Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kumada, Takayuki; Iwahara, Daisuke*; Nishitsuji, Shotaro*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Daisuke; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Torikai, Naoya*; Amino, Naoya*; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 128(21), p.8797 - 8802, 2024/05
We elucidated the entanglement of polybutadiene and silane coupling agent (SCA) molecules bound to Si substrates using spin-contrast-variation (SCV) neutron reflectivity (NR). In an annealed integral blend film of polybutadiene and SCA, a SCA layer generated on the Si substrate was composed of 70 vol. percent SCA molecules extended perpendicularly from the silicon substrate and entangled with 30 vol. percent polybutadiene molecules. By contrast, in an SCA-precoated polybutadiene film, the SCA-precoated layer is composed of densely packed SCA molecules forming crystal-like structure, and thus did not become entangled with the postcoated polybutadiene molecules. This poor entanglement resulted in poor binding between polybutadiene and Si substrate.
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Nagakawa, Yoshiyasu*; Shibayama, Yuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Ikeda-Fukazawa, Tomoko*
Nanoscale, 16(19), p.9400 - 9405, 2024/05
A tough carboxymethyl cellulose nanofiber (CMF)/ zirconium (Zr) hydrogel was obtained by freeze cross-linking method. The hydrogel was prepared by adding HCl solution containing Zr to frozen CMF and thawing it. The hydrogel showed high adsorptivity for fluoride. This simple gelation method provides useful insight for developing hydrogel-metal complexes.
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Hiroi, Kosuke; Oba, Yojiro*; Nagakawa, Yoshiyasu*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Shibayama, Yuki; Ikeda-Fukazawa, Tomoko*
Carbohydrate Polymers, 327, p.121538_1 - 121538_11, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Applied)We describe non-toxic, tough nanocellulose (NC) hydrogels formed from chemically unmodified NC by cellulose crystalline transformation and subsequent freeze cross-linking reaction. Using low-concentration NaOH and freezing together induced the crystalline transformation of NC from cellulose I to II via freeze concentration. After the crystalline transformation, cross-linking between the NC and CA in the freeze concentration layer (FCL) provided a strong NC network structure, forming NC hydrogels with high mechanical strength. The freeze-cross-linked NC hydrogel easily retained powder adsorbents in its inner space by mixing the NC-NaOH sol and the powder, and the hydrogel showed high removal efficiency for heavy metals. The results highlight the versatility of chemically unmodified celluloses in developing functional materials, suggest possible practical applications.
Hagihara, Koji*; Mayama, Tsuyoshi*; Yamasaki, Michiaki*; Harjo, S.; Tokunaga, Toko*; Yamamoto, Kazuki*; Sugita, Mika*; Aoyama, Kairi*; Gong, W.; Nishimoto, Soya*
International Journal of Plasticity, 173, p.103865_1 - 103865_21, 2024/02
Kumada, Takayuki; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Oba, Yojiro; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Sekine, Yurina; Micheau, C.; Ueda, Yuki; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sasaki, Miki; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(6), p.1776 - 1783, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:56.32(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The combination of the existing position-sensitive photomultiplier and the  He main detector with focusing devices, and the newly installed front detectors in SANS-J at JRR-3 covers small-angle neutron scattering signals in the range of the magnitude of the scattering vector Q from 0.002 to 6 nm-1 gaplessly with three standard device layouts. The installation of the front detector and a graphical user interface system largely improved the usability of SANS-J.
He main detector with focusing devices, and the newly installed front detectors in SANS-J at JRR-3 covers small-angle neutron scattering signals in the range of the magnitude of the scattering vector Q from 0.002 to 6 nm-1 gaplessly with three standard device layouts. The installation of the front detector and a graphical user interface system largely improved the usability of SANS-J.
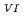 reduction and salicylic acid decomposition
reduction and salicylic acid decompositionSugita, Tsuyoshi; Mori, Masanobu*; Shimoyama, Iwao
Applied Clay Science, 243, p.107074_1 - 107074_8, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Chemistry, Physical)We have investigated the conversion of biotite, a subgroup of clay minerals, into photocatalysts by heat treatment with CaCl . The reaction products obtained after heat treatment were examined in terms of composition, structure, and photocatalytic activity against Cr
. The reaction products obtained after heat treatment were examined in terms of composition, structure, and photocatalytic activity against Cr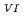 and salicylic acid (SA). When mixtures of biotite and CaCl
and salicylic acid (SA). When mixtures of biotite and CaCl were heated at temperatures up to 600
were heated at temperatures up to 600 C, the biotite crystal structure was retained, whereas a phase transformation from biotite to octahedral wadalite crystals occurred upon heating to 700
C, the biotite crystal structure was retained, whereas a phase transformation from biotite to octahedral wadalite crystals occurred upon heating to 700 C. The photocatalytic reduction rate of Cr
C. The photocatalytic reduction rate of Cr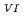 per unit surface area and the photocatalytic degradation efficiency of SA increased significantly with increasing treatment temperature. Even the samples that retained the biotite structure after heat treatment displayed some photocatalytic activity, suggesting that this method may also be suitable for preparing photocatalysts from other common natural materials.
per unit surface area and the photocatalytic degradation efficiency of SA increased significantly with increasing treatment temperature. Even the samples that retained the biotite structure after heat treatment displayed some photocatalytic activity, suggesting that this method may also be suitable for preparing photocatalysts from other common natural materials.
Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Mori, Masanobu*; Kozai, Naofumi
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A; Chemistry, 438, p.114548_1 - 114548_6, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:34.89(Chemistry, Physical)Removal of iodine from water contaminated by nuclear accidents or the release of radioactive waste is complicated and costly because iodine exists in a variety of forms in the water. We investigated the unification of iodine species by photocatalysis as a pretreatment for removing radioactive iodine species from water. The effect of the TiO crystal phase of Pt-TiO
crystal phase of Pt-TiO and solution pH on the photocatalytic redox reactions of iodide (I
and solution pH on the photocatalytic redox reactions of iodide (I ), iodate (IO
), iodate (IO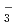 ), and
), and 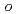 -iodobenzoic acid were evaluated. The choice of TiO
-iodobenzoic acid were evaluated. The choice of TiO crystalline phase and pH allowed the mixture of iodine species to be unified to only I
crystalline phase and pH allowed the mixture of iodine species to be unified to only I or IO
or IO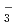 . Regardless of the type of Pt-TiO
. Regardless of the type of Pt-TiO , the iodine in o-iodobenzoic acid was mineralized to I
, the iodine in o-iodobenzoic acid was mineralized to I under alkaline conditions. Because the iodine species can be unified to a single species by selecting the photocatalyst and the solution pH, this photocatalytic treatment could be applied to remove iodine species with high efficiency.
under alkaline conditions. Because the iodine species can be unified to a single species by selecting the photocatalyst and the solution pH, this photocatalytic treatment could be applied to remove iodine species with high efficiency.
Miura, Daisuke*; Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Oba, Yojiro; Hiroi, Kosuke; Ozawa, Tatsuhiko
Carbohydrate Polymer Technologies and Applications (Internet), 4, p.100251_1 - 100251_9, 2022/12
The reaction mechanism of carboxymethyl cellulose nanofiber (CMCF) hydrogel formed by freeze-crosslinking was investigated. We succeeded in observing the hierarchical structural changes during the freeze-crosslinking reaction. Freeze-crosslinked CMCF hydrogels exhibited a characteristic hierarchical alignment structure from the angstrom to micrometer scale that differed from normal cross-linked CMCF hydrogels produced by a conventional method without freezing. It was shown that the characteristic hierarchical structure contributes the excellent mechanical properties of freeze-crosslinked CMCF hydrogels.
Ueda, Yuki; Eguchi, Ayano; Tokunaga, Kohei; Kikuchi, Kei*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Okamura, Hiroyuki; Naganawa, Hirochika
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 61(19), p.6640 - 6649, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.70(Engineering, Chemical)no abstracts in English
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Yamada, Teppei*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nemoto, Yoshihiro*; Takeguchi, Masaki*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Shimoyama, Iwao; Kozai, Naofumi; Morooka, Satoshi
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(2), p.105114_1 - 105114_12, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:50.83(Engineering, Environmental)Remediating toxic ion contamination is crucial for protecting human health and the environment. This study aimed to provide a powerful strategy for effectively utilizing bone waste from the food production and preparation industries for removal of toxic ions. Here, we show that immersing pig bone in NaHCO solution produced a carbonated nanohydroxyapatites (C-NHAP). The C-NHAP exhibited high adsorptivity for Sr
solution produced a carbonated nanohydroxyapatites (C-NHAP). The C-NHAP exhibited high adsorptivity for Sr , Cd
, Cd , Pb
, Pb , and Cu
, and Cu . The strontium adsorptivity was about 250 and 4,500 times higher than that of normal bone and synthetic HAP, respectively. The C-NHAP is an eco-friendly, high-performance material that is simple to prepare and should be useful for tackling problems of food waste disposal and environmental pollution.
. The strontium adsorptivity was about 250 and 4,500 times higher than that of normal bone and synthetic HAP, respectively. The C-NHAP is an eco-friendly, high-performance material that is simple to prepare and should be useful for tackling problems of food waste disposal and environmental pollution.
 from nitrate media; Comparison with a conventional organic phosphate
from nitrate media; Comparison with a conventional organic phosphateUeda, Yuki; Kikuchi, Kei*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Aoyagi, Noboru; Tanaka, Kazuya; Okamura, Hiroyuki
Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 39(5-6), p.491 - 511, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Yunoki, Shunji*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Yamada, Teppei*
ACS Applied Polymer Materials (Internet), 2(12), p.5482 - 5491, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:88.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We developed a cross-linking method using freeze concentration and used it to synthesize a new type of carboxymethyl cellulose nanofiber (CMCF) hydrogel with high compressive strength ( 80 MPa) and high compressive recoverability. The hydrogels were prepared by adding an aqueous solution of citric acid (CA) to a frozen CMCF sol and then thawing the sol. The reaction between the freeze-concentrated CMCF and CA created a rigid porous structure that reflected the ice crystal structure. Their cross-linked structure has a high stability to compressive stress. Bentonite was immobilized on a CMCF hydrogel by adding bentonite to the CMCF sol before freeze cross-linking. The CMCF-bentonite hydrogel showed high adsorptivity for chemical dyes. The physically cross-linked CMCF hydrogels are non-toxic, metal-free, and simple to prepare, and thus they may be useful as sustainable materials in various fields.
80 MPa) and high compressive recoverability. The hydrogels were prepared by adding an aqueous solution of citric acid (CA) to a frozen CMCF sol and then thawing the sol. The reaction between the freeze-concentrated CMCF and CA created a rigid porous structure that reflected the ice crystal structure. Their cross-linked structure has a high stability to compressive stress. Bentonite was immobilized on a CMCF hydrogel by adding bentonite to the CMCF sol before freeze cross-linking. The CMCF-bentonite hydrogel showed high adsorptivity for chemical dyes. The physically cross-linked CMCF hydrogels are non-toxic, metal-free, and simple to prepare, and thus they may be useful as sustainable materials in various fields.
Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Kobayashi, Kentaro*; Yamazaki, Taiki*; Isaka, Mayu*; Itabashi, Hideyuki*; Mori, Masanobu*
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A; Chemistry, 400, p.112662_1 - 112662_8, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:2.37(Chemistry, Physical)In this study, we developed an in-line photocatalytic performance evaluation system in which a flow reactor was connected to the ion chromatography to accurately evaluate the performance of the photocatalyst. This system was used to evaluate the photocatalyst supported by the two-layer support method on the substrate, such as glass beads. The performance of the photocatalyst was evaluated using dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), and it was possible to monitor the decomposition of DMSO by UV and the formation of by-products, such as methane sulfonate (MSO) and sulfate (SA). This system can be expected to be useful not only for evaluating the decomposition performance of an object using a photocatalyst but also for evaluating the byproducts.
 solution; Comparison with tri-
solution; Comparison with tri- -butyl phosphate
-butyl phosphateUeda, Yuki; Kikuchi, Kei; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Motokawa, Ryuhei
Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 37(5), p.347 - 359, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:33.25(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We have newly-designed fluorous phosphate(TFP) for the effective Zr(IV) ion extractant as an alternative extractant against the conventional organic phosphate, tri- -butyl phosphate(TBP). Zr(IV) ion extraction system using the TBP has many problems such as the formation of the third phase during liquid-liquid extraction. Here, we develop the fluorous extraction system based on the TFP-perfluorohexane for the Zr(IV) ion extraction to improve the Zr(IV) ion extraction system with an effective extractability and without the third phase formation. Our main findings were that the significant high extraction performance of the TFP for Zr(IV) ion as compared with TBP, and the origins of the high extraction performance of the TFP are related to the water and HNO
-butyl phosphate(TBP). Zr(IV) ion extraction system using the TBP has many problems such as the formation of the third phase during liquid-liquid extraction. Here, we develop the fluorous extraction system based on the TFP-perfluorohexane for the Zr(IV) ion extraction to improve the Zr(IV) ion extraction system with an effective extractability and without the third phase formation. Our main findings were that the significant high extraction performance of the TFP for Zr(IV) ion as compared with TBP, and the origins of the high extraction performance of the TFP are related to the water and HNO contents in the fluorous phase and the stability of the complex, Zr(No
contents in the fluorous phase and the stability of the complex, Zr(No )
) (TFP)
(TFP) .
.
 -coated wire mesh prepared via a double-layer coating method
-coated wire mesh prepared via a double-layer coating methodMori, Masanobu*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Fujii, Kengo*; Yamazaki, Taiki*; Isaka, Mayu*; Kobayashi, Kentaro*; Iwamoto, Shinji*; Itabashi, Hideyuki*
Analytical Sciences, 34(12), p.1449 - 1453, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.93(Chemistry, Analytical)The photocatalyst coating stainless-steel wire mesh (TiO -WM) was prepared by double-layer coating method. The TiO
-WM) was prepared by double-layer coating method. The TiO -WM was evaluated using flow analytical system, which included the reactor and conductimetric detector (FAS-CD). The DMSO decomposition test through the FAS-CD reveal that photocatalytst was stable coating on the stainless-steel wire mesh.
-WM was evaluated using flow analytical system, which included the reactor and conductimetric detector (FAS-CD). The DMSO decomposition test through the FAS-CD reveal that photocatalytst was stable coating on the stainless-steel wire mesh.
Atanassova, M.*; Okamura, Hiroyuki; Eguchi, Ayano; Ueda, Yuki; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Shimojo, Kojiro
Analytical Sciences, 34(8), p.973 - 978, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:58.64(Chemistry, Analytical)The distribution constants of 4-benzoyl-3-phenyl-5-isoxazolone (HPBI) and deprotonated one (PBI ) between hydrophobic ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([C
) between hydrophobic ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([C C
C im][Tf
im][Tf N]) and aqueous phases were determined, together with the acid-dissociation constant of HPBI. The solvent extraction of three selected lanthanoid ions (La
N]) and aqueous phases were determined, together with the acid-dissociation constant of HPBI. The solvent extraction of three selected lanthanoid ions (La , Eu
, Eu , and Lu
, and Lu ) with HPBI from aqueous nitrate phase into [C
) with HPBI from aqueous nitrate phase into [C C
C im][Tf
im][Tf N] has been investigated. Application of the ionic liquid as the extracting phase greatly enhanced the extraction performance of HPBI for lanthanoid ions compared with that in the chloroform system. The composition of the extracted species was established to be anionic tetrakis entities, Ln(PBI)
N] has been investigated. Application of the ionic liquid as the extracting phase greatly enhanced the extraction performance of HPBI for lanthanoid ions compared with that in the chloroform system. The composition of the extracted species was established to be anionic tetrakis entities, Ln(PBI)
 , for light, middle, and heavy lanthanoid ions in an ionic environment.
, for light, middle, and heavy lanthanoid ions in an ionic environment.
 quantitative analysis of sweat chemistry
quantitative analysis of sweat chemistrySekine, Yurina; Kim, S. B.*; Zhang, Y.*; Bandodkar, A. J.*; Xu, S.*; Choi, J.*; Irie, Masahiro*; Ray, T. R.*; Kohli, P.*; Kozai, Naofumi; et al.
Lab on a Chip, 18(15), p.2178 - 2186, 2018/08
The rich composition of solutes and metabolites in sweat and its relative ease of collection upon excretion from skin pores make this class of biofluid an attractive candidate for point of care analysis. Here, we present a complementary approach that exploits fluorometric sensing modalities integrated into a soft, skin-interfaced microfluidic system which, when paired with a simple smartphone-based imaging module, allows for in-situ measurement of important biomarkers in sweat. A network array of microchannels and a collection of microreservoirs pre-filled with fluorescent probes that selectively react with target analytes in sweat (e.g. probes), enable quantitative, rapid analysis. Field studies on human subjects demonstrate the ability to measure the concentrations of chloride, sodium and zinc in sweat, with accuracy that matches that of conventional laboratory techniques.
 as anionic adsorptive photocatalyst
as anionic adsorptive photocatalystSugita, Tsuyoshi; Kobayashi, Kenichi*; Kobayashi, Kentaro*; Yamazaki, Taiki*; Fujii, Kengo*; Itabashi, Hideyuki*; Mori, Masanobu*
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A; Chemistry, 356, p.71 - 80, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:12.91(Chemistry, Physical)Photocatalysts shows high redox property only by light irradiation. However, the reaction performance is lowered in aqueous phase due to the low contact efficiency between catalyst and targets. In this study, to enhance aqueous adsorption and photodecomposition of anionic organic target, we developed an amino functional-based spacer (3-[2-(2- aminoethylamino)ethylamino]propyl-trimethoxysilane, DETA), and used it to modify TiO . The modified catalyst with positively charged amino groups could enhance the adsorption and photodecomposition of anionic organic targets.
. The modified catalyst with positively charged amino groups could enhance the adsorption and photodecomposition of anionic organic targets.
Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Fujiwara, Iori*; Okamura, Hiroyuki; Oshima, Tatsuya*; Baba, Yoshinari*; Naganawa, Hirochika; Shimojo, Kojiro
Solvent Extraction Research and Development, Japan, 24(2), p.61 - 69, 2017/05
We investigated an influence of amide group in diglycolamic acid-type extractants on extraction property of metal ions. The extraction characteristics of  -dodecyldiglycolamic acid (C
-dodecyldiglycolamic acid (C DGAA), with a secondary amide group, for 56 metal ions have been investigated, and compared with those of
DGAA), with a secondary amide group, for 56 metal ions have been investigated, and compared with those of 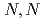 -dioctyldiglycolamic acid (DODGAA) with a tertiary amide group. Compared with DODGAA, C
-dioctyldiglycolamic acid (DODGAA) with a tertiary amide group. Compared with DODGAA, C DGAA has a poor extraction performance and separation ability for rare-earth metal ions, except for Sc(III). However, C
DGAA has a poor extraction performance and separation ability for rare-earth metal ions, except for Sc(III). However, C DGAA tended to provide better extraction for relatively small-sized metal ions than DODGAA. In addition, it was found that C
DGAA tended to provide better extraction for relatively small-sized metal ions than DODGAA. In addition, it was found that C DGAA enables the selective removal of Hg(II) from aqueous solutions containing various divalent metal ions.
DGAA enables the selective removal of Hg(II) from aqueous solutions containing various divalent metal ions.
Sugita, Tsuyoshi
Journal of Flow Injection Analysis, 33(1), p.39 - 40, 2016/06
A novel solvent extraction way, emulsion flow (EF) method, has been developed at JAEA. EF method achieves both good emulsion formation and quick phase separation only by solution sending. In this report, I referred Flow Injection Analysis (FIA) using solvent extraction as a preprocessing technique and introduced an outline of the EF method as such. Furthermore, I mentioned the application possibility of the EF method to the preprocessing in FIA with its advantage for extracting and concentrating a trace component from a large-volume sample.