Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 GeTe
GeTe to hydrostatic pressure
to hydrostatic pressureWang, Y.*; Zeng, X.-T.*; Li, B.*; Su, C.*; Hattori, Takanori; Sheng, X.-L.*; Jin, W.*
Chinese Physics B, 34(4), p.046203_1 - 046203_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Two-dimensional van der Waals ferromagnet Fe GeTe
GeTe (FGT) holds a great potential for applications in spintronic devices, due to its high Curie temperature, easy tunability, and excellent structural stability in air. In this study, we have performed high-pressure neutron powder diffraction (NPD) up to 5 GPa, to investigate the evolution of its structural and magnetic properties with hydrostatic pressure. The NPD data clearly reveal the robustness of the ferromagnetism in FGT, despite of an apparent suppression by hydrostatic pressure. As the pressure increases from 0 to 5 GPa, the Curie temperature is found to decrease monotonically from 225(5) K to 175(5) K, together with a dramatically suppressed ordered moment of Fe, which is well supported by the first-principles calculations. Although no pressure-driven structural phase transition is observed up to 5 GPa, quantitative analysis on the changes of bond lengths and bond angles indicate a significant modification of the exchange interactions, which accounts for the pressure-induced suppression of the ferromagnetism in FGT.
(FGT) holds a great potential for applications in spintronic devices, due to its high Curie temperature, easy tunability, and excellent structural stability in air. In this study, we have performed high-pressure neutron powder diffraction (NPD) up to 5 GPa, to investigate the evolution of its structural and magnetic properties with hydrostatic pressure. The NPD data clearly reveal the robustness of the ferromagnetism in FGT, despite of an apparent suppression by hydrostatic pressure. As the pressure increases from 0 to 5 GPa, the Curie temperature is found to decrease monotonically from 225(5) K to 175(5) K, together with a dramatically suppressed ordered moment of Fe, which is well supported by the first-principles calculations. Although no pressure-driven structural phase transition is observed up to 5 GPa, quantitative analysis on the changes of bond lengths and bond angles indicate a significant modification of the exchange interactions, which accounts for the pressure-induced suppression of the ferromagnetism in FGT.
Fujisawa, Yuita*; Krishnadas, A*; Nakamura, Tomonori*; Hsu, C.-H.*; Smith, B. R. M.*; Pardo-Almanza, M*; Hiyane, Hoshu*; Nagai, Yuki; Machida, Tadashi*; Okada, Yoshinori*
Physical Review B, 110(22), p.224511_1 - 224511_5, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Understanding the nature of vortices in type-II superconductors has been vital for deepening the physics of exotic superconductors and applying superconducting materials to future electronic devices. A recent study has shown that the LiTi O
O (111) thin film offers a unique experimental platform to unveil the nature of the vortex along the curved Josephson junction. This study successfully visualized individual Josephson vortices along the curved Josephson junctions using in-situ spectroscopic scanning tunneling microscopy on LiTi
(111) thin film offers a unique experimental platform to unveil the nature of the vortex along the curved Josephson junction. This study successfully visualized individual Josephson vortices along the curved Josephson junctions using in-situ spectroscopic scanning tunneling microscopy on LiTi O
O (111) epitaxial thin films. Notably, the local curvature of the Josephson junction was discovered to control the position of Josephson vortices. Furthermore, the numerical simulation reproduces the critical role of the curvature of the Josephson junction. This study provides guidelines to control Josephson vortices through geometrical ways, such as mechanical controlling of superconducting materials and their devices.
(111) epitaxial thin films. Notably, the local curvature of the Josephson junction was discovered to control the position of Josephson vortices. Furthermore, the numerical simulation reproduces the critical role of the curvature of the Josephson junction. This study provides guidelines to control Josephson vortices through geometrical ways, such as mechanical controlling of superconducting materials and their devices.
Ueda, Yuki; Micheau, C.; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Yamada, Masako*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Bourgeois, D.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei
Langmuir, 40(46), p.24257 - 24271, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Microscopic structures in liquid-liquid extraction, such as structuration between extractants or extracted complexes in bulk organic phases and at interfaces, can influence macroscopic phenomena, such as the distribution behavior of solutes, including extraction efficiency, selectivity, and phase separation of the organic phase. In this study, we correlated the macroscopic behavior of the extraction of Zr(IV) ions from nitric acid solutions with microscopic structural information in order to understand at the molecular level the key factors contributing to the higher metal ion extraction performance in the fluorous extraction system comprising fluorous phosphate (TFP) in perfluorohexane as compared to the analogous organic extraction system comprising organic phosphate (THP) in n-hexane. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure, neutron reflectometry, and small-angle neutron scattering revealed the local coordination structure around the Zr(IV) ion, the accumulation of extractant molecules at the interface, and the structuration of extractant molecules in the bulk extraction phase, respectively. In the fluorous extraction system, extractant aggregates with were formed after contact with nitric acid. In contrast, in the organic extraction system, only extractant dimers were formed. We speculate that differences in the local coordination structure around the Zr(IV) ion and the structuration of the extractant molecules in the bulk extraction phase contribute to the high Zr(IV) extraction performance in the fluorous extraction system. In particular, the size of the aggregates hardly changed with increasing Zr(IV) concentration in the fluorous phase, which may be closely related to the absence of phase splitting in the fluorous extraction system.
Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; Xu, P. G.; Zhang, H.*; Zhou, L.*; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; Shobu, Takahisa; Wu, S. C.*
International Journal of Fatigue, 185, p.108336_1 - 108336_13, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:93.27(Engineering, Mechanical)Miyazaki, Kanako*; Takehara, Masato*; Minomo, Kenta*; Horie, Kenji*; Takehara, Mami*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Saito, Takumi*; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Takano, Masahide; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; et al.
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 470(15), p.134104_1 - 134104_11, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.14(Engineering, Environmental)Micheau, C.; Ueda, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Yamada, Norifumi*; Yamada, Masako*; Moussaoui, S. A.*; Makombe, E.*; Meyer, D.*; Berthon, L.*; et al.
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 401, p.124372_1 - 124372_12, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:60.60(Chemistry, Physical)Hu, Q.*; Wang, Q. M.*; Zhang, T.*; Zhao, C.*; Iltaf, K. H.*; Liu, S. Q.*; Fukatsu, Yuta
Energy Reports (Internet), 9, p.3661 - 3682, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:64.37(Energy & Fuels) Mo hot atoms made by a neutron capture method from
Mo hot atoms made by a neutron capture method from  -MoO
-MoO to water
to waterQuach, N. M.*; Ngo, M. C.*; Yang, Y.*; Nguyen, T. B.*; Nguyen, V. T.*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Do, T. M. D.*; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(10), p.4057 - 4064, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:71.02(Chemistry, Analytical)Technetium-99m ( Tc) is the most widely used medical radioisotope in the world and is produced from molybdenum-99 (
Tc) is the most widely used medical radioisotope in the world and is produced from molybdenum-99 ( Mo). Production of
Mo). Production of  Mo via the neutron capture method draws attention as an alternative to fission-derived
Mo via the neutron capture method draws attention as an alternative to fission-derived  Mo due to non-proliferation issues, but the specific radioactivity of
Mo due to non-proliferation issues, but the specific radioactivity of  Mo is extremely low. In this work, a porous
Mo is extremely low. In this work, a porous  -MoO
-MoO wire was prepared as an irradiation target in order to improve the specific activity by extracting
wire was prepared as an irradiation target in order to improve the specific activity by extracting  Mo. Porous
Mo. Porous  -MoO
-MoO wire is synthesized from Mo metal wire by a two-step heating procedure. The hot atom effect of
wire is synthesized from Mo metal wire by a two-step heating procedure. The hot atom effect of  Mo was confirmed by activity and isotope measurements of the porous
Mo was confirmed by activity and isotope measurements of the porous  -MoO
-MoO wire after neutron irradiation and the water used for extraction. In term of the extraction effectiveness, the effectiveness of
wire after neutron irradiation and the water used for extraction. In term of the extraction effectiveness, the effectiveness of  Mo extraction in the porous
Mo extraction in the porous  -MoO
-MoO wire was comparable to that of commercial
wire was comparable to that of commercial  -MoO
-MoO powder.
powder.
Toyoda, Shin*; Inoue, Kazuhiko*; Yamaguchi, Ichiro*; Hoshi, Masaharu*; Hirota, Seiko*; Oka, Toshitaka; Shimazaki, Tatsuya*; Mizuno, Hideyuki*; Tani, Atsushi*; Yasuda, Hiroshi*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(14), p.1557 - 1564, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Environmental Sciences)Interlaboratory comparison studies are important for radiation dosimetry in order to demonstrate how the technique is universally available. The set of standard samples are examined in each participating laboratory in the present study. After a set of standard samples together with the samples with unknown doses, which were prepared in the same laboratory as the standard samples, are measured at a participating laboratory, those samples are sent to another participating laboratory for next measurement. There is some small difference observed in the sensitivity (the slope of the dose response line) of the standard samples while the differences in the obtained doses for the samples with unknown doses are rather systematic, implying that the difference is mostly due to the samples but not to measurements.
 -MoO
-MoO whiskers in
whiskers in  Mo/
Mo/ Tc radioisotope production and
Tc radioisotope production and  Mo/
Mo/ Tc extraction using hot atoms
Tc extraction using hot atomsNgo, M. C.*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Do, T. M. D.*; Seki, Misaki; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Niihara, Koichi*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(32), p.13140 - 13147, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:60.95(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Technetium-99m ( Tc) is one of the most important radioisotopes for diagnostic radio-imaging applications.
Tc) is one of the most important radioisotopes for diagnostic radio-imaging applications.  Tc is a daughter product of the
Tc is a daughter product of the  Mo isotope. There are two methods used to produce
Mo isotope. There are two methods used to produce  Mo/
Mo/ Tc: the nuclear fission (n,f) and the neutron capture (n,
Tc: the nuclear fission (n,f) and the neutron capture (n, ) methods. Between them, the (n,f) method is the main route, used for approximately 90% of the world's production. However, the (n,f) method faces numerous problems, including the use of highly enriched uranium, the release of highly radioactive waste, and nonproliferation problems. Therefore, the (n,
) methods. Between them, the (n,f) method is the main route, used for approximately 90% of the world's production. However, the (n,f) method faces numerous problems, including the use of highly enriched uranium, the release of highly radioactive waste, and nonproliferation problems. Therefore, the (n, ) method is being developed as a future replacement for the (n,f) method. In this work,
) method is being developed as a future replacement for the (n,f) method. In this work,  -MoO
-MoO whiskers prepared by the thermal evaporation method and
whiskers prepared by the thermal evaporation method and  -MoO
-MoO particles were irradiated in a nuclear reactor to produce
particles were irradiated in a nuclear reactor to produce  Mo/
Mo/ Tc via neutron capture. The irradiated targets were dispersed into water to extract the
Tc via neutron capture. The irradiated targets were dispersed into water to extract the  Mo/
Mo/ Tc. As a result,
Tc. As a result,  -MoO
-MoO whisker yielded higher
whisker yielded higher  Mo extraction rate than that from
Mo extraction rate than that from  -MoO
-MoO . In addition, by comparing the dissolved
. In addition, by comparing the dissolved  Mo concentrations in water, we clarified a prominent hot-atom of
Mo concentrations in water, we clarified a prominent hot-atom of  -MoO
-MoO whiskers. This research is the first demonstration of
whiskers. This research is the first demonstration of  -MoO
-MoO being used as an irradiation target in the neutron capture method. On the basis of the results,
being used as an irradiation target in the neutron capture method. On the basis of the results,  -MoO
-MoO is considered a promising irradiation target for producing
is considered a promising irradiation target for producing  Mo/
Mo/ Tc by neutron capture and using water for the radioisotope extraction process in the future.
Tc by neutron capture and using water for the radioisotope extraction process in the future.
Fueda, Kazuki*; Komiya, Tatsuki*; Minomo, Kenta*; Horie, Kenji*; Takehara, Mami*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Grambow, B.*; Law, G. T. W.*; et al.
Chemosphere, 328, p.138566_1 - 138566_12, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:50.39(Environmental Sciences)Ao, N.*; Zhang, H.*; Xu, H. H.*; Wu, S. C.*; Liu, D.*; Xu, P. G.; Su, Y. H.; Kang, Q. H.*; Kang, G. Z.*
Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 281, p.109166_1 - 109166_14, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:82.23(Mechanics)Yuan, X.*; Hu, Q.*; Lin, X.*; Zhao, C.*; Wang, Q.*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Hamamoto, Shoichiro*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Li, X.*
Journal of Hydrology, 618, p.129172_1 - 129172_15, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:58.63(Engineering, Civil)Micheau, C.; Ueda, Yuki; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Bourgeois, D.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei
Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 41(2), p.221 - 240, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:41.44(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) Mo/
Mo/ Tc generator by (n,
Tc generator by (n,  ) method, 4
) method, 4Fujita, Yoshitaka; Seki, Misaki; Ngo, M. C.*; Do, T. M. D.*; Hu, X.*; Yang, Y.*; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; Yoshinaga, Hisao*; et al.
KURNS Progress Report 2021, P. 118, 2022/07
no abstracts in English
 C control rods in Fukushima Daiichi nuclear reactors during meltdown; B-Li isotopic signatures in cesium-rich microparticles
C control rods in Fukushima Daiichi nuclear reactors during meltdown; B-Li isotopic signatures in cesium-rich microparticlesFueda, Kazuki*; Takami, Ryu*; Minomo, Kenta*; Morooka, Kazuya*; Horie, Kenji*; Takehara, Mami*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Saito, Takumi*; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Onuki, Toshihiko*; et al.
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 428, p.128214_1 - 128214_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:66.41(Engineering, Environmental)Fujita, Yoshitaka; Niizeki, Tomotake*; Fukumitsu, Nobuyoshi*; Ariga, Katsuhiko*; Yamauchi, Yusuke*; Malgras, V.*; Kaneti, Y. V.*; Liu, C.-H.*; Hatano, Kentaro*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*; et al.
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 95(1), p.129 - 137, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.41(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)In this work, the mechanisms responsible for the adsorption of molybdate ions on alumina are investigated using in-depth surface analyses carried out on alumina specimens immersed in solutions containing different molybdate ions at different pH values. The obtained results reveal that when alumina is immersed in an acidic solution containing molybdate ions, the hydroxyl groups present on the surface are removed to generate positively charged sites, and molybdate ions (MoO
 or AlMo
or AlMo O
O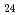 H
H
 ) are adsorbed by electrostatic interaction. Alumina dissolves slightly in an acidic solution to form AlMo
) are adsorbed by electrostatic interaction. Alumina dissolves slightly in an acidic solution to form AlMo O
O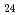 H
H
 , which is more easily desorbed than MoO
, which is more easily desorbed than MoO
 . Furthermore, the enhancement in the Mo adsorption or desorption property may be achieved by enriching the surface of the alumina adsorbent with many -OH groups and optimizing Mo solution to adsorb molybdate ions on alumina as MoO
. Furthermore, the enhancement in the Mo adsorption or desorption property may be achieved by enriching the surface of the alumina adsorbent with many -OH groups and optimizing Mo solution to adsorb molybdate ions on alumina as MoO
 ions. These findings will assist researchers in engineering more efficient and stable alumina-based adsorbents for molybdenum adsorption used in medical radioisotope (
ions. These findings will assist researchers in engineering more efficient and stable alumina-based adsorbents for molybdenum adsorption used in medical radioisotope ( Mo/
Mo/ Tc) generators.
Tc) generators.
 anomaly at high temperature with lattice chiral fermions
anomaly at high temperature with lattice chiral fermionsAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Kaneko, Takashi*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 103(7), p.074506_1 - 074506_18, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:84.12(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We investigate the axial  anomaly of two-flavor QCD at temperatures 190-330 MeV. In order to preserve precise chiral symmetry on the lattice, we employ the M
anomaly of two-flavor QCD at temperatures 190-330 MeV. In order to preserve precise chiral symmetry on the lattice, we employ the M bius domain-wall fermion action as well as overlap fermion action implemented with a stochastic reweighting technique. Compared to our previous studies, we reduce the lattice spacing to 0.07 fm, simulate larger multiple volumes to estimate finite size effect, and take more than four quark mass points, including one below physical point to investigate the chiral limit. We measure the topological susceptibility, axial
bius domain-wall fermion action as well as overlap fermion action implemented with a stochastic reweighting technique. Compared to our previous studies, we reduce the lattice spacing to 0.07 fm, simulate larger multiple volumes to estimate finite size effect, and take more than four quark mass points, including one below physical point to investigate the chiral limit. We measure the topological susceptibility, axial  susceptibility, and examine the degeneracy of
susceptibility, and examine the degeneracy of  partners in meson/baryon correlators. All the data above the critical temperature indicate that the axial
partners in meson/baryon correlators. All the data above the critical temperature indicate that the axial  violation is consistent with zero within statistical errors. The quark mass dependence suggests disappearance of the
violation is consistent with zero within statistical errors. The quark mass dependence suggests disappearance of the  anomaly at a rate comparable to that of the
anomaly at a rate comparable to that of the 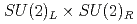 symmetry breaking.
symmetry breaking.
Rohrhofer, C.*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Gattringer, C.*; Glozman, L. Ya.*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Lang, C. B.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 363, p.227_1 - 227_7, 2020/08
Properties of QCD matter change significantly around the chiral crossover temperature, and the effects on 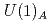 and topological susceptibilities, as well as the meson spectrum have been studied with much care. Baryons and the effect of parity doubling in this temperature range have been analyzed previously by various other groups employing different setups. Here we construct suitable operators to investigate chiral and axial
and topological susceptibilities, as well as the meson spectrum have been studied with much care. Baryons and the effect of parity doubling in this temperature range have been analyzed previously by various other groups employing different setups. Here we construct suitable operators to investigate chiral and axial 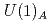 symmetries in the baryon spectrum. Measurements for different volumes and quark-masses are done with two flavors of chirally symmetric domain-wall fermions at temperatures above the critical one. The possibility of emergent
symmetries in the baryon spectrum. Measurements for different volumes and quark-masses are done with two flavors of chirally symmetric domain-wall fermions at temperatures above the critical one. The possibility of emergent 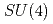 and
and 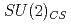 symmetries is discussed.
symmetries is discussed.
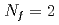 lattice QCD
lattice QCDSuzuki, Kei; Aoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 363, p.178_1 - 178_7, 2020/08
We investigate the high-temperature phase of QCD using lattice QCD simulations with 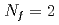 dynamical M
dynamical M bius domain-wall fermions. On generated configurations, we study the axial
bius domain-wall fermions. On generated configurations, we study the axial  symmetry, overlap-Dirac spectra, screening masses from mesonic correlators, and topological susceptibility. We find that some of the observables are quite sensitive to lattice artifacts due to a small violation of the chiral symmetry. For those observables, we reweight the M
symmetry, overlap-Dirac spectra, screening masses from mesonic correlators, and topological susceptibility. We find that some of the observables are quite sensitive to lattice artifacts due to a small violation of the chiral symmetry. For those observables, we reweight the M bius domain-wall fermion determinant by that of the overlap fermion. We also check the volume dependence of observables. Our data near the chiral limit indicates a strong suppression of the axial
bius domain-wall fermion determinant by that of the overlap fermion. We also check the volume dependence of observables. Our data near the chiral limit indicates a strong suppression of the axial  anomaly at temperatures
anomaly at temperatures  220 MeV.
220 MeV.