Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kurita, Keisuke; Iikura, Hiroshi; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Shinohara, Takenao; Odaira, Naoya*; Ito, Daisuke*; Saito, Yasushi*; Matsubayashi, Masahito
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2605, p.012005_1 - 012005_6, 2023/10
The Japan Research Ractor-3 (JRR-3) is operation resumed on February 26, 2021, and the shared use was also restarted in July, 2021. With the resumption of JRR-3 operation, two imaging facilities called TNRF and CNRF have also resumed their utilization. In this presentation, we report the details of these two neutron facilities.
Ito, Daisuke*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Odaira, Naoya*; Saito, Yasushi*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 569, p.153921_1 - 153921_6, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:51.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) He
He
 excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron-
excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron- He absorption reaction
He absorption reactionSonnenschein, V.*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kokuryu, Shoma*; Kubo, Wataru*; Suzuki, So*; Tomita, Hideki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Matsushita, Taku*; Wada, Nobuo*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(3), p.033318_1 - 033318_12, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Oba, Yojiro; Ito, Daisuke*; Saito, Yasushi*; Onodera, Yohei*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Oikawa, Kenichi
Materials Research Proceedings, Vol.15, p.160 - 164, 2020/02
Lead Bismuth eutectic (LBE) is a promising candidate of the coolant for accelerator driven system (ADS) and fast breeder reactor. Neutron transmission imaging is a powerful technique to investigate the LBE in flow channel. However, previous studies have focused on the analysis of the neutron transmission spectra due to Bragg diffraction (Bragg edge transmission) from the solid phase of the LBE. If the neutron transmission spectra due to the diffraction from a liquid phase can be observed, it is useful to study the behavior of the molten LBE in the flow channel. Therefore, the energy-resolved neutron transmission imaging measurements of the molten LBE was carried out. The observed neutron transmission spectra can be explained by those calculated from the scattering profiles of the molten LBE. This indicates that the structure of the molten LBE can be characterized and mapped using the neutron transmission imaging.
 He
He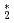 clusters via neutron-
clusters via neutron- He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulence
He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulenceMatsushita, Taku*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Guo, W.*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hirota, Katsuya*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Ito, Daisuke*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 196(1-2), p.275 - 282, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.89(Physics, Applied)Ito, Daisuke*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Saito, Yasushi*; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya
Journal of Visualization, 22(5), p.889 - 895, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.33(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)Nagai, Yuki; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Futamura, Yasunori*; Sakurai, Tetsuya*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 86(1), p.014708_1 - 014708_9, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.61(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Otobe, Tomohito; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*
Physical Review B, 93(4), p.045124_1 - 045124_9, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:86.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically investigate the dynamical Franz-Keldysh effect in femtosecond time resolution, that is, the time-dependent modulation of a dielectric function at around the band gap under an irradiation of an intense laser field. We develop a pump-probe formalism in two distinct approaches: first-principles simulation based on real-time time-dependent density functional theory and analytic consideration of a simple two-band model. We find that, while time-average modulation may be reasonably described by the static Franz-Keldysh theory, a remarkable phase shift is found to appear between the dielectric response and the applied electric field.
Sato, Shunsuke*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Lee, K.-M.*; Bertsch, G. F.*
Physical Review B, 92(20), p.205413_1 - 205413_6, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:84.86(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We calculate the energy deposition by very short laser pulses in SiO (
( -quartz) with a view to establishing systematics for predicting damage and nanoparticle production. The theoretical framework is time-dependent density functional theory, implemented by the real-time method in a multiscale representation. We find that the deposited energy in the medium can be accurately modeled as a function of the local electromagnetic pulse fluence. The energy deposition function can in turn be quite well fitted to the strong-field Keldysh formula. We find reasonable agreement between the damage threshold and the energy required to melt the substrate. The ablation threshold estimated by the energy to convert the substrate to an atomic fluid is higher than the measurement, indicating significance of nonthermal nature of the process. A fair agreement is found for the depth of the ablation.
-quartz) with a view to establishing systematics for predicting damage and nanoparticle production. The theoretical framework is time-dependent density functional theory, implemented by the real-time method in a multiscale representation. We find that the deposited energy in the medium can be accurately modeled as a function of the local electromagnetic pulse fluence. The energy deposition function can in turn be quite well fitted to the strong-field Keldysh formula. We find reasonable agreement between the damage threshold and the energy required to melt the substrate. The ablation threshold estimated by the energy to convert the substrate to an atomic fluid is higher than the measurement, indicating significance of nonthermal nature of the process. A fair agreement is found for the depth of the ablation.
Sato, Shunsuke*; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Yabana, Kazuhiro*
Physical Review B, 90(17), p.174303_1 - 174303_8, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:83.05(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We calculate the dielectric response of excited crystalline silicon in electron thermal equilibrium by adiabatic time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) to model the response to irradiation by high-intensity laser pulses. We find that the extracted effective mass are in the range of 0.22-0.36 and lifetimes are in the range of 1-14 fs depending on the temperature.
 shear Alfv
shear Alfv n modes driven by energetic N-NB ions in JT-60U
n modes driven by energetic N-NB ions in JT-60UBierwage, A.; Todo, Yasushi*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji
Nuclear Fusion, 54(10), p.104001_1 - 104001_14, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:66.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Bierwage, A.; Shinohara, Koji; Todo, Yasushi*; Yagi, Masatoshi
Proceedings of 25th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2014) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/10
 -quartz irradiated with an ultrashort intense laser pulse
-quartz irradiated with an ultrashort intense laser pulseLee, K.-M.*; Kim, C. M.*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Otobe, Tomohito; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Yabana, Kazuhiro; Jeong, T. M.*
Journal of Applied Physics, 115(5), p.053519_1 - 053519_8, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:70.20(Physics, Applied)A computational method based on a first-principles multiscale simulation has been used for calculating the optical response and the ablation threshold of an optical material irradiated with an ultrashort intense laser pulse. The method was applied to investigate the changes in the optical reflectance of quartz bulk, half-wavelength thin-film and quarter-wavelength thin-film and to estimate their ablation thresholds. Despite the adiabatic local density approximation used in calculating the exchange-correlation potential, the reflectance and the ablation threshold obtained from our method agree well with the previous theoretical and experimental results. The method can be applied to estimate the ablation thresholds for optical materials in general.
Sato, Shunsuke*; Yabana, Kazuhiro; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Bertsch, G. F.*
Physical Review B, 89(6), p.064304_1 - 064304_8, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:68 Percentile:90.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We calculate the dielectric response of crystalline silicon following irradiation by a high-intensity laser pulse, modeling the dynamics by the time-dependent Kohn-Sham equations in the presence of the laser field. As expected, the excited silicon shows features of an electron-hole plasma of nonequilibrium phase in its response, characterized by a negative divergence in the real part of the dielectric function at small frequencies. We also find that the imaginary part of the dielectric function can be negative, particularly for the parallel polarization of pump and probe fields.
Nagai, Yuki; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Futamura, Yasunori*; Ota, Yukihiro*; Sakurai, Tetsuya*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 82(9), p.094701_1 - 094701_10, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:70.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 =1 energetic particle modes for N-NB ion dynamics in JT-60U
=1 energetic particle modes for N-NB ion dynamics in JT-60UBierwage, A.; Shinohara, Koji; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Todo, Yasushi*
Nuclear Fusion, 53(7), p.073007_1 - 073007_12, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:63.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Iwata, Junichi*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*
Nihon Butsuri Gakkai-Shi, 67(10), p.685 - 689, 2012/10
Coherent phonon is the macroscopic coherent oscillation of atoms in a solid state generating under the ultrafast laser pulse which is shorter than the frequency of the phonon. Some physical processes for the coherent phonon have been proposed. We are studying the computational method describing the dynamics of the electron and atom employing the time-dependent density functional theory. Our computational results show the origine of the coherent phonon in Si quantitatively.
Bierwage, A.; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji; Todo, Yasushi*; Deng, W.*; Ishikawa, Masao; Matsunaga, Go; Yagi, Masatoshi
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2012/10
Shinohara, Yasushi*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Iwata, Junichi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Bertsch, G. F.*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 137(22), p.22A527_1 - 22A527_8, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:69.72(Chemistry, Physical)The time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) is the leading computationally feasible theory to treat excitations by strong electromagnetic fields. Here the theory is applied to coherent optical phonon generation. We examine the process in the crystalline semimetal antimony (Sb), where nonadiabatic coupling and optical phonon of different symmetries can be observed. The TDDFT is able to account for a number of qualitative features of the observed coherent phonon.
Bierwage, A.; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Todo, Yasushi*; Deng, W.*; Ishikawa, Masao; Matsunaga, Go; Shinohara, Koji; Yagi, Masatoshi
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 7(Sp.1), p.2403081_1 - 2403081_4, 2012/07