Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -ray analysis
-ray analysisShozugawa, Katsumi*; Matsuo, Motoyuki*; Sano, Yuji*; Toh, Yosuke; Murakami, Yukihiro*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kimura, Atsushi; Hara, Kaoru; Kin, Tadahiro; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 291(2), p.341 - 346, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.98(Chemistry, Analytical)Multiple prompt  -ray analysis (MPGA), a new quantification method with high energy resolution, was applied to sediments from a marine shallow-water hydrothermal mound. Surface sediments around mounds were collected from the Wakamiko submarine crater located in Kagoshima Bay, southwest Japan, where the hydrothermal system was different from those at other marine shallow-water hydrothermal mounds. All samples were desalted and MPGA measurements were performed for 4,500 s (real time). Event data were obtained using eight CLOVER Ge detectors. We could obtain concentrations of
-ray analysis (MPGA), a new quantification method with high energy resolution, was applied to sediments from a marine shallow-water hydrothermal mound. Surface sediments around mounds were collected from the Wakamiko submarine crater located in Kagoshima Bay, southwest Japan, where the hydrothermal system was different from those at other marine shallow-water hydrothermal mounds. All samples were desalted and MPGA measurements were performed for 4,500 s (real time). Event data were obtained using eight CLOVER Ge detectors. We could obtain concentrations of  S,
S,  Mn,
Mn,  As,
As,  Gd,
Gd, 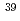 K,
K,  Sm,
Sm,  Fe, and
Fe, and  Rb with high sensitivity by MPGA. Furthermore,
Rb with high sensitivity by MPGA. Furthermore,  S,
S,  Rb, and
Rb, and  Mn have characteristic concentrations only at a mound, suggesting that sediments were sulfated by magmatic fluids at this mound.
Mn have characteristic concentrations only at a mound, suggesting that sediments were sulfated by magmatic fluids at this mound.
 -ray analysis method
-ray analysis methodOshima, Masumi; Matsuo, Motoyuki*; Shozugawa, Katsumi*
Oyo Butsuri, 80(11), p.948 - 954, 2011/11
The multiple  -ray detection method has been proved to be a high-resolution and high-sensitivity method in application to nuclide quantification. The neutron prompt
-ray detection method has been proved to be a high-resolution and high-sensitivity method in application to nuclide quantification. The neutron prompt  -ray analysis method is successfully extended by combining it with the
-ray analysis method is successfully extended by combining it with the  -ray detection method, which is called Multiple prompt
-ray detection method, which is called Multiple prompt  -ray analysis, MPGA. In this review we show the principle of this method and its characteristics. Several examples of its application to environmental samples, especially river sediments in the urban area and sea sediment samples are also described.
-ray analysis, MPGA. In this review we show the principle of this method and its characteristics. Several examples of its application to environmental samples, especially river sediments in the urban area and sea sediment samples are also described.