Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 10
10 W/cm
W/cm
Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Ryazantsev, S. N.*; Kulikov, R. K.*; Sedov, M. V.*; Filippov, E. D.*; Pikuz, S. A.*; Asai, Takafumi*; Kanasaki, Masato*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Jinno, Satoshi; et al.
Photonics (Internet), 10(11), p.1250_1 - 1250_11, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:18.07(Optics)It is challenging to clearly distinguish the impacts of the optical field and collisional ionization in the evolution of the charge state of a plasma produced when matter interacts with high-intensity laser pulses. In this work, time-dependent calculations of plasma kinetics are used to show that it is possible only when low-density gaseous targets with sufficiently small clusters are used. In the case of Ar plasma, the upper limit of the cluster radius was estimated to be 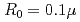 m.
m.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko*; Sakaki, Hironao*; Esirkepov, T. Zh.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Pikuz, T. A.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Orlandi, R.; Pirozhkov, A. S.*; Sagisaka, Akito*; et al.
Plasma Physics Reports, 42(4), p.327 - 337, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:55.10(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A combination of a petawatt laser and nuclear physics techniques can crucially facilitate the measurement of exotic nuclei properties. With numerical simulations and laser-driven experiments we show prospects for the Laser-driven Exotic Nuclei extraction-acceleration method proposed in [M. Nishiuchi et al., Phys. Plasmas 22, 033107 (2015)]: a femtosecond petawatt laser, irradiating a target bombarded by an external ion beam, extracts from the target and accelerates to few GeV highly charged short-lived heavy exotic nuclei created in the target via nuclear reactions.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Pikuz, T.*; Faenov, A.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Orlandi, R.; Sako, Hiroyuki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 22(3), p.033107_1 - 033107_8, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:96.10(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Almost fully stripped Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated with a 200 TW femtosecond high-intensity laser irradiating a micron-thick Al foil with Fe impurity on the surface. An energetic low-emittance high-density beam of heavy ions with a large charge-to-mass ratio can be obtained, which is useful for many applications, such as a compact radio isotope source in combination with conventional technology.
Jinno, Satoshi; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Yogo, Akifumi; Kanasaki, Masato; Kondo, Kiminori; Faenov, A. Y.; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Pikuz, T.; Boldarev, A. S.*; et al.
Progress in Ultrafast Intense Laser Science XI; Springer Series in Chemical Physics, Vol.109, p.215 - 233, 2015/00
Clusters formed in supersonic gas expansion through a three-staged conical nozzle have been verified by measuring the angular distribution of the light scattered from cluster target. The size distirbutions of the clusters are calculated based on the Mie theory. The reliability of the size measurement is verified to be an experimental error of 10% using standard particles. The mean sizes of CO clusters for the cases of CO
clusters for the cases of CO /H
/H and CO
and CO /He mixed-gas targets are estimated to be 0.26
/He mixed-gas targets are estimated to be 0.26  m and 0.22
m and 0.22  m, respectively. For the CO
m, respectively. For the CO /H
/H , the cluster density is estimated to be 5.5
, the cluster density is estimated to be 5.5 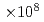 clusters/cm
clusters/cm by measuring the attenuation of the laser beam intensity. Furthermore, total gas density profiles are obtained via the Abel inversion from the phase shift of the light passing through the target using an interferometer. The variation of the cluster mass fraction along the radial direction of the target is almost constant, which is consistent with a Boldarev's model.
by measuring the attenuation of the laser beam intensity. Furthermore, total gas density profiles are obtained via the Abel inversion from the phase shift of the light passing through the target using an interferometer. The variation of the cluster mass fraction along the radial direction of the target is almost constant, which is consistent with a Boldarev's model.
 clusters formed in a supersonic expansion of a gas mixture
clusters formed in a supersonic expansion of a gas mixtureJinno, Satoshi; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Yogo, Akifumi; Kanasaki, Masato; Kondo, Kiminori; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Pikuz, T.; Boldarev, A. S.*; et al.
Optics Express (Internet), 21(18), p.20656 - 20674, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:72.56(Optics)A detailed mathematical model is presented for a submicron-sized cluster formation in a binary gas mixture flowing through a three-staged conical nozzle. In order to experimentally confirm this model, the cluster sizes have been evaluated using the Mie scattering method, which is to measure the angular distribution of light scattered from targets. The mean sizes of CO clusters produced in the gas mixtures of CO
clusters produced in the gas mixtures of CO (30%)/H
(30%)/H (70%) and CO
(70%) and CO (10%)/He(90%) are estimated to be 0.28
(10%)/He(90%) are estimated to be 0.28 0.03
0.03  m and 0.26
m and 0.26 0.04
0.04  m, respectively. In addition, total gas density profiles measured with an interferometer were found to be agreed with the numerical modeling within a factor of two. The dryness (
m, respectively. In addition, total gas density profiles measured with an interferometer were found to be agreed with the numerical modeling within a factor of two. The dryness (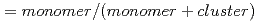 ratio) in the targets was found to support the numerical modeling. Thus, our mathematical model of cluster formation was proved to be reliable enough for the binary gas mixture by the experimental results.
ratio) in the targets was found to support the numerical modeling. Thus, our mathematical model of cluster formation was proved to be reliable enough for the binary gas mixture by the experimental results.
 clusters formed with a supersonic expansion of a mixed-gas using a three-staged nozzle
clusters formed with a supersonic expansion of a mixed-gas using a three-staged nozzleJinno, Satoshi; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Yogo, Akifumi; Kanasaki, Masato; Kondo, Kiminori; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Pikuz, T.; Boldarev, A. S.*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 102(16), p.164103_1 - 164103_4, 2013/04
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:69.49(Physics, Applied)The size of CO clusters, produced in a supersonic expansion of a mixed-gas of CO
clusters, produced in a supersonic expansion of a mixed-gas of CO /He or CO
/He or CO /H
/H through a three-staged conical nozzle designed based on the Boldarev's model, has been evaluated by measuring the angular distribution of light scattered from the clusters. The data are analyzed utilizing the Mie scattering theory, and the sizes of CO
through a three-staged conical nozzle designed based on the Boldarev's model, has been evaluated by measuring the angular distribution of light scattered from the clusters. The data are analyzed utilizing the Mie scattering theory, and the sizes of CO clusters are estimated as 0.22
clusters are estimated as 0.22  m and 0.25
m and 0.25  m for the cases of CO
m for the cases of CO /He and CO
/He and CO /H
/H gas mixtures, respectively. The results confirm that the Boldarev's model is reliable enough for the production of micron-sized clusters.
gas mixtures, respectively. The results confirm that the Boldarev's model is reliable enough for the production of micron-sized clusters.
Faenov, A. Ya.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Pikuz, T.; Pikuz, S. A.*; Fortov, V. E.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Hayashi, Yukio; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Shimomura, Takuya; et al.
Laser and Particle Beams, 30(3), p.481 - 488, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:41.90(Physics, Applied)Inogamov, N. A.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Zhakhovsky, V. V.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Petrov, Y. V.*; Khokhlov, V. A.*; Shepelev, V. V.*; Anisimov, S. I.*; Fortov, V. E.*; et al.
Contributions to Plasma Physics, 51(5), p.419 - 426, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:62.13(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Warm dense matter, arising under the action of ultrashort EUV-FEL pulse onto LiF dielectric crystal, is characterized by high temperature of conduction electrons, with their number density achieving values of the order of atom number density at maximum laser fluences in our experiments. Expansion of matter, heated and pressurized through the electron-ion energy exchange, gives rise to the spallative ablation at small fluences and gaseous outflow from a target in the case of large fluences. Ablation threshold is low in comparison with a longer nanosecond XRL.
 contrast femtosecond-pulse laser irradiation of argon clusters
contrast femtosecond-pulse laser irradiation of argon clustersColgan, J.*; Abdallah, J. Jr.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Hayashi, Yukio; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kawase, Keigo*; Shimomura, Takuya; et al.
High Energy Density Physics, 7(2), p.77 - 83, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:63.68(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A study is made of the ultra-short laser pulse irradiation of Ar cluster targets. Experiments have been performed with large cluster sizes and using very high laser contrasts, which have allowed clear and unambiguous observation of exotic inner-shell transitions in near-neutral Ar ions. The interaction of the main laser pulse with the unperturbed target is a necessary requirement for observing these lines. Our measurements are supported by kinetics calculations in which a very detailed atomic model is used. The calculations predict all of the spectral features found experimentally, and support the notion that the X-ray emission arises from many ion stages of the Ar plasma, from near-neutral through He-like ions, and from a range of plasma temperatures and densities.
Ishino, Masahiko; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Tanaka, Momoko; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovskii, V. V.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 109(1), p.013504_1 - 013504_6, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:75.63(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Faenov, A. Y.; Pikuz, T. A.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Kando, Masaki; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Homma, Takayuki; Kawase, Keigo; Kameshima, Takashi*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Yogo, Akifumi; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 95(10), p.101107_1 - 101107_3, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:77.04(Physics, Applied)Faenov, A. Y.; Magunov, A. I.*; Pikuz, S. A.*; Gasilov, S. V.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Palchan, T.*; Zigler, A.*; Henis, Z.*
Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics, 107(3), p.351 - 355, 2008/09
Colgan, J.*; Abdallah, J. Jr.*; Faenov, A. Y.; Pikuz, T. A.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*
Physica Scripta, 78(1), p.015302_1 - 015302_6, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.68(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Gasilov, S. V.*; Faenov, A. Y.; Pikuz, T. A.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Calegari, F.*; Vozzi, C.*; Nisoli, M.*; Sansone, G.*; Valentini, G.*; De Silvestri, S.*; et al.
JETP Letters, 87(5), p.238 - 242, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:66.22(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Palchan, T.*; Henis, Z.*; Faenov, A. Y.; Magunov, A. I.*; Pikuz, S. A.*; Gasilov, S. V.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Zigler, A.*
Applied Physics Letters, 91(25), p.251501_1 - 251501_3, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:48.20(Physics, Applied)Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovsky, V. V.*; Ashitkov, S.*; Eminov, Yu.*; Faenov, A.*; Petrov, Y. V.*; Khokhlov, V.*; Ishino, Masahiko; Demaske, B.*; Tanaka, Momoko; et al.
no journal, ,
Faenov, A.*; Pikuz, T.; Ishino, Masahiko; Starikov, S. V.*; Stegailov, V. V.*; Norman, G.*; Fortov, V. E.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Tanaka, Momoko; et al.
no journal, ,
Jinno, Satoshi; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Yogo, Akifumi; Kanasaki, Masato; Kondo, Kiminori; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Pikuz, T.; Boldarev, A. S.*; et al.
no journal, ,
In the laser drive ion acceleration using cluster-gas targets, the three-step conical nozzle specially designed based on the Boldarev's model is used to prepare the large-sized clusters. In the present work, the target diagnosis apparatus applying Mie scattering and interferometry has been developed to investigate the ion acceleration mechanism and search the optimal condition. The sub-micron sized CO clusters were verified by measuring the angular distribution of the scattering light from the gas jet of the mixture gas of CO
clusters were verified by measuring the angular distribution of the scattering light from the gas jet of the mixture gas of CO (30%) and H
(30%) and H (70%). Moreover, the gas density was obtained by the interferometry.
(70%). Moreover, the gas density was obtained by the interferometry.
Jinno, Satoshi; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Yogo, Akifumi; Kanasaki, Masato; Kondo, Kiminori; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Pikuz, T.; Boldarev, A. S.*; et al.
no journal, ,
We perform the laser driven ion acceleration using a gas jet target including large sized clusters which is formed by the special nozzle designed based on the Boldarev's model. The information of the cluster size and the gas jet profile is necessary for the investigation of the ion acceleration mechanism and the optimization of the acceleration condition. Therefore, we have developed a target diagnosis apparatus applying Mie scattering and interferometry. The sub-micron sized CO clusters were verified by measuring the angular distribution of the scattering light from the gas jet of the mixture gas of CO
clusters were verified by measuring the angular distribution of the scattering light from the gas jet of the mixture gas of CO (30%) and H
(30%) and H (70%). Moreover, the gas density profile was obtained by using the interferometer.
(70%). Moreover, the gas density profile was obtained by using the interferometer.
Jinno, Satoshi; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Yogo, Akifumi; Kanasaki, Masato; Kondo, Kiminori; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Pikuz, T.; Boldarev, A. S.*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have achieved high-energy ion generation in the laser driven ion acceleration using cluster-gas targets, which has been prepared by using the nozzle specially designed based on the Boldarev's model. However, a characterization of the cluster-gas targets is not sufficient to further investigate the ion acceleration mechanism and optimize the acceleration condition. In present work, the target diagnosis apparatus applying Mie scattering and interferometry has been developed. The sub-micron sized CO clusters were verified by measuring the angular distribution of the scattering light from the mixed gas target of CO
clusters were verified by measuring the angular distribution of the scattering light from the mixed gas target of CO (30%) and H
(30%) and H (70%). Moreover, the gas density profile was obtained by the interferometry. We will discuss the relation between gas density and a cluster size in the presentation.
(70%). Moreover, the gas density profile was obtained by the interferometry. We will discuss the relation between gas density and a cluster size in the presentation.