Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
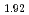 Sr
Sr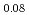 CuO
CuO
Lin, J. Q.*; Liu, X.*; Blackburn, E.*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Ding, H.*; Islam, Z.*; Sinha, S. K.*
Physical Review Letters, 120(19), p.197001_1 - 197001_6, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.25(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The nanometer scale lattice deformation brought about by the dopants in the high temperature superconducting cuprate La Sr
Sr CuO
CuO
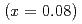 was investigated by measuring the associated X-ray diffuse scattering around multiple Bragg peaks. Our results address the long-term concern of dopant introduced local lattice inhomogeneity, and show that the associated nanometer scale lattice deformation is marginal and cannot be responsible for the patched variation in the spectral gaps observed with scanning tunneling microscopy in the cuprates.
was investigated by measuring the associated X-ray diffuse scattering around multiple Bragg peaks. Our results address the long-term concern of dopant introduced local lattice inhomogeneity, and show that the associated nanometer scale lattice deformation is marginal and cannot be responsible for the patched variation in the spectral gaps observed with scanning tunneling microscopy in the cuprates.
Kim, J.*; Sinha, J.*; Mitani, Seiji*; Hayashi, Masamitsu*; Takahashi, Saburo*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Yamanouchi, Michihiko*; Ohno, Hideo*
Physical Review B, 89(17), p.174424_1 - 174424_8, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:91 Percentile:94.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have studied the underlayer thickness and temperature dependencies of the current-induced effective field in CoFeB/MgO heterostructures with Ta-based underlayers. The underlayer thickness at which the effective field saturates is found to be different between the two orthogonal components of the effective field; i.e., the dampinglike term tends to saturate at a smaller underlayer thickness than the fieldlike term. For large underlayer thickness films in which the effective field saturates, we find that the measurement temperature significantly influences the size of the effective field. A striking difference is found in the temperature dependence of the two components: the dampinglike term decreases whereas the fieldlike term increases with increasing temperature. Using a simple spin diffusion-spin transfer model, we find that all of these results can be accounted for provided the real and imaginary parts of an effective spin mixing conductance are negative. These results imply that either spin transport in this system is different from conventional metallic interfaces or effects other than spin diffusion into the magnetic layer need to be taken into account in order to model the system accurately.