato, Osamu*; Kato, Masaru*; Koyama, Tomio*; Machida, Masahiko; Sato, Kazuo*; et al.
Physica C, 468(7-10), p.576 - 580, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.18(Physics, Applied)The extended Little-Parks effect of superconducting network is known as a periodic 
 variation as a function of magnetic field. Superconducting Pb honeycomb networks of matching field 0.106 G and triangular microhole lattice of Pb of matching field 0.425 G have been fabricated by the combination of electron-beam lithography and a lift-off process of evaporated Pb films. The application of magnetic field corresponds to the vortex filling into superconducting networks. We measured the magnetization of the networks systematically by using a SQUID magnetometer. We found that flux jump appears rather periodically as a function of magnetic field. Flux jumps may be induced by a periodic decrease of the critical current density of the network. To the authors' knowledge, this is for the first time to observe the regular flux jumps due to the critical current modification coming from the extended Little-Parks effect of the superconducting networks.
variation as a function of magnetic field. Superconducting Pb honeycomb networks of matching field 0.106 G and triangular microhole lattice of Pb of matching field 0.425 G have been fabricated by the combination of electron-beam lithography and a lift-off process of evaporated Pb films. The application of magnetic field corresponds to the vortex filling into superconducting networks. We measured the magnetization of the networks systematically by using a SQUID magnetometer. We found that flux jump appears rather periodically as a function of magnetic field. Flux jumps may be induced by a periodic decrease of the critical current density of the network. To the authors' knowledge, this is for the first time to observe the regular flux jumps due to the critical current modification coming from the extended Little-Parks effect of the superconducting networks.