Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
神沼 拓也*; 鈴木 義行*; 白井 克幸*; 水井 利幸*; 野田 真永*; 吉田 由香里*; 舟山 知夫; 高橋 健夫*; 小林 泰彦; 白尾 智明*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 51(6), p.627 - 631, 2010/11
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:33.86(Biology)The direct biological effects of radiation, particularly accelerated heavy particle ions, on neurons are not fully known. Hence, the direct effect of carbon-ion beams on immature neurons was investigated by comparing to the effect of X-rays  using primary hippocampal neurons. Primary neurons were prepared from hippocampi of fetal rats at embryonic day 18 from timed pregnant Wistar rats and cultured with Banker's methods. At 7 Days
using primary hippocampal neurons. Primary neurons were prepared from hippocampi of fetal rats at embryonic day 18 from timed pregnant Wistar rats and cultured with Banker's methods. At 7 Days 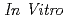 (DIV), the cells were irradiated with 140 kV X-ray and 18.3 MeV/amu carbon-ion beams (LET = 108 keV/
(DIV), the cells were irradiated with 140 kV X-ray and 18.3 MeV/amu carbon-ion beams (LET = 108 keV/ m). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at 12 hours after irradiation. Then, the cells were treated with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and DAPI staining for measuring the percentage of apoptosis (apoptotic index: AI). AI in sham-irradiated hippocampal neurons was 18%. The value of AI (AIs) of the cells irradiated with X-rays at 10 or 30 Gy were 15% or 23%, respectively. AI in cells irradiated with carbon-ion beams at 1 Gy, 3 Gy, 5 Gy and 10 Gy were 22%, 23%, 24% and 33%, respectively. AI was significantly increased by carbon-ion beams at 10 Gy (p
m). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at 12 hours after irradiation. Then, the cells were treated with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and DAPI staining for measuring the percentage of apoptosis (apoptotic index: AI). AI in sham-irradiated hippocampal neurons was 18%. The value of AI (AIs) of the cells irradiated with X-rays at 10 or 30 Gy were 15% or 23%, respectively. AI in cells irradiated with carbon-ion beams at 1 Gy, 3 Gy, 5 Gy and 10 Gy were 22%, 23%, 24% and 33%, respectively. AI was significantly increased by carbon-ion beams at 10 Gy (p  0.001). The apoptosis of hippocampal neurons increased in a dose-dependent manner following both X-ray and carbon-ion beams irradiation. Carbon-ion beams were about 10-fold more effective than X-rays for apoptosis induction in immature hippocampal neurons.
0.001). The apoptosis of hippocampal neurons increased in a dose-dependent manner following both X-ray and carbon-ion beams irradiation. Carbon-ion beams were about 10-fold more effective than X-rays for apoptosis induction in immature hippocampal neurons.
鈴木 義行*; 吉田 由香里*; 白井 克幸*; 浜田 信行*; 水井 利幸*; 野田 真永*; 舟山 知夫; 坂下 哲哉; 小林 泰彦; 白尾 智明*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 107, 2007/02
Damage to normal brain tissue caused by irradiation has not been studied in detail. In this study, we investigated the effect of X- and  C-irradiation on cultured normal neurons (immature and mature) and cultured organotypic brain slice tissues. The radiosensitivity of immature neurons was significantly higher than that of mature neurons. The effect of
C-irradiation on cultured normal neurons (immature and mature) and cultured organotypic brain slice tissues. The radiosensitivity of immature neurons was significantly higher than that of mature neurons. The effect of  C-irradiation on immature neurons was about 6 times higher than that of X-irradiation. In organotypic slice culture, X- and
C-irradiation on immature neurons was about 6 times higher than that of X-irradiation. In organotypic slice culture, X- and  C-irradiation induced the remarkable morphological change, especially, in the external granule cell layer. The effect of
C-irradiation induced the remarkable morphological change, especially, in the external granule cell layer. The effect of  C-irradiation was about 2 times higher than that of X-irradiation.
C-irradiation was about 2 times higher than that of X-irradiation.
白井 克幸*; 水井 利幸*; 鈴木 義行*; 小林 泰彦; 中野 隆史*; 白尾 智明*
Neuroscience Letters, 399(1-2), p.57 - 60, 2006/05
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:34.97(Neurosciences)神経ニューロン原基細胞へのX線照射は成長後の脳の機能不全を引き起こしうる。しかし、発達期のニューロン細胞の放射線感受性の程度や、最も感受性の高い時期などの詳細についてはわかっていなかった。そこで、ラット胎児脳の海馬初代培養神経細胞を用いて、培養開始後7日目及び21日目に30GyのX線を照射し、照射の12時間後あるいは24時間後に固定、細胞の形態変化やアポトーシス誘発を調べた。その結果、培養7日目の細胞に比べて、より成熟した培養21日目の細胞は感受性が有意に低く、発達期のニューロン細胞の放射線感受性は発生ステージに依存することが示された。
鈴木 義行*; 白井 克幸*; 水井 利幸*; 浜田 信行*; 野田 真永*; 舟山 知夫; 吉田 由香里*; 小林 泰彦; 白尾 智明*; 中野 隆史*
no journal, ,
炭素線照射の正常神経細胞に対する影響については、現在までのところ報告が皆無である。今回、培養ラット未熟神経細胞を用い、炭素線照射により誘発されるアポトーシスを指標として、炭素線のX線に対する生物学的効果比について検討した。胎生18日目のラット海馬より神経細胞を採取し、Banker法にて6日間培養した後、X線0 30Gy, 220MeV炭素線0
30Gy, 220MeV炭素線0 10Gyを照射した。照射後12時間に4%パラフォルムアルデヒドで固定した後、DAPI及びTUNEL法にて蛍光染色し、放射線により誘発されるアポトーシスの頻度を計測した。非照射細胞におけるアポトーシスの頻度は26%であった。X線で10Gy及び30Gy照射された場合のアポトーシスの頻度は、それぞれ、28%, 37%で、炭素線で1, 3, 5, 10Gy照射された場合のアポトーシスの頻度は、それぞれ、30%, 39%, 36%, 47%であり、X線及び炭素線照射によりアポトーシスの頻度は線量依存的に増加した。また、炭素線の効果は、同線量のX線に比べ6.0倍強かった。すなわち培養ラット未熟神経細胞において、炭素線照射により線量依存的にアポトーシスの増加が見られ、炭素線のX線に対する生物学的効果比は6.0であった。
10Gyを照射した。照射後12時間に4%パラフォルムアルデヒドで固定した後、DAPI及びTUNEL法にて蛍光染色し、放射線により誘発されるアポトーシスの頻度を計測した。非照射細胞におけるアポトーシスの頻度は26%であった。X線で10Gy及び30Gy照射された場合のアポトーシスの頻度は、それぞれ、28%, 37%で、炭素線で1, 3, 5, 10Gy照射された場合のアポトーシスの頻度は、それぞれ、30%, 39%, 36%, 47%であり、X線及び炭素線照射によりアポトーシスの頻度は線量依存的に増加した。また、炭素線の効果は、同線量のX線に比べ6.0倍強かった。すなわち培養ラット未熟神経細胞において、炭素線照射により線量依存的にアポトーシスの増加が見られ、炭素線のX線に対する生物学的効果比は6.0であった。
鈴木 義行*; 白井 克幸*; 水井 利幸*; 浜田 信行*; 野田 真永*; 舟山 知夫; 吉田 由香里*; 小林 泰彦; 白尾 智明*; 中野 隆史*
no journal, ,
炭素線照射がニューロンに及ぼす効果はこれまでに知られていない。そこで、本研究では、ラット胎児より単離した海馬ニューロンに及ぼす炭素線の照射効果を解析した。その結果、線量依存的にアポトーシスが誘発されること、そして、未熟ニューロンにアポトーシスを誘発する効果は、炭素線の方がX線よりも6倍高いことがわかった。
白井 克幸*; 鈴木 義行*; 水井 利幸*; 浜田 信行*; 野田 真永*; 舟山 知夫; 吉田 由香里*; 小林 泰彦; 白尾 智明*; 中野 隆史*
no journal, ,
炭素線照射の正常神経細胞に対する影響については、現在までのところ報告がない。われわれはこれまでに、培養ラット未熟正常神経細胞において、X線照射によりアポトーシスが誘導されることを報告しており、炭素線照射でも同様にアポトーシスが誘導されると考えられる。そこで、培養ラット未熟神経細胞を用い、放射線誘発アポトーシスを指標とし、炭素線のX線に対する生物学的効果比について検討した。胎生18日目のラット海馬より神経細胞を採取し、Banker法にて1週間培養した未熟細胞を用い、X線0 30Gy, 炭素線0
30Gy, 炭素線0 10Gyを照射した。照射後12時間に4%パラフォルムアルデヒド固定した後、DAPI及びTUNEL法にて蛍光染色し、放射線により誘発されるアポトーシスの頻度を計測した。非照射細胞におけるアポトーシスの頻度は25.8%であった。X線で10Gy及び30Gy照射におけるアポトーシスの頻度は、それぞれ、28.4%, 37.3%で、炭素線で1, 3, 5, 10Gy照射におけるアポトーシスの頻度は、それぞれ、30.0%, 38.7%, 35.7%, 46.5%であり、X線及び炭素線照射によりアポトーシスの頻度は線量依存的に増加した。また、炭素線の効果は同線量のX線に比べ約6倍と考えられた。培養ラット未熟神経細胞において、炭素線照射により線量依存的にアポトーシスの増加が見られ、炭素線のX線に対する生物学的効果比は約6であった。
10Gyを照射した。照射後12時間に4%パラフォルムアルデヒド固定した後、DAPI及びTUNEL法にて蛍光染色し、放射線により誘発されるアポトーシスの頻度を計測した。非照射細胞におけるアポトーシスの頻度は25.8%であった。X線で10Gy及び30Gy照射におけるアポトーシスの頻度は、それぞれ、28.4%, 37.3%で、炭素線で1, 3, 5, 10Gy照射におけるアポトーシスの頻度は、それぞれ、30.0%, 38.7%, 35.7%, 46.5%であり、X線及び炭素線照射によりアポトーシスの頻度は線量依存的に増加した。また、炭素線の効果は同線量のX線に比べ約6倍と考えられた。培養ラット未熟神経細胞において、炭素線照射により線量依存的にアポトーシスの増加が見られ、炭素線のX線に対する生物学的効果比は約6であった。