Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Takasaki, Koji; Yasumune, Takashi; Onishi, Takashi; Nakamura, Keisuke; Ishimi, Akihiro; Ito, Chikara; Osaka, Masahiko; Ono, Masashi*; Hatakeyama, Shuichi*; Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2013-043, 33 Pages, 2014/01
In the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, it is assumed that the core fuels melted partially or wholly, and the normal technique of accounting for a fuel assembly is not applicable. Therefore, it is necessary to develop the transparent and rational technique of accounting in the process of collection and storage of fuel debris. In this research, an application of the superconducting phase Transition Edge Sensor microcalorimeter (TES microcalorimeter) is studied for the accounting of nuclear materials in the fuel debris. It is expected that the detailed information of nuclear materials and fission products in fuel debris is obtained by using a high-resolution characteristic of TES microcalorimeter. In this report, the principle of TES microcalorimeter, the measurement experiment using TES in JAEA, and the simulated calculation using the EGS5 code system are summarized.
Sugita, Akihiro; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yamada, Hidetaka; Inoue, Norihiro*; Aoyama, Makoto; Yamakawa, Koichi
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 46(1), p.226 - 228, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.00(Physics, Applied)Generation of broadband mid-infrared (MIR) laser pulses by difference frequency mixing (DFM) is reported. Two-color femtosecond pulses from a Ti: Sapphire laser system is mixed in an AgGaS crystal utilizing a noncollinear phase matching scheme. The relative bandwidth of the generated MIR pulse has been measured to be 23 % to the central frequency, the broadest in DFM-based MIR sources reported so far. It is found that the type-I crystal can give broader phase matching range of spectrum than the type-II crystal within this scheme.
crystal utilizing a noncollinear phase matching scheme. The relative bandwidth of the generated MIR pulse has been measured to be 23 % to the central frequency, the broadest in DFM-based MIR sources reported so far. It is found that the type-I crystal can give broader phase matching range of spectrum than the type-II crystal within this scheme.

 ) and Cs(7
) and Cs(7
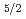 ) by femtosecond laser pulses
) by femtosecond laser pulsesYamada, Hidetaka; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Teranishi, Yoshiaki*; Sugita, Akihiro; Shirai, Toshizo*; Aoyama, Makoto; Akahane, Yutaka; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki*; Yamakawa, Koichi; et al.
Physical Review A, 72(6), p.063404_1 - 063404_5, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:31.16(Optics)A demonstration of coherent quantum control for ultrafast precise selection of closely-lying states is reported. A phase-locked pair of femtosecond laser pulses is generated through a pulse shaper to excite the ground-state cesium atom to the Cs(7
 ) and Cs(7
) and Cs(7
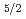 ) states by two-photon absorption. The excited state population is measured by detecting fluorescence from each spin-orbit state. By controlling the phase-difference of the pulse pair, an ultrafast precise selection is accomplished. The contrast ratio of the maximal to minimal selection ratio exceeds 10
) states by two-photon absorption. The excited state population is measured by detecting fluorescence from each spin-orbit state. By controlling the phase-difference of the pulse pair, an ultrafast precise selection is accomplished. The contrast ratio of the maximal to minimal selection ratio exceeds 10 with the delay less than 400 fs.
with the delay less than 400 fs.
Yokoyama, Keiichi; Teranishi, Yoshiaki; Toya, Yukio; Shirai, Toshizo; Fukuda, Yuji; Aoyama, Makoto; Akahane, Yutaka; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki; Yamakawa, Koichi; et al.
Journal of Chemical Physics, 120(20), p.9446 - 9449, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:18.69(Chemistry, Physical)Optimal laser control for ultrafast selection of closely-lying excited states, whose energy separation is smaller than the laser bandwidth, is reported on the two-photon transition of atomic cesium; Cs(6S  7D
7D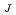 , J = 5/2 and 3/2). Selective excitation was carried out by pulse shaping of ultrashort laser pulses which were adaptively modulated in a closed-loop learning system handling eight parameters representing the electric field. Two-color fluorescence from the respective excited states was monitored to measure the selectivity. The fitness used in the learning algorithm was evaluated from the ratio of the fluorescence yield. After fifty generations, a pair of nearly transform-limitted pulses were obtained as an optimal pulse shape, proving the effectiveness of "Ramsey fringes" mechanism. The contrast of the selection ratio was improved by
, J = 5/2 and 3/2). Selective excitation was carried out by pulse shaping of ultrashort laser pulses which were adaptively modulated in a closed-loop learning system handling eight parameters representing the electric field. Two-color fluorescence from the respective excited states was monitored to measure the selectivity. The fitness used in the learning algorithm was evaluated from the ratio of the fluorescence yield. After fifty generations, a pair of nearly transform-limitted pulses were obtained as an optimal pulse shape, proving the effectiveness of "Ramsey fringes" mechanism. The contrast of the selection ratio was improved by  30 % from the simple "Ramsey fringes" experiment.
30 % from the simple "Ramsey fringes" experiment.
Suzuki, Tadakazu*; Sugita, Takeshi*; Kinase, Sakae; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Kitamura, Akihiro
no journal, ,
An optimization analysis sequence OPAS was developed and applied to prediction models for radioactive cesium distribution. The method and results will be presented.
Torii, Tatsuo; Okuyama, Shinichi; Ishizuka, Akihiro; Nozaki, Tatsuo; Nawa, Yasunori*; Sugita, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
 ray dose-rate increases associated with winter thunderstorm activities have been observed at the coastal area of the Sea of Japan. The features are clarified from the measured data obtained by environmental radiation monitors. In order to investigate the generation of energetic radiation which originates in thunderstorm electric fields, we have calculated the behavior of secondary cosmic rays (electromagnetic component; muon) in electric fields with Monte Carlo method. In the calculation, the electron and photon fluxes have increased greatly in the region where the field strength exceeds about 280 P(z) kV/m-atm, where P(z) is the atmospheric pressure (atm) at altitude z (m),.and these energy spectra show a large increase in the energy region up to a few tens of MeV. We have also carried out the Monte Carlo calculations of the beta and
ray dose-rate increases associated with winter thunderstorm activities have been observed at the coastal area of the Sea of Japan. The features are clarified from the measured data obtained by environmental radiation monitors. In order to investigate the generation of energetic radiation which originates in thunderstorm electric fields, we have calculated the behavior of secondary cosmic rays (electromagnetic component; muon) in electric fields with Monte Carlo method. In the calculation, the electron and photon fluxes have increased greatly in the region where the field strength exceeds about 280 P(z) kV/m-atm, where P(z) is the atmospheric pressure (atm) at altitude z (m),.and these energy spectra show a large increase in the energy region up to a few tens of MeV. We have also carried out the Monte Carlo calculations of the beta and  rays emitted by radon progenies in thunderstorm electric fields. By the calculation for the radon progeny, the electron flux shows notable increases in the strong electric field region, while the photon flux does not fluctuate significantly. As well as the secondary cosmic rays, the radon progeny products form a large part of the energetic charged particles in the atmosphere. Therefore, they can serve as the source of a considerable amount of runaway electrons, through their ionization process with air molecules. These results indicate that the production of energetic electrons plays an important role in the intensive ionization of the air, and as a result a significant growth of electric conductivity in thunderstorm electric fields. These productions may also induce the lightning discharge by these processes.
rays emitted by radon progenies in thunderstorm electric fields. By the calculation for the radon progeny, the electron flux shows notable increases in the strong electric field region, while the photon flux does not fluctuate significantly. As well as the secondary cosmic rays, the radon progeny products form a large part of the energetic charged particles in the atmosphere. Therefore, they can serve as the source of a considerable amount of runaway electrons, through their ionization process with air molecules. These results indicate that the production of energetic electrons plays an important role in the intensive ionization of the air, and as a result a significant growth of electric conductivity in thunderstorm electric fields. These productions may also induce the lightning discharge by these processes.
Ishizuka, Akihiro; Nozaki, Tatsuo; Kokubun, Yuji; Okubo, Koichi; Torii, Tatsuo; Takata, Takushi*; Kume, Kyo*; Hasegawa, Takashi*; Sugita, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
The assessment methods of types and distributions of a radioactivity unexpectedly released to atmosphere from nuclear power plants have been studied with a help of examination of data measured by  -ray detectors at several radiation monitoring equipments. The principle was verified with a
-ray detectors at several radiation monitoring equipments. The principle was verified with a  -ray source in room, and an existing nuclear power station was simulated as an application example.
-ray source in room, and an existing nuclear power station was simulated as an application example.
Sugita, Akihiro; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Itakura, Ryuji; Yamada, Hidetaka
no journal, ,
Selective excitation to the closely lying state of potassiium atoms were examined as a fundamental research of a new laser-isotope-separation technique. Using time-resolved photon counting to measure the fluorescence intensity, the scatterd light from the pump beam and the fluorescence of interest were perfectly distinguished. Owing to this experimental setup, a high contrast more than 1000 was obtained for the selectivity. In addition, the excitation behavior when the laser intensity increased was recorded through the laser power dependence of the fluorescence intensity. As a result, it is found that the destructive interference between two excited states becomes incomplete with increasing laser power. Moreover, the relative population of the two states exhibit the power dependence expected by a computer simulation, indicating that the laser power required for the selective complete excitation is achieved.
Yokoyama, Keiichi; Sugita, Akihiro; Teranishi, Yoshiaki*; Itakura, Ryuji; Matsuoka, Leo; Yokoyama, Atsushi
no journal, ,
State-selective excitation of atomic cesium and potassium to their spin-orbit states, Cs(7D-6S) and K(4P-4S), are carried out by a coherent quantum control technique. In the weak field regime, ultrafast and highly selective excitation of cesium atoms has been successfully demonstrated with a pair of identical transform-limited pulses in which the control parameter is the phase difference between the two pulses alone. However, the excitation probability is very small (0.001) due to the weak laser field. To perform the selective excitation with large excitation probability (1), one-photon process of the K(4P-4S) transition is examined. The excitation probability is expected to become large while the selectivity degrades if the control parameter is the phase difference alone. The obtained laser intensity dependence agrees well with the theoretical prediction, indicating the excitation indeed in the non-perturbative regime.