Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

 reductase by X-ray crystallography; New insights into regulation of efficient electron transfer
reductase by X-ray crystallography; New insights into regulation of efficient electron transferYamada, Mitsugu*; Tamada, Taro; Takeda, Kazuki*; Matsumoto, Fumiko*; Ono, Hiraku*; Kosugi, Masayuki*; Takaba, Kiyofumi*; Shoyama, Yoshinari*; Kimura, Shigenobu*; Kuroki, Ryota; et al.
Journal of Molecular Biology, 425(22), p.4295 - 4306, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:52.94(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)NADH-Cytochrome 
 reductase (b5R), a flavoprotein consisting of NADH and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) binding domains, catalyzes electron transfer from the two-electron carrier NADH to the one-electron carrier cytochrome
reductase (b5R), a flavoprotein consisting of NADH and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) binding domains, catalyzes electron transfer from the two-electron carrier NADH to the one-electron carrier cytochrome 
 (Cb5). The crystal structures of both the fully reduced form and the oxidized form of porcine liver b5R were determined. In the reduced b5R structure determined at 1.68
(Cb5). The crystal structures of both the fully reduced form and the oxidized form of porcine liver b5R were determined. In the reduced b5R structure determined at 1.68 resolution, the relative configuration of the two domains was slightly shifted in comparison with that of the oxidized form. This shift resulted in an increase in the solvent-accessible surface area of FAD and created a new hydrogen-bonding interaction between the N5 atom of the isoalloxazine ring of FAD and the hydroxyl oxygen atom of Thr66, which is considered to be a key residue in the release of a proton from the N5 atom. The isoalloxazine ring of FAD in the reduced form is flat as in the oxidized form and stacked together with the nicotinamide ring of NAD
resolution, the relative configuration of the two domains was slightly shifted in comparison with that of the oxidized form. This shift resulted in an increase in the solvent-accessible surface area of FAD and created a new hydrogen-bonding interaction between the N5 atom of the isoalloxazine ring of FAD and the hydroxyl oxygen atom of Thr66, which is considered to be a key residue in the release of a proton from the N5 atom. The isoalloxazine ring of FAD in the reduced form is flat as in the oxidized form and stacked together with the nicotinamide ring of NAD . Determination of the oxidized b5R structure, including the hydrogen atoms, determined at 0.78
. Determination of the oxidized b5R structure, including the hydrogen atoms, determined at 0.78 resolution revealed the details of a hydrogen-bonding network from the N5 atom of FAD to His49 via Thr66. Both of the reduced and oxidized b5R structures explain how backflow in this catalytic cycle is prevented and the transfer of electrons to one-electron acceptors such as Cb5 is accelerated. Furthermore, crystallographic analysis by the cryo-trapping method suggests that re-oxidation follows a two-step mechanism. These results provide structural insights into the catalytic cycle of b5R.
resolution revealed the details of a hydrogen-bonding network from the N5 atom of FAD to His49 via Thr66. Both of the reduced and oxidized b5R structures explain how backflow in this catalytic cycle is prevented and the transfer of electrons to one-electron acceptors such as Cb5 is accelerated. Furthermore, crystallographic analysis by the cryo-trapping method suggests that re-oxidation follows a two-step mechanism. These results provide structural insights into the catalytic cycle of b5R.
 1-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) synthase, the enzyme controlling the psychoactivity of
1-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) synthase, the enzyme controlling the psychoactivity of 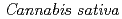
Shoyama, Yoshinari*; Tamada, Taro; Kurihara, Kazuo; Takeuchi, Ayako*; Taura, Futoshi*; Arai, Shigeki; Blaber, M.*; Shoyama, Yukihiro*; Morimoto, Satoshi*; Kuroki, Ryota
Journal of Molecular Biology, 423(1), p.96 - 105, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:90 Percentile:89.94(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology) 1-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) synthase catalyzes the oxidative cyclization of cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) into THCA, the precursor of the primary psychoactive agent
1-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) synthase catalyzes the oxidative cyclization of cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) into THCA, the precursor of the primary psychoactive agent  1-tetrahydrocannabinol in
1-tetrahydrocannabinol in 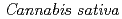 . The structure-function relationship of THCA synthase was investigated by X-ray structure determination (2.75
. The structure-function relationship of THCA synthase was investigated by X-ray structure determination (2.75  resolution) and mutational analysis. Specific amino acid residues were identified in the active site of THCA synthase that are involved in the oxidative cyclization of the CBGA substrate.
resolution) and mutational analysis. Specific amino acid residues were identified in the active site of THCA synthase that are involved in the oxidative cyclization of the CBGA substrate.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Kimura, Kaname*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(12), p.4641 - 4646, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:114 Percentile:90.42(Multidisciplinary Sciences)To further understand the catalytic mechanism and inhibitor recognition of HIV-1 protease, we need to determine the locations of key hydrogen atoms in the catalytic aspartates Asp25 and Asp125. The structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with transition-state analog KNI-272 was determined by combined neutron crystallography at 1.9  resolution and X-ray crystallography at 1.4
resolution and X-ray crystallography at 1.4  resolution. The resulting structural data shows that the catalytic residue Asp25 is protonated and that Asp125 is deprotonated. The proton on Asp25 makes a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group of the allophenylnorstatine group in KNI-272. The deprotonated Asp125 bonds to the hydroxyl proton of Apns. The results provide direct experimental evidence for proposed aspects of the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease; and can therefore contribute substantially to the development of specific inhibitors for therapeutic application.
resolution. The resulting structural data shows that the catalytic residue Asp25 is protonated and that Asp125 is deprotonated. The proton on Asp25 makes a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group of the allophenylnorstatine group in KNI-272. The deprotonated Asp125 bonds to the hydroxyl proton of Apns. The results provide direct experimental evidence for proposed aspects of the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease; and can therefore contribute substantially to the development of specific inhibitors for therapeutic application.
 chain and interleukin-13 receptor
chain and interleukin-13 receptor  1 chain by a silkworm-baculovirus system
1 chain by a silkworm-baculovirus systemHonjo, Eijiro; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Tamada, Taro; Shigematsu, Hideki*; Hatanaka, Takaaki*; Kanaji, Sachiko*; Arima, Kazuhiko*; Ito, Yuji*; Izuhara, Kenji*; Kuroki, Ryota
Protein Expression and Purification, 60(1), p.25 - 30, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:32.55(Biochemical Research Methods)The receptor binding to Interleukin (IL)-13 is composed of the IL-13 receptor  1 chain (IL-13R
1 chain (IL-13R  1) and the IL-4 receptor
1) and the IL-4 receptor  chain (IL-4R
chain (IL-4R  ). In order to investigate the interaction of IL-13 with IL-13R
). In order to investigate the interaction of IL-13 with IL-13R  1 and IL-4R
1 and IL-4R  , the DNA fragments coding the extracellular regions of human IL-13R
, the DNA fragments coding the extracellular regions of human IL-13R  1 and the IL-4R
1 and the IL-4R  were fused with mouse Fc and expressed by a silkworm-baculovirus system. The expressed receptors were successfully purified by affinity chromatography using protein A, and the Fc region was removed by thrombin digestion. Size exclusion chromatography and SPR analysis revealed that mixture of IL-13 and IL-13R
were fused with mouse Fc and expressed by a silkworm-baculovirus system. The expressed receptors were successfully purified by affinity chromatography using protein A, and the Fc region was removed by thrombin digestion. Size exclusion chromatography and SPR analysis revealed that mixture of IL-13 and IL-13R 1 showed predominant affinity to IL-4R
1 showed predominant affinity to IL-4R , although neither detectable affinity of IL-13 nor IL-13R
, although neither detectable affinity of IL-13 nor IL-13R 1 was observed against IL-4R
1 was observed against IL-4R . Combining these data with the moderate affinity of IL-13 to IL-13R
. Combining these data with the moderate affinity of IL-13 to IL-13R 1, this indicates that IL-13 first binds to IL-13R
1, this indicates that IL-13 first binds to IL-13R 1 and recruits consequently to IL-4R.
1 and recruits consequently to IL-4R.
Taguchi, Chiho; Taura, Futoshi*; Tamada, Taro; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Shoyama, Yukihiro*; Tanaka, Hiroyuki*; Kuroki, Ryota; Morimoto, Satoshi*
Acta Crystallographica Section F, 64(3), p.217 - 220, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:35.30(Biochemical Research Methods)Shoyama, Yoshinari; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota; Kimura, Shigenobu*; Takeda, Kazuki*; Hayashi, Takuro*; Miki, Kunio*
no journal, ,
NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase (b5R) is a pyridine nucleotide-dependent flavin reductase which contains a FAD in a molecule. The b5R catalyzes the electron transfer from NADH to cytochrome b5. The b5R is related to fatty acid metabolism and reduction of cytochrome P450. In order to clarify detailed structure of b5R, we carried out purification of b5R from E coli cell according to the method previously reported. Since a large-size crystal is necessary for the neutron structure analysis, we addressed enlargement of crystal by macroseeding method and periodical addition of protein sample to the crystallization solution. We succeeded in a preparation of large-scale crystal with a size of 1.0 0.5
0.5 0.3 mm, which is suitable for preliminary neutron diffraction study.
0.3 mm, which is suitable for preliminary neutron diffraction study.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Kimura, Kaname*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
HIV-1 protease is a dimeric aspartic protease that cleaves the nascent polyproteins of HIV-1 and plays an essential role in viral replication. To further understand the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease, we have determined the crystal structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with a transition state mimetic tripeptide inhibitor, KNI-272 to 1.9  resolution by neutron crystallography in combination with 1.4
resolution by neutron crystallography in combination with 1.4  resolution X-ray diffraction data. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
resolution X-ray diffraction data. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.

 reductase aimed to neutron crystallography
reductase aimed to neutron crystallographyShoyama, Yoshinari; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota; Kimura, Shigenobu*; Takeda, Kazuki*; Hayashi, Takuro*; Miki, Kunio*
no journal, ,
NADH-cytochrome 
 reductase (b5R) is a pyridine nucleotide-dependent flavin reductase which contains a FAD in a molecule. The b5R catalyzes the electron transfer from NADH to cytochrome b5. The b5R is related to fatty acid metabolism and reduction of cytochrome P450. In order to clarify detailed structure of b5R, we carried out purification of b5R from E coli cell according to the method previously reported. Since a large-size crystal is necessary for the neutron structure analysis. We addressed enlargement of crystal by macroseeding method and periodical addition of protein sample to the crystallization solution. We succeeded in a preparation of large-scale crystal with volume of 4 mm
reductase (b5R) is a pyridine nucleotide-dependent flavin reductase which contains a FAD in a molecule. The b5R catalyzes the electron transfer from NADH to cytochrome b5. The b5R is related to fatty acid metabolism and reduction of cytochrome P450. In order to clarify detailed structure of b5R, we carried out purification of b5R from E coli cell according to the method previously reported. Since a large-size crystal is necessary for the neutron structure analysis. We addressed enlargement of crystal by macroseeding method and periodical addition of protein sample to the crystallization solution. We succeeded in a preparation of large-scale crystal with volume of 4 mm , and we did preliminary neutron diffraction study using this crystal. Then we got 2
, and we did preliminary neutron diffraction study using this crystal. Then we got 2 resolution neutron diffraction data at BIX4.
resolution neutron diffraction data at BIX4.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Sugiyama, Shigeru*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
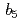 reductase
reductaseHirano, Yu; Yamada, Mitsugu*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Shoyama, Yoshinari*; Kuroki, Ryota; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Kimura, Shigenobu*; Takeda, Kazuki*; Miki, Kunio*; Tamada, Taro
no journal, ,
NADH-cytochrome 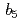 reductase (b5R), a flavoprotein consisting of NADH- and FAD- domains, catalyzes electron transfer from the two-electron carrier NADH to the one-electron carrier cytochrome
reductase (b5R), a flavoprotein consisting of NADH- and FAD- domains, catalyzes electron transfer from the two-electron carrier NADH to the one-electron carrier cytochrome 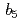 . The reaction catalyzed by
. The reaction catalyzed by 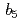 plays a role in fatty acid synthesis, cholesterol synthesis, and xenobiotic oxidation as a member of the electron transport chain on the endoplasmic reticulum. We have already determined the crystal structures of both the fully reduced and oxidized forms of porcine liver b5R by X-ray crystallography, but, its detail mechanism, especially hydride/proton transfers and exact states of semiquinone, still remains unknown. The hydrogen information obtained by neutron crystallography will be essential for the real understanding of catalytic cycle of the
plays a role in fatty acid synthesis, cholesterol synthesis, and xenobiotic oxidation as a member of the electron transport chain on the endoplasmic reticulum. We have already determined the crystal structures of both the fully reduced and oxidized forms of porcine liver b5R by X-ray crystallography, but, its detail mechanism, especially hydride/proton transfers and exact states of semiquinone, still remains unknown. The hydrogen information obtained by neutron crystallography will be essential for the real understanding of catalytic cycle of the 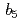 . A large crystal with the size of almost 2 mm
. A large crystal with the size of almost 2 mm was transferred to cryo-protectant solution by stepwise soaking method, and then were flash-frozen in a cold nitrogen gas stream. Using this crystal, we collected neutron data to 1.4
was transferred to cryo-protectant solution by stepwise soaking method, and then were flash-frozen in a cold nitrogen gas stream. Using this crystal, we collected neutron data to 1.4 resolution at BL03 (iBIX), MLF, J-PARC, and then collected to 0.85
resolution at BL03 (iBIX), MLF, J-PARC, and then collected to 0.85 resolution at BL5A, PF, KEK. Crystallographic refinement using both neutron and X-ray data is in progress.
resolution at BL5A, PF, KEK. Crystallographic refinement using both neutron and X-ray data is in progress.
Shoyama, Yoshinari; Tamada, Taro; Takeuchi, Ayako*; Taura, Futoshi*; Adachi, Motoyasu; Shoyama, Yukihiro*; Kuroki, Ryota; Morimoto, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shoyama, Yoshinari; Tamada, Taro; Takeuchi, Ayako*; Taura, Futoshi*; Shoyama, Yukihiro*; Kuroki, Ryota; Morimoto, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
Shoyama, Yoshinari; Tamada, Taro; Takeuchi, Ayako*; Taura, Futoshi*; Shoyama, Yukihiro*; Morimoto, Satoshi*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro*; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Adachi, Hiroaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
To understand the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease, we have determined the crystal structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with a transition state mimetic inhibitor, KNI-272 by neutron crystallography. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of allophenylnorstatine forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro*; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Sugiyama, Shigeru*; et al.
no journal, ,
In this study, we determined crystal structures of HIV-1 protease complexed with inhibitor by neutron and X-ray crystallography. Finally, we refined the structures to R-factor of 17.3% and free R-factor 20.3% by neutron crystallography and to R-factor of 10.4 % and free R-factor 12.4% by X-ray crystallography. The result shows that Asp 25 residue is protonated and Asp 125 is deprotonated. These information is important to resolve catalytic mechanism and design of new potent inhibitor.
Taguchi, Chiho*; Taura, Futoshi*; Morimoto, Satoshi*; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota; Shoyama, Yukihiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro*; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari*; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Adachi, Hiroaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
HIV-1 protease is a dimeric aspartic protease that cleaves the nascent polyproteins of HIV-1 and plays an essential role in viral replication. To further understand the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease, we have determined the crystal structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with a transition state mimetic tripeptide inhibitor, KNI-272 to 1.9  ; resolution by neutron crystallography in combination with 1.4
; resolution by neutron crystallography in combination with 1.4  ; resolution X-ray diffraction data. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine (Apns) in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
; resolution X-ray diffraction data. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine (Apns) in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
Tamada, Taro; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Honjo, Eijiro; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 1 chain and IL-4 receptor
1 chain and IL-4 receptor 
Honjo, Eijiro; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Tamada, Taro; Arima, Kazuhiko*; Kanaji, Sachiko*; Izuhara, Kenji*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
The receptor binding to Interleukin (IL)-13 is composed of the IL-13 receptor  1 chain (IL-13R
1 chain (IL-13R 1) and the IL-4 receptor
1) and the IL-4 receptor  chain (IL-4R
chain (IL-4R ). In order to investigate the interaction of IL-13 with IL-13R
). In order to investigate the interaction of IL-13 with IL-13R 1 and IL-4R
1 and IL-4R , the DNA fragments coding the extracellular regions of human IL-13R
, the DNA fragments coding the extracellular regions of human IL-13R 1 and the IL-4R
1 and the IL-4R , containing a cytokine receptor homologous region, were fused with human Fc and expressed by silkworm-baculovirus system. Size exclusion chromatography did not reveal association between IL-13 and IL-13R
, containing a cytokine receptor homologous region, were fused with human Fc and expressed by silkworm-baculovirus system. Size exclusion chromatography did not reveal association between IL-13 and IL-13R 1 under these conditions, but the clear association of IL-13 and IL-13R
1 under these conditions, but the clear association of IL-13 and IL-13R 1 was observed after adding IL-4R
1 was observed after adding IL-4R . This indicates that both extracellular regions of IL-13R
. This indicates that both extracellular regions of IL-13R 1 and IL-4R
1 and IL-4R have functions, and the association between IL-13 and IL-4R
have functions, and the association between IL-13 and IL-4R increases the IL-13 affinity to IL-13R
increases the IL-13 affinity to IL-13R 1.
1.
Adachi, Motoyasu; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Honjo, Eijiro; Okazaki, Nobuo; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Matsumura, Hiroyoshi*; Sugiyama, Shigeru*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have determined a crystal structure of HIV-1 protease by neutron crystallography. The development of HIV-1 protease inhibitors is regarded as a major success of structure-based drug design and contributes to establish highly active anti-retroviral therapy for AIDS. To further understand the catalytic mechanism of HIV-1 protease and interaction between HIV-1 protease and its inhibitor, we have determined the crystal structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with a inhibitor, KNI-272 to 2.3  resolution by neutron crystallography. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine (Apns) in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
resolution by neutron crystallography. Our results indicates that the carbonyl group of allophenylnorstatine (Apns) in KNI-272 forms a significant hydrogen bond with protonated Asp 25, and the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group of Apns forms a remarkable hydrogen bond with the deprotonated Asp125. These results show direct evidence that Asp25 provides a proton to carbonyl group of substrate and Asp125 contributes to activate the attacking water molecule as a nucleophile.
Shoyama, Yoshinari*; Takeuchi, Ayako*; Taura, Futoshi*; Shoyama, Yukihiro*; Adachi, Motoyasu; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English