Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Song, K.*; Ito, Kei*; Ito, Daisuke*; Odaira, Naoya*; Saito, Yasushi*; Matsushita, Kentaro; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
Gas entrainment (GE) phenomena caused by a free surface vortex may cause the disturbance in core power of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR). For this reason, the entrained gas flow rate by the GE should be evaluated accurately for the practical safety design of SFRs. In this study, for the purpose of examining the applicability of CFD for the accurate evaluation of GE phenomena, a CFD is applied to the simulation of the free surface vortex and accompanied GE phenomena in a cylindrical vessel with a suction pipe, and the CFD results and the experimental data of the GE are compared. As a result, the CFD and experiments show similar two-phase flow pattern inside the suction pipe, and the shape of the gas core at the free surface is also very similar. Therefore, it is confirmed that the CFD can predict the GE phenomena triggered by a free surface vortex properly and accurately within the acceptable error range.
Pellegrini, M.*; Herranz, L.*; Sonnenkalb, M.*; Lind, T.*; Maruyama, Yu; Gauntt, R.*; Bixler, N.*; Morreale, A.*; Dolganov, K.*; Sevon, T.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 206(9), p.1449 - 1463, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:97.82(Nuclear Science & Technology)Pellegrini, M.*; Herranz, L.*; Sonnenkalb, M.*; Lind, T.*; Maruyama, Yu; Gauntt, R.*; Bixler, N.*; Morreale, A.*; Dolganov, K.*; Sevon, T.*; et al.
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.1147 - 1162, 2019/08
Kristo, M. J.*; Williams, R.*; Gaffney, A. M.*; Kayzar-Boggs, T. M.*; Schorzman, K. C.*; Lagerkvist, P.*; Vesterlund, A.*; Rameb ck, H.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; Kotze, D.*; et al.
ck, H.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; Kotze, D.*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 315(2), p.425 - 434, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:79.90(Chemistry, Analytical)In a recent international exercise, 10 international nuclear forensics laboratories successfully performed radiochronometry on three low enriched uranium oxide samples, providing 12 analytical results using three different parent-daughter pairs serving as independent chronometers. The vast majority of the results were consistent with one another and consistent with the known processing history of the materials. In general, for these particular samples, mass spectrometry gave more accurate and more precise analytical results than decay counting measurements. In addition, the concordance of the  U-
U-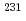 Pa and
Pa and  U-
U- Th chronometers confirmed the validity of the age dating assumptions, increasing confidence in the resulting conclusions.
Th chronometers confirmed the validity of the age dating assumptions, increasing confidence in the resulting conclusions.
Ho, D. M. L.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; Okubo, Ayako; Rameb ck, H.*; Song, K.*; Han, S.-H.*; Hancke, J. J.*; Holmgren, S.*; Jonsson, S.*; Kataoka, Osamu; et al.
ck, H.*; Song, K.*; Han, S.-H.*; Hancke, J. J.*; Holmgren, S.*; Jonsson, S.*; Kataoka, Osamu; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 315(2), p.353 - 363, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.04(Chemistry, Analytical)The Fourth Collaborative Material Exercise (CMX-4) of the Nuclear Forensics International Technical Working Group (ITWG) registered the largest participation for this exercise in nuclear forensics, with seven of the 17 laboratories participating for the first time. In this paper, participants from five of the first-time laboratories shared their individual experience in this exercise, from preparation to analysis of samples. The exercise proved to be highly useful for testing procedures, repurposing established methods, exercising skills, and improving the understanding of nuclear forensic signatures and their interpretation trough the post-exercise review meeting.
Lee, C.-G.*; Suzuki, Daisuke; Esaka, Fumitaka; Magara, Masaaki; Song, K.*
Talanta, 141, p.92 - 96, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:48.65(Chemistry, Analytical)Thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS) with a continuous heating technique is known as an effective method for measuring the isotope ratio in trace amounts of uranium. In this study, the analytical performance of thermal ionization mass spectrometry with a continuous heating technique was investigated using a standard plutonium solution (SRM 947). The influence of the heating rate of the evaporation filament on the precision and accuracy of the isotope ratios was examined using a plutonium solution sample at the fg level. Changing the heating rate of the evaporation filament on samples ranging from 0.1 fg to 1000 fg revealed that the influence of the heating rate on the precision and accuracy of the isotope ratios was slight around the heating rate range of 100 to 250 mA/min. All of the isotope ratios of plutonium (SRM 947),  Pu/
Pu/ Pu,
Pu,  Pu/
Pu/ Pu,
Pu,  Pu/
Pu/ Pu and
Pu and  Pu/
Pu/ Pu, were measured down to sample amounts of 70 fg. The ratio of
Pu, were measured down to sample amounts of 70 fg. The ratio of  Pu/
Pu/ Pu was measured down to a sample amount of 0.1 fg, which corresponds to a PuO
Pu was measured down to a sample amount of 0.1 fg, which corresponds to a PuO particle with a diameter of 0.2
particle with a diameter of 0.2  m. Moreover, the signals of
m. Moreover, the signals of  Pu could be detected with a sample amount of 0.03 fg, which corresponds to the detection limit of
Pu could be detected with a sample amount of 0.03 fg, which corresponds to the detection limit of  Pu of 0.006 fg as estimated by the 3
Pu of 0.006 fg as estimated by the 3  criterion.
criterion.  Pu and
Pu and  Am formed by the decay of
Am formed by the decay of  Pu could be discriminated owing to the difference in the evaporation temperature. As a result,
Pu could be discriminated owing to the difference in the evaporation temperature. As a result,  Pu/
Pu/ Pu as well as
Pu as well as  Pu/
Pu/ Pu and
Pu and  Pu/
Pu/ Pu in plutonium samples could be measured by TIMS with a continuous heating technique and without any chemical separation processes.
Pu in plutonium samples could be measured by TIMS with a continuous heating technique and without any chemical separation processes.
Yang, H. L.*; Kim, Y. S.*; Park, Y. M.*; Bae, Y. S.*; Kim, H. K.*; Kim, K. M.*; Lee, K. S.*; Kim, H. T.*; Bang, E. N.*; Joung, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Because the 2010 operation of Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR) mainly aims to achieve strongly elongated and diverted plasma, all the necessary hardware systems to provide an essential circumstance for the plasma shaping were newly installed and upgraded in 2010. In this paper, general configuration of the upgraded systems described earlier will be outlined. Moreover, several key performances and test results of the systems will be also reported in summary.
Bae, Y. S.*; Park, Y. M.*; Kim, J. S.*; Han, W. S.*; Kwak, S. W.*; Chang, Y. B.*; Park, H. T.*; Song, N. H.*; Chang, D. H.*; Jeong, S. H.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2011/03
The neutral beam injection (NBI) system is designed to provide the ion heating and current drive for the high performance operation and long pulse operation of the Korean Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR). The KSTAR NBI consists of two beam lines. Each beam line contains three ion sources of which one ion source has been designed to deliver more than 2.5 MW of deuterium neutral beam power with maximum 120-keV beam energy. Consequently, the final goal of the KSTAR NBI system aims to inject more than 14 MW of deuterium beam power with the two beam lines. According to the planned NBI system, the first NBI system is to demonstrate the beam injection from one ion source into the KSTAR tokamak plasma in 2010 campaign including the system commissioning of each components and subsystems. In this paper, the construction and the commissioning of the first NBI system with one ion source is presented.
Kataoka, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Masaki*; Sakamoto, Yuta*; Song, G. S.*; Fujimori, Atsushi*; Chang, F.-H.*; Lin, H.-J.*; Huang, D. J.*; Chen, C. T.*; Okochi, Takuo*; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 107(3), p.033718_1 - 033718_7, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:86.15(Physics, Applied) orbitals in the oxide-based diluted magnetic semiconductor In
orbitals in the oxide-based diluted magnetic semiconductor In V
V O
O
Kobayashi, Masaki*; Ishida, Yukiaki*; Hwang, J. I.*; Song, G. S.*; Takizawa, Masaru*; Fujimori, Atsushi; Takeda, Yukiharu; Okochi, Takuo*; Okane, Tetsuo; Saito, Yuji; et al.
Physical Review B, 79(20), p.205203_1 - 205203_5, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:31.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Glugla, M.*; Beloglazov, S.*; Carlson, B.*; Cho, S.*; Cristescu, I.*; Cristecu, I.*; Chung, H.*; Girard, J.-P.*; Hayashi, Takumi; Mardoch, D.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Ito, Kei*; Ito, Daisuke*; Odaira, Naoya*; Saito, Yasushi*; Song, K.*; Ezure, Toshiki; Matsushita, Kentaro; Tanaka, Masaaki
no journal, ,
The entrained gas flow rate by a bathtub vortex must be evaluated to achieve stable operation of a sodium-cooled fast reactor. In this study, a simple vortex-type gas entrainment experiment is conducted to evaluated the entrained gas flow rate under various conditions of free surface level, downstream pressure and suction pipe diameter. As a result, it is clarified that the entrained gas flow rate increases with the decrease in the downstream pressure. Based on the experimental result, we model the annular two-phase flow in the suction pipe and propose a new evaluation model of the entrained gas flow rate in which the influence of the downstream pressure.
Lee, C. G.*; Suzuki, Daisuke; Esaka, Fumitaka; Magara, Masaaki; Song, K.*
no journal, ,
In this study, analytical performances of TIMS with a continuous heating method were investigated using plutonium standard solution (SRM 947) and mixed particulate sample containing plutonium (SRM947) and uranium (U500). In order to examine the analytical performance of plutonium solution sample, the influence of heating rate of evaporation filament on precision and accuracy of isotope ratios was studied using plutonium solution sample of fg level. Changing the heating rate of evaporation filament on samples ranging from 0.1 fg to 1000 fg revealed that no influence of heating rate on precision and accuracy of isotope ratios occurred over the heating rate range from 100 to 250 mA/min. All of the isotope ratios on plutonium were measured down to sample amounts of 70 fg. In the mixture samples of plutonium and uranium,  Pu and
Pu and  U were clearly distinguished due to the difference of evaporation temperature between
U were clearly distinguished due to the difference of evaporation temperature between  Pu and
Pu and  U. As a result, the ratios of plutonium sample were successfully measured by TIMS with a continuous heating technique without any chemical separations.
U. As a result, the ratios of plutonium sample were successfully measured by TIMS with a continuous heating technique without any chemical separations.