Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Kimura, Kaname*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(12), p.4641 - 4646, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:114 Percentile:90.42(Multidisciplinary Sciences)To further understand the catalytic mechanism and inhibitor recognition of HIV-1 protease, we need to determine the locations of key hydrogen atoms in the catalytic aspartates Asp25 and Asp125. The structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with transition-state analog KNI-272 was determined by combined neutron crystallography at 1.9  resolution and X-ray crystallography at 1.4
resolution and X-ray crystallography at 1.4  resolution. The resulting structural data shows that the catalytic residue Asp25 is protonated and that Asp125 is deprotonated. The proton on Asp25 makes a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group of the allophenylnorstatine group in KNI-272. The deprotonated Asp125 bonds to the hydroxyl proton of Apns. The results provide direct experimental evidence for proposed aspects of the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease; and can therefore contribute substantially to the development of specific inhibitors for therapeutic application.
resolution. The resulting structural data shows that the catalytic residue Asp25 is protonated and that Asp125 is deprotonated. The proton on Asp25 makes a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group of the allophenylnorstatine group in KNI-272. The deprotonated Asp125 bonds to the hydroxyl proton of Apns. The results provide direct experimental evidence for proposed aspects of the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease; and can therefore contribute substantially to the development of specific inhibitors for therapeutic application.
Kasugai, Atsushi; Sakamoto, Keishi; Hayashi, Kenichi*; Takahashi, Koji; Shoyama, Hiroaki*; Kajiwara, Ken*; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Kariya, Tsuyoshi*; Mitsunaka, Yoshika*; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; et al.
JAERI-Research 2002-027, 57 Pages, 2002/11
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Koji; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Sakamoto, Keishi; Kobayashi, Noriyuki*; Mori, Seiji*; Mori, Kensuke*; Ito, Yasuyuki*; Shoyama, Hiroaki; Kasugai, Atsushi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 56-57, p.587 - 592, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:47.93(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
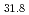 mode with depressed collector
mode with depressed collectorShoyama, Hiroaki; Sakamoto, Keishi; Hayashi, Kenichi*; Kasugai, Atsushi; Tsuneoka, Masaki; Takahashi, Koji; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Kariya, Tsuyoshi*; Mitsunaka, Yoshika*; Imai, Tsuyoshi
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 2, 40(8B), p.L906 - L908, 2001/08
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:72.18(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Kasugai, Atsushi; Sakamoto, Keishi; Takahashi, Koji; Kajiwara, Ken; Shoyama, Hiroaki; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Tsuneoka, Masaki; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Kariya, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 53(1-4), p.399 - 406, 2001/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:75.70(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Shoyama, Hiroaki; Sakamoto, Keishi; Hayashi, Kenichi*; Kasugai, Atsushi; Takahashi, Koji; Tsuneoka, Masaki; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Kariya, Tsuyoshi*; Mitsunaka, Yoshika*; Imai, Tsuyoshi
Shingaku Giho, 100(506), p.39 - 44, 2000/12
no abstracts in English
Imai, Tsuyoshi; Sakamoto, Keishi; Kasugai, Atsushi; Tsuneoka, Masaki; Takahashi, Koji; Shoyama, Hiroaki; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Kajiwara, Ken; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; et al.
Heisei-12-Nendo Denki Gakkai Genshiryoku Kenkyu Shiryo (NE-00-4), p.19 - 24, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Keishi; Kasugai, Atsushi; Shoyama, Hiroaki; Hayashi, Kenichi*; Takahashi, Koji; Tsuneoka, Masaki; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Kajiwara, Ken; Moriyama, Shinichi; et al.
25th International Conference on Infrared and Millimeter Waves Conference Digest, p.11 - 12, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Shoyama, Hiroaki; Kasugai, Atsushi; Sakamoto, Keishi; Takahashi, Koji; Tsuneoka, Masaki; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Kajiwara, Ken; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Kariya, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.3, p.368 - 371, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Keishi; Kasugai, Atsushi; Shoyama, Hiroaki; Takahashi, Koji; Tsuneoka, Masaki; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Kajiwara, Ken; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Kariya, Tsuyoshi*; Mitsunaka, Yoshika*; et al.
Shingaku Giho, 99(498), p.37 - 42, 1999/12
no abstracts in English
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Sugiyama, Shigeru*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have determined a crystal structure of HIV-1 protease by neutron crystallography. The development of HIV-1 protease inhibitors is regarded as a major success of structure-based drug design and contributes to establish highly active anti-retroviral therapy for AIDS. To further understand the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease and interaction between HIV-1 protease and its inhibitor, we have determined the crystal structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with a inhibitor, KNI-272 to 2.3  resolution by neutron crystallography. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine (Apns) in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
resolution by neutron crystallography. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine (Apns) in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Kimura, Kaname*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
HIV-1 protease is a dimeric aspartic protease that cleaves the nascent polyproteins of HIV-1 and plays an essential role in viral replication. To further understand the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease, we have determined the crystal structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with a transition state mimetic tripeptide inhibitor, KNI-272 to 1.9  resolution by neutron crystallography in combination with 1.4
resolution by neutron crystallography in combination with 1.4  resolution X-ray diffraction data. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
resolution X-ray diffraction data. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Sugiyama, Shigeru*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro*; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Adachi, Hiroaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
To understand the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease, we have determined the crystal structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with a transition state mimetic inhibitor, KNI-272 by neutron crystallography. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of allophenylnorstatine forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro*; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Sugiyama, Shigeru*; et al.
no journal, ,
In this study, we determined crystal structures of HIV-1 protease complexed with inhibitor by neutron and X-ray crystallography. Finally, we refined the structures to R-factor of 17.3% and free R-factor 20.3% by neutron crystallography and to R-factor of 10.4 % and free R-factor 12.4% by X-ray crystallography. The result shows that Asp 25 residue is protonated and Asp 125 is deprotonated. These information is important to resolve catalytic mechanism and design of new potent inhibitor.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro*; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Adachi, Hiroaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
HIV-1 protease is a dimeric aspartic protease that cleaves the nascent polyproteins of HIV-1 and plays an essential role in viral replication. To further understand the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease, we have determined the crystal structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with a transition state mimetic tripeptide inhibitor, KNI-272 to 1.9  ; resolution by neutron crystallography in combination with 1.4
; resolution by neutron crystallography in combination with 1.4  ; resolution X-ray diffraction data. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine (Apns) in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
; resolution X-ray diffraction data. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine (Apns) in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.