Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oishi, Kazuki*; Igarashi, Daisuke*; Tatara, Ryoichi*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Suzuki, Junichi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nishimura, Shoichiro*; Koda, Akihiro*; Komaba, Shinichi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2462, p.012048_1 - 012048_5, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Nanjo, Kotaro; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Pellegrini, M.*; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1407 - 1416, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:73.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yamashita, Keishiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Klotz, S.*; Fabelo, O.*; Fern ndez-D
ndez-D az, M. T.*; Abe, Jun*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Shimmei, Toru*; et al.
az, M. T.*; Abe, Jun*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Shimmei, Toru*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(40), p.e2208717119_1 - e2208717119_6, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:36.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Here we present the first elucidation of the disordered structure of ice VII, the dominant high-pressure form of water, at 2.2 GPa and 298 K from both single-crystal and powder neutron diffraction techniques. We reveal the three-dimensional atomic distributions from the maximum entropy method and unexpectedly find a ring-like distribution of hydrogen in contrast to the commonly-accepted discrete sites. In addition, total scattering analysis at 274 K clarified the difference in the intermolecular structure from ice VIII, the ordered counterpart of ice VII, despite an identical molecular geometry. Our complementary structure analyses robustly demonstrate the unique disordered structure of ice VII. Furthermore, these noble findings are related to the proton dynamics which drastically vary with pressure, and will contribute to an understanding of the structural origin of anomalous physical properties of ice VII under pressures.
Komatsu, Yuya*; Shimizu, Ryota*; Sato, Ryuhei*; Wilde, M.*; Nishio, Kazunori*; Katase, Takayoshi*; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Miyauchi, Masahiro*; Adelman, J. R.*; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 34(8), p.3616 - 3623, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:75.48(Chemistry, Physical) studied with high-pressure
studied with high-pressure  SR
SRSugiyama, Jun; Higemoto, Wataru; Andreica, D.*; Forslund, O. K.*; Nocerino, E.*; M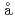 nsson, M.*; Sassa, Y.*; Gupta, R.*; Khasanov, R.*; Ota, Hiroto*; et al.
nsson, M.*; Sassa, Y.*; Gupta, R.*; Khasanov, R.*; Ota, Hiroto*; et al.
Physical Review B, 103(10), p.104418_1 - 104418_10, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:50.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The magnetic nature of a quasi-one-dimensional compound, BaVSe , has been investigated with positive muon spin rotation and relaxation measurements at ambient and high pressures. At ambient pressure, the spectrum recorded under zero external magnetic field exhibited a clear oscillation below the Curie temperature due to the formation of quasistatic ferromagnetic order. As pressure increased from ambient pressure,
, has been investigated with positive muon spin rotation and relaxation measurements at ambient and high pressures. At ambient pressure, the spectrum recorded under zero external magnetic field exhibited a clear oscillation below the Curie temperature due to the formation of quasistatic ferromagnetic order. As pressure increased from ambient pressure, 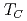 was found to decrease slightly up to about 1.5 GPa, at which point
was found to decrease slightly up to about 1.5 GPa, at which point 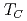 started to increase rapidly with the further increase of the pressure. Based on a strong ferromagnetic interaction along the
started to increase rapidly with the further increase of the pressure. Based on a strong ferromagnetic interaction along the  -axis, the result revealed that there are two magnetic interactions in the ab-plane.
-axis, the result revealed that there are two magnetic interactions in the ab-plane.
Kubo, Kotaro; Zheng, X.; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2020 (ASRAM 2020) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2020/11
Dynamic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) enables a more realistic and detailed analysis than classical PRA. However, the trade-off for these improvements is the enormous computational cost associated with performing a large number of thermal-hydraulic (TH) analyses. In this study, based on machine learning (ML), we aim to reduce these costs by skipping the TH analysis. For the ML algorithm, we selected a support vector machine; we built it using a high-fidelity/high-cost detailed model and low-fidelity/low-cost simplified model. As a result, the computational costs could be reduced by approximately 80% without significantly decreasing the accuracy under the assumed conditions.
 Li
Li in rutile TiO
in rutile TiO
Chatzichristos, A.*; Sugiyama, Jun; 12 of others*
Physical Review Letters, 123(9), p.095901_1 - 095901_5, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.53(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report measurements of the diffusion rate of isolated ion-implanted  Li
Li within 120 nm of the surface of oriented single-crystal rutile TiO
within 120 nm of the surface of oriented single-crystal rutile TiO using a radiotracer technique. The
using a radiotracer technique. The  particles from the
particles from the  Li
Li decay provide a sensitive monitor of the distance from the surface and how the depth profile of Li evolves with time. The main findings are that the implanted Li diffuses and traps at the (001) surface. The
decay provide a sensitive monitor of the distance from the surface and how the depth profile of Li evolves with time. The main findings are that the implanted Li diffuses and traps at the (001) surface. The  dependence of the diffusivity is described by a bi-Arrhenius expression above 200 K, whereas at lower temperatures it has a much smaller barrier. We consider possible origins for the surface trapping, as well the nature of the low-
dependence of the diffusivity is described by a bi-Arrhenius expression above 200 K, whereas at lower temperatures it has a much smaller barrier. We consider possible origins for the surface trapping, as well the nature of the low- barrier.
barrier.
Tamaki, Hitoshi; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.100 - 111, 2019/08
JAEA participated in the OECD/NEA BSAF2 project with our integrated severe accident analysis code, THALES2/KICHE, in order to analyze and discuss the accident progression and source term of the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi NPS. One of important characteristics of THALES2/KICHE code is that it has the capability of predicting iodine chemistry based on reaction kinetics in the aqueous phase. JAEA performed the three week analysis for the accident at unit 2 on the basis of the boundary conditions and assumptions proposed by the BSAF2 project and our own assumptions. One of focusing points in the BSAF2 project was the trend of measured data of reactor vessel from 20:00 March 14 to 02:00 March 15. An assumption was made that the lower part of the suppression chamber failed to form a water leakage path. The released iodine and cesium within three weeks after the earthquake were predicted to be approximately 3% and 0.1% of the initial inventory, respectively.
Tamaki, Hitoshi; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.72 - 82, 2019/08
JAEA participated in the OECD/NEA BSAF2 project with our integrated severe accident analysis code, THALES2/KICHE, in order to analyze and discuss the accident progression and source term of the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi NPS. One of important characteristics of THALES2/KICHE code is that it has the capability of predicting iodine chemistry based on reaction kinetics in the aqueous phase. JAEA performed the three week analysis for the accident at unit 1 on the basis of the boundary conditions and assumptions proposed by the BSAF2 project and our own assumptions. In addition to the failure of the drywell, it was assumed in the present analysis that continuous leakage occurred through the containment venting line due to incomplete closing of valves in the line. The releases of fission products, especially for iodine and cesium, within three weeks after the earthquake were estimated to be approximately 6% and 1% of the initial inventory, respectively.
Ishikawa, Jun; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.536 - 547, 2019/08
Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Ito, Hiroto*; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 11th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-11) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2018/11
Tamaki, Hitoshi; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2018 (ASRAM 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2018/10
In the accidents at Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station, Tsunami caused loss of electric power supply and this event led to core melt and failure of Containment vessel. Finally, fission products were released to the environment. Currently, the activities for understanding of accident progressions are carried out based on the measured data during the accident, accident progression analysis using integrated severe accident analysis codes and investigation of inside of reactor buildings and containment vessels. On the other hand, there are some research activities with combination of accident progression analysis and accident consequence analysis. In Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), the research project of combination of these analyses using the computational simulation codes has been started. The results obtained from the combination analysis are expected to have broad width of uncertainty because of many uncertainty factors in this combined analysis. In order to perform the analysis efficiently, sensitivity analysis for failure location on containment vessel and its failure size were carried out by THALES2/KICHE developed by JAEA at first. This analysis was performed on unit 1, since it was the first plant to release radioactive materials to the environment during the accident and its consequence had no effect from other plants. The authors focused on the failure of containment vessel head flange, penetration seal and vacuum breaker pipe, and possibility of partial open of vent valve based on the investigations of reactor building inside performed by TEPCO. This paper presents the results obtained from this sensitivity analysis.
Ishikawa, Jun; Zheng, X.; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2018 (ASRAM 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2018/10
Zheng, X.; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management (PSAM-14) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2018/09
Sugiyama, Jun*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Nozaki, Hiroshi*; Higemoto, Wataru; Hamada, Koji*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Koda, Akihiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Kubo, Kenya*
Physical Review Letters, 121(8), p.087202_1 - 087202_5, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:71.69(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(4), p.363 - 373, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:46.08(Nuclear Science & Technology) C/steel interaction and oxidation during severe accidents
C/steel interaction and oxidation during severe accidentsIshikawa, Jun; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2017/07
Oba, Yojiro*; Morooka, Satoshi; Oishi, Kazuki*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Takata, Shinichi; Sato, Nobuhiro*; Inoue, Rintaro*; Tsuchiyama, Toshihiro*; Gilbert, E. P.*; Sugiyama, Masaaki*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 50(2), p.334 - 339, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Zheng, X.; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 49(2), p.434 - 441, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.39(Nuclear Science & Technology)Oba, Yojiro*; Morooka, Satoshi; Oishi, Kazuki*; Sato, Nobuhiro*; Inoue, Rintaro*; Adachi, Nozomu*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Tsuchiyama, Toshihiro*; Gilbert, E. P.*; Sugiyama, Masaaki*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 49(5), p.1659 - 1664, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:63.27(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)