Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Sakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Shimozawa, Yoko; Fukamoto, Kana*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sora, Sakura*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
Biological Sciences in Space, 26, p.21 - 25, 2012/10
High linear energy transfer (LET) radiation is important cosmic rays that has neurobiological effects: it is known to induce conditioned taste aversion, and suppress neurogenesis that may underlie cognitive impairment. However, the impact of high-LET radiation on other learning effects remains largely unknown. Here, we focus on kinetics of the radiation response for the salt chemotaxis learning (SCL) behavior in the nameatode,  , because the SCL during the learning conditioning was modulated after low-LET
, because the SCL during the learning conditioning was modulated after low-LET  -irradiation. Firstly, the SCL ability was examined following high-LET irradiation (
-irradiation. Firstly, the SCL ability was examined following high-LET irradiation ( C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/
C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/ m), revealing its dose-dependent decrease after high- and low-LET exposure. Next, we demonstrate that the SCL at the early phase of the learning conditioning is greatly affected by high- and low-LET irradiation, and interestingly, the magnitude of these effects by high-LET radiation was smaller than that by low-LET one. Moreover, the analysis of
m), revealing its dose-dependent decrease after high- and low-LET exposure. Next, we demonstrate that the SCL at the early phase of the learning conditioning is greatly affected by high- and low-LET irradiation, and interestingly, the magnitude of these effects by high-LET radiation was smaller than that by low-LET one. Moreover, the analysis of 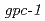 mutant showed that the G-protein
mutant showed that the G-protein  subunit, GPC-1 is responsible for such early phase response. This study is the first to provide the evidence for the kinetics of changes in SCL after high-LET irradiation of C.
subunit, GPC-1 is responsible for such early phase response. This study is the first to provide the evidence for the kinetics of changes in SCL after high-LET irradiation of C. 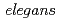 .
.
 against high-LET radiation exposure
against high-LET radiation exposureSakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Shimozawa, Yoko; Fukamoto, Kana*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sora, Sakura*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
Biological Sciences in Space, 26, p.7 - 11, 2012/07
Here, we investigated the resistance to high-LET radiation exposure for two behaviors of the nematode,  , which is known as a model organism for the nervous system. Tested behaviors were locomotion and chemotaxis to NaCl. In addition, egg hatchability was examined as an indicator of high-LET radiation sensitivity. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of high-LET radiation (
, which is known as a model organism for the nervous system. Tested behaviors were locomotion and chemotaxis to NaCl. In addition, egg hatchability was examined as an indicator of high-LET radiation sensitivity. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of high-LET radiation ( C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/
C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/ m) relative to low-LET radiation for hatchability was 4.5, whereas RBEs for locomotion and chemotaxis were 1.4 and 1.1, respectively. This study shows that the behavioral system for locomotion and chemotaxis of
m) relative to low-LET radiation for hatchability was 4.5, whereas RBEs for locomotion and chemotaxis were 1.4 and 1.1, respectively. This study shows that the behavioral system for locomotion and chemotaxis of  is highly resistant to high-LET radiation exposure.
is highly resistant to high-LET radiation exposure.
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Iwakawa, Mayumi*; Imadome, Kaori*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Sora, Sakura*; Ni, M.*; Imai, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Journal of Radiation Research, 50(Suppl.A), P. A118, 2009/05
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Kataoka, Keiko*; Sora, Sakura*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Omura, Motoko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Nakano, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Radiotherapy and Oncology, 89(2), p.227 - 230, 2008/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:35.33(Oncology)Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Omura, Motoko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Sora, Sakura; Yokota, Yuichiro; Nakano, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Radiotherapy and Oncology, 89(2), p.231 - 236, 2008/11
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:59.14(Oncology) -rays and energetic heavy ions
-rays and energetic heavy ionsHamada, Nobuyuki*; Ni, M.*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Sora, Sakura*; Nakano, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Uchu Seibutsu Kagaku, 22(2), p.41 - 45, 2008/10
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Omura, Motoko*; Ni, M.*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Sora, Sakura*; Nakano, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Uchu Seibutsu Kagaku, 22(2), p.46 - 53, 2008/10
Sora, Sakura*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Yokota, Yuichiro; Nakano, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Uchu Seibutsu Kagaku, 22(2), p.54 - 58, 2008/10
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Omura, Motoko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Sora, Sakura*; Nakano, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Cancer Letters, 268(1), p.76 - 81, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:22.85(Oncology)Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kataoka, Keiko*; Sora, Sakura; Omura, Motoko*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kataoka, Keiko*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Sora, Sakura; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sora, Sakura; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Ni, M.; Iwakawa, Mayumi*; Imadome, Kaori*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Sora, Sakura*; Imai, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Ni, M.; Kanasugi, Yuichi*; Iwakawa, Mayumi*; Imadome, Kaori*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Sora, Sakura*; Imai, Takashi*; Takakura, Kaoru*; et al.
no journal, ,
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Sora, Sakura; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
Sora, Sakura; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kataoka, Keiko*; Suzuki, Michiyo; Fukamoto, Kana; Yokota, Yuichiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kataoka, Keiko*; Sora, Sakura; Suzuki, Michiyo; Fukamoto, Kana; Yokota, Yuichiro; Omura, Motoko*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 following high-LET radiation exposure
following high-LET radiation exposureSakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Fukamoto, Kana; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sora, Sakura*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
We investigated various behavioral responses of well-fed adult  exposed to accelerated carbon ions (
exposed to accelerated carbon ions ( C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113.3 keV/
C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113.3 keV/ m). Following carbon-ion irradiation, locomotion, basal slowing response and salt chemotaxis learning were not significantly affected, whereas chemosensation to NaCl of animals during learning was altered. These results suggest that sensitivity of the
m). Following carbon-ion irradiation, locomotion, basal slowing response and salt chemotaxis learning were not significantly affected, whereas chemosensation to NaCl of animals during learning was altered. These results suggest that sensitivity of the  nervous system to high-LET heavy ions differs with the types of behaviors.
nervous system to high-LET heavy ions differs with the types of behaviors.
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Kataoka, Keiko*; Sora, Sakura*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Yokota, Yuichiro; Omura, Motoko*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Hara, Takamitsu*; Kataoka, Keiko*; Sora, Sakura*; Omura, Motoko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Yokota, Yuichiro; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English