Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishii, Eiichi; Ozaki, Yusuke; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Sugawara, Kentaro*
Hydrogeology Journal, 33(1), p.63 - 85, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)This study performed virtual packer tests on modeled single fractures on computer and derived the relationship between flow dimension and mappable indicator, DI, which is defined by the mean stress, groundwater pressure, and rock tensile strength. The greater DI results in the smaller flow area in faults or fractures, subject to fracture-normal closure. Comparing the derived relationship with results from in situ hydraulic tests on natural faults in rock with few fracture-mineral-fillings revealed that flow-path connectivity is high (flow dimension 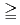 1.5) when DI was
1.5) when DI was  2.0 while was low (flow dimension
2.0 while was low (flow dimension  1.5) when DI was
1.5) when DI was 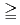 2.0. This relationship was valid even when DI was varied, or faults were sheared, during injection tests on faults, and even in rock with abundant fracture-mineral-fillings. However, flow-path connectivity in minor fractures far from faults could be also low even when DI was
2.0. This relationship was valid even when DI was varied, or faults were sheared, during injection tests on faults, and even in rock with abundant fracture-mineral-fillings. However, flow-path connectivity in minor fractures far from faults could be also low even when DI was  2.0 probably due to poor connection to the main fault network or sealing effects of fracture-mineral-fillings. When the permeability of intact rock is high, flow-path connectivity in fractures was high even when DI was
2.0 probably due to poor connection to the main fault network or sealing effects of fracture-mineral-fillings. When the permeability of intact rock is high, flow-path connectivity in fractures was high even when DI was 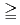 2.0. These findings can be helpful to map the spatial distribution of flow-path connectivity in faults or fractures from limited borehole data.
2.0. These findings can be helpful to map the spatial distribution of flow-path connectivity in faults or fractures from limited borehole data.
Kotegawa, Hisashi*; Nakamura, Akira*; Huyen, V. T. N.*; Arai, Yuki*; To, Hideki*; Sugawara, Hitoshi*; Hayashi, Junichi*; Takeda, Keiki*; Tabata, Chihiro; Kaneko, Koji; et al.
Physical Review B, 110(21), p.214417_1 - 214417_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sugawara, Yu*; Igarashi, Takahiro
Tetsu To Hagane, 110(15), p.1179 - 1186, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Degradation due to atmospheric corrosion is an important problem for steel structures such as bridges. In order to maintain steel structures safely over a long period of time, there is a need for a low-cost and easy-to-use method to evaluate corrosion degradation. In this study, corrosion morphology under atmospheric corrosion environment was focused on. The relation between the surface appearance and the distribution of corrosion depth of the carbon steel specimen after atmospheric exposure was analyzed, and the prediction of corrosion morphology under rust layers by surface observation of steel specimens was examined. It was found that deeply-corroded areas were possible to be located within the dark brown regions in the rusted specimen after the atmospheric exposure. As the exposure period increased, the correspondence between the dark brown regions in the rusted specimen and deeply-corroded areas became clearer.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Sugawara, Yu*; Otani, Kyohei; Aoyama, Takahito
Tetsu To Hagane, 110(15), p.1244 - 1250, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Using two types of image processing techniques without machine learning, edge extraction processing and keypoint extraction processing, progressively corroded regions under rust layer from images of corroded steel surfaces was extracted. We found that there is a relatively good correlation between the keypoint strength obtained from the keypoint extraction processing for HSL transformed and histogram flattened corroded surface photographs and the corrosion depth after removing rust removal.
Yamashita, Susumu; Kondo, Nao; Sugawara, Takanori; Monji, Hideaki*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(6), p.740 - 761, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)To confirm the validity of the thermal-hydraulics design tool based on the Ansys Fluent, we used a detailed computational fluid dynamics code named JAEA Utility Program for Interdisciplinary Thermal-hydraulics Engineering and Research (JUPITER) for the thermal-hydraulics around the beam window (BW) of the Accelerator-Driven System (ADS). The Fluent uses the Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) model and can quickly calculate the turbulent flow around the BW as a BW design tool. At first, we compared the results of JUPITER with the experimental results using a mock-up BW system in water to confirm the validity of JUPITER. As a result, we confirmed that numerical results are in good agreement with the experimental results. Thus, we showed that JUPITER could be used as a benchmark code. We also performed a benchmark simulation for the Fluent calculation using validated JUPITER to show the applicability of JUPITER as an alternative of experiments. As a result, the mean values around the BW agreed with each other, e.g., the mean velocity profile for stream and horizontal directions. Therefore, we confirmed that JUPITER showed a good performance in validating the thermal-hydraulics design tool as a fluid dynamics solver. Moreover, Fluent has enough accuracy as a thermal-hydraulics design tool for the ADS.
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kimura, Atsushi; Tada, Kenichi; Sugawara, Takanori; Yokoyama, Kenji
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (133), p.1 - 6, 2022/10
no abstracts in English
Tobita, Daiki*; Monji, Hideaki*; Yamashita, Susumu; Horiguchi, Naoki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Sugawara, Takanori
Proceedings of 12th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS12) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/10
Ozaki, Yusuke; Ishii, Eiichi; Sugawara, Kentaro*
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 31, p.100311_1 - 100311_13, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.36(Energy & Fuels)This study analyzed the long-term hydraulic pressure data during the excavation of Horonobe URL to estimate the variation of effective-hydraulic-conductivity. We performed the numerical simulation with the poroelastic effect for the estimation because the observed hydraulic pressure is highly affected by the Mandel-Cryer effect. The evaluation of the observed data based on our simulation results showed that the effective-hydraulic-conductivity gradually decreases from 400 m to 500 m in depth and is as low as the intact rock at depths greater than 500 m. Not only the analysis based on our simulation results but also the analysis based on analytical solution indicate the domain with different hydraulic properties in the Wakkanai Formation. These results suggest that the fracture-hydraulic-connectivity changes not abruptly but gradually over several tens of meters around the predicted boundary.
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Aoi, Nori*; Azaiez, F.*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Kimura, Atsushi; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 103(3), p.034327_1 - 034327_8, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.33(Physics, Nuclear)Ozaki, Yusuke; Ishii, Eiichi; Sugawara, Kentaro*
Extended abstract of International Conference on Coupled Processes in Fractured Geological Media; Observation, Modeling, and Application (CouFrac 2020) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/11
We perform the numerical simulation of the response of hydraulic head observed in HDB-6 during the excavation of the Horonobe URL to verify the existence of low effective permeable domain in the subsurface. The low permeable domain as an intact rock due to the low hydraulic fracture connectivity is estimated to exist in the deep domain while the permeability of the shallow domain is relatively high due to the hydraulic fracture connectivity there. Our simulation shows that the observed hydraulic head is affected by the Mandel-Cryer effect due to the hydrogeological structure and the effect for the duration of over years requires the low permeability as an intact rock in the deep domain. These results verify the existence of the low effective permeable domain in the deep subsurface estimated by the previous study.
 Sb
Sb uncovered by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
uncovered by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroismSaito, Yuji; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Yasui, Akira*; Kadono, Toshiharu*; Sugawara, Hitoshi*; Kikuchi, Daisuke*; Sato, Hideyuki*; Suga, Shigemasa*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Sekiyama, Akira*; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(16), p.165152_1 - 165152_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.40(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Se
Se ultrathin films on van der Waals ferromagnet Cr
ultrathin films on van der Waals ferromagnet Cr Si
Si Te
Te
Kato, Takemi*; Sugawara, Katsuaki*; Ito, Naohiro*; Yamauchi, Kunihiko*; Sato, Takumi*; Oguchi, Tamio*; Takahashi, Takashi*; Shiomi, Yuki*; Saito, Eiji; Sato, Takafumi*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 4(8), p.084202_1 - 084202_6, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:19.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yamashita, Susumu; Sugawara, Takanori; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2019/05
In order to simulate detailed flow behavior of LBE around the beam window, a numerical simulation code that can evaluate the complicated flow behavior is required. To simulate complicated and large-scale flow behavior, we apply JUPITER which originally developed in JAEA for melt relocation behavior in SAs and that can treat complicated flow behavior and has a capacity of massively parallel computing. In this paper, by using JUPITER, numerical simulations were performed for unsteady thermal-hydraulics simulation around the beam window to know tendency of LBE flow field. In addition, problems to be solved and important parameters to simulate thermal-hydraulic behavior around the beam window will be discussed.

 generation; The Role of NO
generation; The Role of NO
 in the crevice corrosion repassivation of type 316L stainless steel
in the crevice corrosion repassivation of type 316L stainless steelAoyama, Takahito; Sugawara, Yu*; Muto, Izumi*; Hara, Nobuyoshi*
Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 166(10), p.C250 - C260, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:12.85(Electrochemistry)The role of NO
 in the repassivation of crevice corrosion of Type 316L stainless steel was investigated. In crevice corrosion tests, the solution was changed from 1 M NaCl to NaCl-NaNO
in the repassivation of crevice corrosion of Type 316L stainless steel was investigated. In crevice corrosion tests, the solution was changed from 1 M NaCl to NaCl-NaNO . NO
. NO
 led to complete repassivation. Repassivation of the crevice corrosion was found to take place in two steps. In the first step, the estimated current density inside the crevice gradually decreased from ca. 5 mA cm
led to complete repassivation. Repassivation of the crevice corrosion was found to take place in two steps. In the first step, the estimated current density inside the crevice gradually decreased from ca. 5 mA cm to ca. 5
to ca. 5  A cm
A cm . After that, the current density suddenly decreased to less than 0.1
. After that, the current density suddenly decreased to less than 0.1  A cm
A cm . From the potentiodynamic polarization in acidic solutions simulated inside the crevice (pH 0.2) and in situ observations of the crevice corrosion morphology, the first step was thought to be generated by the suppression of active dissolution by NO
. From the potentiodynamic polarization in acidic solutions simulated inside the crevice (pH 0.2) and in situ observations of the crevice corrosion morphology, the first step was thought to be generated by the suppression of active dissolution by NO
 . It would appear that the generation of NH
. It would appear that the generation of NH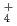 results in a pH increase and the further suppression of active dissolution, and then repassivation occurs.
results in a pH increase and the further suppression of active dissolution, and then repassivation occurs.
Sugawara, Takanori; Eguchi, Yuta; Obayashi, Hironari; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Matsuda, Hiroki; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2018/07
A new beam window concept for accelerator-driven system (ADS) is investigated by changing the design condition. The most important factor for the beam window design is the proton beam current. The design condition will be mitigated if the proton beam current will be reduced. To reduce the proton beam current, a subcriticality adjustment rod (SAR) which was a B C control rod was employed and neutronics calculations were performed by ADS3D code. The results of the neutronics calculation indicated that the proton beam current was reduced from 20mA to 13.5mA by the installation of SARs. Based on the mitigated calculation condition, the investigation of the beam window was performed by the couple analyses of the particle transport, the thermal hydraulics and the structural analysis. Through these coupled analyses, more feasible beam window concept which was the hemispherical shape, the outer diameter = 470mm, the thickness at the top = 3.5mm and factor of safety =9 was presented.
C control rod was employed and neutronics calculations were performed by ADS3D code. The results of the neutronics calculation indicated that the proton beam current was reduced from 20mA to 13.5mA by the installation of SARs. Based on the mitigated calculation condition, the investigation of the beam window was performed by the couple analyses of the particle transport, the thermal hydraulics and the structural analysis. Through these coupled analyses, more feasible beam window concept which was the hemispherical shape, the outer diameter = 470mm, the thickness at the top = 3.5mm and factor of safety =9 was presented.
Eguchi, Yuta; Sugawara, Takanori; Nishihara, Kenji; Tazawa, Yujiro; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2018/07
In order to investigate the basic neutronics characteristics of the accelerator-driven subcritical system (ADS), JAEA has a plan to construct a new critical assembly in the J-PARC project, Transmutation Physics Experimental Facility (TEF-P). This study aims to evaluate the natural cooling characteristics of TEF-P core which has large decay heat by minor actinide (MA) fuel, and to achieve a design that does not damage the core and the fuels during the failure of the core cooling system. In the evaluation of the TEF-P core temperature, empty rectangular lattice tube outer of the core has a significant effect on the heat transfer characteristics. The experiments by using the mockup device were performed to validate the heat transfer coefficient and experimental results were obtained. By using the obtained experimental results, the three-dimensional heat transfer analysis of TEF-P core were performed, and the maximum core temperature was obtained, 294 C. This result shows TEF-P core temperature would be less than 327
C. This result shows TEF-P core temperature would be less than 327 C that the design criterion of temperature.
C that the design criterion of temperature.
Sugawara, Takanori; Eguchi, Yuta; Obayashi, Hironari; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 331, p.11 - 23, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:73.48(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study aims to perform the coupled analysis for the feasible beam window concept. To mitigate the design condition, namely to reduce the necessary proton beam current, subcriticality adjustment rod (SAR) was installed to the ADS core. The burnup analysis was performed for the ADS core with SAR and the results indicated that the maximum proton beam current during the burnup cycle was reduced from 20 to 13.5 mA. Based on the burnup analysis result, the coupled analysis; particle transport, thermal hydraulics and structural analyses, was performed. As the final result, the most robust beam window design; the hemisphere shape, the outer radius = 235 mm, the thickness at the top of the beam window = 3.5 mm and the factor of safety for the buckling = 9.0, was presented. The buckling pressure was 2.2 times larger than the previous one and more feasible beam window concept was presented through this study.
Pyeon, C. H.*; Vu, T. M.*; Yamanaka, Masao*; Sugawara, Takanori; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nishihara, Kenji; Kim, S. H.*; Takahashi, Yoshiyuki*; Nakajima, Ken*; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(2), p.190 - 198, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:79.90(Nuclear Science & Technology)At the Kyoto University Critical Assembly, a series of reaction rate experiments is conducted on the accelerator-driven system (ADS) with spallation neutrons generated by the combined use of 100 MeV protons and a lead and bismuth target in the subcritical state. The reaction rates are measured by the foil activation method to obtain neutron spectrum information on ADS. Numerical calculations are performed with MCNP6.1 and JENDL/HE-2007 for high-energy protons and spallation process, JENDL-4.0 for transport and JENDL/D-99 for reaction rates. The reaction rates depend on subcriticality is revealed by the accuracy of the C/E (calculation/experiment) values. Nonetheless, the accuracy of the reaction rates at high-energy thresholds remains an important issue in the fixed-source calculations.
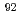 Zr and a large
Zr and a large 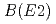 value between the
value between the 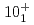 and
and 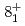 states
statesSugawara, Masahiko*; Toh, Yosuke; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Oshima, Masumi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kin, Tadahiro*; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Kusakari, Hideshige*
Physical Review C, 96(2), p.024314_1 - 024314_7, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.26(Physics, Nuclear)Pyeon, C. H.*; Fujimoto, Atsushi*; Sugawara, Takanori; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nishihara, Kenji; Takahashi, Yoshiyuki*; Nakajima, Ken*; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 185(3), p.460 - 472, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:67.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sensitivity and uncertainty analyses of lead (Pb) isotope cross sections are conducted with the use of sample reactivity experiments at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). With the combined use of the SRAC2006 and MARBLE code systems, attempts are made to precisely examine the contributions of the reactions and energy regions of Pb isotope cross sections to reactivity based on the covariance data of JENDL-4.0. Moreover, the effect of decreasing uncertainty is discussed in terms of the accuracy of sample reactivity by applying the cross section adjustment method to the uncertainty analyses. From the results of the sensitivity and uncertainty analyses, the reliability of Pb isotope cross sections, such as the Pb isotope covariance data of JENDL-4.0, is compared with the JENDL-3.3, ENDF/B-VII.0, and JEFF-3.1 libraries.