Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kusano, Kanya*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Ishii, Mamoru*; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Akiyoshi, Hideharu*; Asai, Ayumi*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Goto, Tadanori*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.159_1 - 159_29, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:38.33(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The PSTEP is a nationwide research collaboration in Japan and was conducted from April 2015 to March 2020, supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. It has made a significant progress in space weather research and operational forecasts, publishing over 500 refereed journal papers and organizing four international symposiums, various workshops and seminars, and summer school for graduate students at Rikubetsu in 2017. This paper is a summary report of the PSTEP and describes the major research achievements it produced.
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Aoi, Nori*; Azaiez, F.*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Kimura, Atsushi; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 103(3), p.034327_1 - 034327_8, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.33(Physics, Nuclear)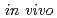 dosimetry system based on an optical fiber-coupled microsized photostimulable phosphor for stereotactic body radiation therapy
dosimetry system based on an optical fiber-coupled microsized photostimulable phosphor for stereotactic body radiation therapyYada, Ryuichi*; Maenaka, Kazusuke*; Miyamoto, Shuji*; Okada, Go*; Sasakura, Aki*; Ashida, Motoi*; Adachi, Masashi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Wang, T.*; Akasaka, Hiroaki*; et al.
Medical Physics, 47(10), p.5235 - 5249, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:50.10(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)The 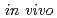 dosimeter system is capable of real-time, accurate, and precise measurement under stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) conditions. The probe is smaller than a conventional dosimeter, has excellent spatial resolution, and can be valuable in SBRT with a steep dose distribution over a small field. The developed PSP dosimeter system appears to be suitable for in vivo SBRT dosimetry.
dosimeter system is capable of real-time, accurate, and precise measurement under stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) conditions. The probe is smaller than a conventional dosimeter, has excellent spatial resolution, and can be valuable in SBRT with a steep dose distribution over a small field. The developed PSP dosimeter system appears to be suitable for in vivo SBRT dosimetry.
Uchiyama, Yusuke*; Azuma, Kohei*; Odani, Sachika*; Iwasaki, Toshiki*; Tsumune, Daisuke*; Kamidaira, Yuki; Shimizu, Yasuyuki*; Onda, Yuichi*
Doboku Gakkai Rombunshu, B2 (Kaigan Kogaku) (Internet), 73(2), p.I_685 - I_690, 2017/10
no abstracts in English
Abe, Ryoji*; Nagoshi, Kohei*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Takagi, Hideaki*; Shimizu, Nobutaka*; Koka, Masashi*; Sato, Takahiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 404, p.173 - 178, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:51.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)Morita, Koji*; Zhang, S.*; Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Inoue, Fusao*; Yugo, Hiroaki*; Naito, Masanori*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 241(12), p.4672 - 4681, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:78.40(Nuclear Science & Technology)A five-year research project has been initiated in 2005 to develop a code based on the MPS (Moving Particle Semi-implicit) method for detailed analysis of key phenomena in core disruptive accidents (CDAs) of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). The code is named COMPASS (Computer Code with Moving Particle Semi-implicit for Reactor Safety Analysis). The key phenomena include (1) fuel pin failure and disruption, (2) molten pool boiling, (3) melt freezing and blockage formation, (4) duct wall failure, (5) low-energy disruptive core motion, (6) debris-bed coolability, (7) metal-fuel pin failure. Validation study of COMPASS is progressing for these key phenomena. In this paper, recent COMPASS results of detailed analyses for the several key phenomena are summarized. The present results demonstrate COMPASS will be useful to understand and clarify the key phenomena of CDAs in SFRs in details.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; Uehara, Yasushi*; et al.
Proceedings of 8th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-8) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2010/10
In this paper, FY2009 results of the COMPASS code development are reported. Validation calculations for melt freezing and blockage formation, eutectic reaction of metal fuel, duct wall failure (thermal-hydraulic analysis), fuel pin failure and disruption and duct wall failure (structural analysis) are shown. Phase diagram calculations, classical and first-principles molecular dynamics were used to investigate physical properties of eutectic reactions: metallic fuel/steel and control rod material/steel. Basic studies for the particle method and SIMMER code calculations supported the COMPASS code development. COMPASS is expected to clarify the basis of experimentally-obtained correlations used in SIMMER. Combination of SIMMER and COMPASS will be useful for safety assessment of CDAs as well as optimization of the core design.
Morita, Koji*; Zhang, S.*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Inoue, Fusao*; Yugo, Hiroaki*; et al.
Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-18) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2010/05
A five-year research project has been initiated in 2005 to develop a code based on the MPS (Moving Particle Semi-implicit) method for detailed analysis of specific phenomena in core disruptive accidents (CDAs) of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). The code is named COMPASS (Computer Code with Moving Particle Semi-implicit for Reactor Safety Analysis). The specific phenomena include (1) fuel pin failure and disruption, (2) molten pool boiling, (3) melt freezing and blockage formation, (4) duct wall failure, (5) low-energy disruptive core motion, (6) debris-bed coolability, and (7) metal-fuel pin failure. Validation study of COMPASS is progressing for these key phenomena. In this paper, recent COMPASS results of detailed analyses for the several specific phenomena are summarized.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Zhang, S.*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-13) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2009/09
Dispersion and freezing of molten core material was calculated by the COMPASS code to compare with the experimental data of GEYSER. Molten core material flowed up with freezing on the pipe inner surface. As a molten pool behavior, CABRI-TPA2 experiment was analyzed, where a sphere of solid steel was surrounded by solid fuel. Power was injected to cause melting and boiling of the steel sphere. SCARABEE-BE+3 test was analyzed by COMPASS as a validation of failure of duct walls.
Yamamoto, Yuichi*; Hirano, Etsujo*; Oue, Masaya*; Shimizu, Sensuke*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Morita, Koji*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Tobita, Yoshiharu
Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-17) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2009/06
The COMPASS code is designed to analyze multi-physics problems involving thermal hydraulics, structure and phase change, in a unified framework of MPS method. In FY2006 and 2007, development of the basic functions of COMPASS was completed and fundamental verification calculations were carried out. In FY2007, the integrated verification program using available experimental data for key phenomena in CDAs was also started. In this paper, we show the basic verification calculations for the phase change model of COMPASS and the results of experimental analyses, together with the outline of the formulation of MPS method and the conceptual design of the COMPASS code.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Liu, J.*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Zhang, S.*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 2009 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '09) (CD-ROM), 1 Pages, 2009/05
A computer code, named COMPASS, is developed for multi-physics analysis of core disruptive accidents of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). A meshless method, called MPS method, is employed since complex thermal-hydraulics and structural problems with various phase change processes have to be analyzed. Verification for separeted basic processes and validation for practical phenomena are carried out. COMPASS is also expected to investigate molten fuel discharge to avoid re-criticality in large size SFR cores. Both MOX and metal fuels are considered. Eutectic reactions between the metal fuel and the cladding material are investigated by phase diagram calculation, classical and first-principles molecular dynamics. Basic studies relevant to the numerical methods support the code development of COMPASS. Parallel processing is implemented by OpenMP to treat large-scale problems. A visualization tool is also prepared by using AVS.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Zhang, S.*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Naito, Masanori*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
A computer code, named COMPASS, is being developed for various complex phenomena of core disruptive accidents (CDAs) in sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). The COMPASS is designed to analyze multi-physics problems involving thermal hydraulics, structure and phase change, in a unified framework of the MPS (Moving Particle Semi-implicit) method. The project has been carried out by six organizations for five years from FY2005 to FY2009. In this paper, the outcomes of the project in FY2007 are presented. Three validation calculations were completed by following the validation plan: melt freezing and blockage formation, molten pool boiling, and duct wall failure. The COMPASS code development was supported by basic studies of the numerical method, material science for eutectic reaction of the metal fuel, and SIMMER-III analyses.

Matsuo, Yoichiro*; Nishijima, Shigehiro*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Sakamoto, Ayako; Yokota, Yuichiro; Narumi, Issei; Shimizu, Kikuo*
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 86, 2008/03
no abstracts in English
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Liu, J.*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Zhang, S.*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of IAEA Topical Meeting on Advanced Safety Assessment Methods for Nuclear Reactors (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2007/10
A computer code, named COMPASS (Computer Code with Moving Particle Semi-implicit for Reactor Safety Analysis), is being developed for various complex phenomena of core disruptive accidents (CDAs) in sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). Theoretical studies are performed about a unified algorithm for compressible and incompressible flows, fluid flow with solid debris, and algorithm improvement for free surface flows. Code verification and validation procedures are established by exploiting the past experiences in those of SIMMER-III code. COMPASS will be used for separated phenomena in CDAs, while the whole core will be analyzed by SIMMER-III. COMPASS is expected to clarify the detailed process in duct wall failure and fuel discharge to avoid re-criticality during CDAs in large size SFRs.
Shimizu, Yoshio; Suitsu, Yuichi; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Yuri, Akiya
Proceedings of 8th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC 2007), p.335 - 340, 2007/05
Nuclear criticality safety evaluations for the fast breeder reactor's MOX fuel fabrication facility were performed. In the parametric studies made with SCALE, following three cases are here introduced. (1) The effect of the plutonium isotopic ratio on Pu (
( U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu) mass control were evaluated. The design conditions of the plutonium isotopic ratio under the operating condition were adjusted from the evaluation. (2) The moderation effects of organic materials in MOX fuel fabrication facility were evaluated. The water contents equivalent moderation effects to organic contents were obtained from the evaluation. (3) The effects of nonuniform mixture of MOX powder and water were evaluated by two-phase model and SMORES. The
Pu) mass control were evaluated. The design conditions of the plutonium isotopic ratio under the operating condition were adjusted from the evaluation. (2) The moderation effects of organic materials in MOX fuel fabrication facility were evaluated. The water contents equivalent moderation effects to organic contents were obtained from the evaluation. (3) The effects of nonuniform mixture of MOX powder and water were evaluated by two-phase model and SMORES. The  k, which differ from the k
k, which differ from the k of uniform model, were evaluated.
of uniform model, were evaluated.
Okamura, Masachika*; Momose, Masayuki*; Watanabe, Satomi*; Shimizu, Akira*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Yokota, Yuichiro; Tanaka, Atsushi
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 82, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kawashima, Hisato; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Sakurai, Shinji; Fujita, Takaaki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Nakano, Tomohide; Kubo, Hirotaka; Higashijima, Satoru; Hayashi, Takao; et al.
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (CD-ROM), 31F, 4 Pages, 2007/00
Divertor design for the JT-60 SA has been progressing in order to handle large heat flux during full pulse duration of 100 s. Divertor should be suitable for single null plasma experiments with the full power injection of 41 MW. The simulation results using 2D fluid (plasma) and Monte-Carlo (neutral) code are summarized. Lower single-null divertor is designed for ITER-like plasma configuration in order to study physics concept of the ITER divertor: control of the plasma detachment. Simulation results for various divertor geometries showed that the vertical target with V-shaped corner can produce plasma detachment near the outer strike-point for medium edge plasma density. It was also demonstrated that the divertor plasma became attached to move the outer strike point above the V-corner, suggesting that recover from sever detachment can be achieved by changing the plasma location. USN divertor will be designed for high- plasma experiments with the highest shaping plasma of S=6.
plasma experiments with the highest shaping plasma of S=6.
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Akiba, Masato; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fujita, Takaaki; Fujiwara, Masami*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Hosogane, Nobuyuki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Inoue, Nobuyuki; et al.
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 49, p.S428 - S432, 2006/12
To contribute DEMO and ITER, the design to modify the present JT-60U into superconducting coil machine, named National Centralized Tokamak (NCT), is being progressed under nationwide collaborations in Japan. Mission, design and strategy of this NCT program is summarized.

Matsuo, Yuichiro*; Nishijima, Shigehiro*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Sakamoto, Ayako; Tanaka, Atsushi; Shimizu, Kikuo*
Mutation Research; Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 602(1-2), p.7 - 13, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:59.45(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)no abstracts in English
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Liu, J.*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Hosoda, Seigo*; Araki, Kazuhiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 5th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-5), p.472 - 479, 2006/11
A 5-year research project started in FY2005 in the framework of Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program funded by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology in Japan. A computer code, named COMPASS (Computer Code with Moving Particle Semi-implicit for Reactor Safety Analysis), is being developed using the Moving Particle Semi-implicit (MPS) method for various complex phenomena of severe accidents in fast breeder reactors. Both MOX and metal fuels are considered. Eutectic reactions between the metal fuel and the cladding material are being investigated by molecular dynamics and molecular orbital methods. The molten metal flow with solidification was analyzed by MPS. The elastic analysis of a hexagonal wrapper tube was analyzed by the MPS method as well. The results were compared with an experiment and an calculation using an commercial code. Eutectic reactions were calculated by molecular dynamics and compared with the references. We found that the combination of the above numerical methods was useful for multi-physics and multi-scale phenomena of core disruptive accidents in fast breeder reactors.