Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Keisuke; Nakagawa, Takuya; Shimojo, Hiroto; Kijima, Jun; Miura, Daiya; Onose, Yoshihiko*; Namba, Koji*; Uchida, Hiroaki*; Sakamoto, Kazuhiko*; Ono, Chika*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-019, 211 Pages, 2025/02
The uranium enrichment facilities at the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) were constructed sequentially to develop uranium enrichment technology with centrifugal separation method. The developed technologies were transferred to Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited until 2001. And the original purpose has been achieved. Wastewater Treatment Facility, one of the uranium enrichment facilities, was constructed in 1976 to treat radioactive liquid waste generated at the facilities, and it finished the role in 2008. In accordance with the Medium/Long-Term Management Plan of JAEA Facilities, interior equipment installed in this facility had been dismantled and removed since November 2021 to August 2023. This report summarizes the findings obtained through the work related to the contamination inspection methods cancellation the controlled area of Wastewater Treatment Facility from September 2023 to March 2024.
Suguro, Toshiyasu; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Watahiki, Takashi*; Kagawa, Akio
JAEA-Technology 2013-023, 22 Pages, 2013/10
For safety assessment of TRU waste disposal, solubility of plutonium was investigated under hardened cement paste porewater condition. Polycarboxylic acid compound, which have the possibility to be used for the TRU waste disposal, was selected as the cement admixture for the experiment. Initial concentration of Pu was 10 M in the experiment. The porewater of hardened cement paste was obtained by squeezing out the kneading of ordinary portland cement and deionized water with the cement admixture. The porewater of hardened cement paste without cement admixture is also used for the experiment. The maximum experimental period was 154 days. The experiment was carried out at room temperature (298
M in the experiment. The porewater of hardened cement paste was obtained by squeezing out the kneading of ordinary portland cement and deionized water with the cement admixture. The porewater of hardened cement paste without cement admixture is also used for the experiment. The maximum experimental period was 154 days. The experiment was carried out at room temperature (298  5 K) under argon atmosphere, in which oxygen concentration was lower than 1 ppm. Pu concentration in the porewater of hardened cement paste with or without the cement admixture were in the order of 10
5 K) under argon atmosphere, in which oxygen concentration was lower than 1 ppm. Pu concentration in the porewater of hardened cement paste with or without the cement admixture were in the order of 10 mol/dm
mol/dm after 154 days. This value is comparable to the solubility of Pu(IV) under high pH condition, suggesting that the solubility of Pu was not affected by the cement admixture in hardened cement paste.
after 154 days. This value is comparable to the solubility of Pu(IV) under high pH condition, suggesting that the solubility of Pu was not affected by the cement admixture in hardened cement paste.
Suguro, Toshiyasu; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Watahiki, Takashi*; Kagawa, Akio; Iijima, Kazuki
JAEA-Technology 2010-048, 32 Pages, 2011/03
Cementitious materials are considered to be necessary for the construction of TRU waste repository. The cement additives are used for cements and concretes in order to provide their fluidity. Many kinds of cement additives contain organic compounds which may increase radionuclide solubility by complex formation. Therefore, it is important to obtain the solubility data with cement additives for safety assessment of TRU waste disposal. In this work, two types of cement additives, such as sodium formaldehyde acid polymer and poly carboxylic acid polymer which are expected to be applied to the TRU waste disposal system, are selected. Since the chemical condition of the repository is considered to be reducing, the authors carried out batch-type experiments of plutonium solubility under reducing (Na S
S O
O added as reducant) and anoxic condition ([O
added as reducant) and anoxic condition ([O ]
]  1 ppm). Other experimental conditions are (1)initial plutonium concentration; 10
1 ppm). Other experimental conditions are (1)initial plutonium concentration; 10 M, (2) temperature; 298
M, (2) temperature; 298 5 K, (3)experimental period; 7, 14, 28 and 56 days and (4) molecular weight of cement additives; without fractionation
5 K, (3)experimental period; 7, 14, 28 and 56 days and (4) molecular weight of cement additives; without fractionation  5,000 and
5,000 and  5,000. The plutonium concentration in the absence of the cement additives was in the order of 10
5,000. The plutonium concentration in the absence of the cement additives was in the order of 10 mol dm
mol dm , while, those in the presence of cement additives were two or three orders of magnitude higher. Additionally, low molecular weight fraction of cement additives brought relatively higher plutonium concentration than high molecular weight fraction.
, while, those in the presence of cement additives were two or three orders of magnitude higher. Additionally, low molecular weight fraction of cement additives brought relatively higher plutonium concentration than high molecular weight fraction.
Suguro, Toshiyasu; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Komuro, Takashi*; Kagawa, Akio; Kashiwazaki, Hiroshi; Yamada, Kazuo
JAEA-Technology 2007-058, 20 Pages, 2007/11
For safety assessment of TRU waste disposal, data on sorption data of plutonium on Tuff have been obtained by a static batch-type experiment. Because the repository condition will be reducing and be affected by considerable amount of nitrate in waste, the authors carried out the experiments using Tuff under the reducing (Na S
S O
O as added as reductant) and anoxic condition (O
as added as reductant) and anoxic condition (O
 1 ppm) and solution of 0 to 0.5 M NaNO
1 ppm) and solution of 0 to 0.5 M NaNO . The experimental results suggest that distribution coefficient (Kd) ranges 0.2 to 0.7 m
. The experimental results suggest that distribution coefficient (Kd) ranges 0.2 to 0.7 m kg
kg in case of L/S=0.1 m
in case of L/S=0.1 m kg
kg . Similarly the Kd ranges, 1 to 7 m
. Similarly the Kd ranges, 1 to 7 m kg
kg at L/S=1 m
at L/S=1 m kg
kg . However, almost samples of the solution after experiments were plutonium solubility less than detection limit(10
. However, almost samples of the solution after experiments were plutonium solubility less than detection limit(10 mol/dm
mol/dm ) of alpha spectrometer. The reason, it is guessed plutonium coprecipitation with calcium hydroxide, because experiments using saturated calcium hydroxide in the liquid.
) of alpha spectrometer. The reason, it is guessed plutonium coprecipitation with calcium hydroxide, because experiments using saturated calcium hydroxide in the liquid.
Honda, Akira; Suguro, Toshiyasu; Sasaki, Ryoichi
JNC TN8400 2004-029, 43 Pages, 2005/03
Radioactive Iodine in the spent nuclear fuel is trapped by Iodine-adsorber in the off-gas process of reprocessing plant. The radioactive iodine includes very long half-lived nuclide (I-129;Half life=1.57x10 y).The I-129 cannot be expected to decay due to containment by the barrier system because of its long half life. The Iodine have soluble and poorly sorbing nature in the geological disposal condition, because the element can take the chemical form of I
y).The I-129 cannot be expected to decay due to containment by the barrier system because of its long half life. The Iodine have soluble and poorly sorbing nature in the geological disposal condition, because the element can take the chemical form of I in the reducing condition such as the condition of deep underground. Therefore Iodine can migrate in barrier system easily and strongly contribute to the peak of dose in the performance assessment of TRU waste disposal. An effective measure for reducing the dose peak is the controlled release of Iodine from the waste package in the low flux. The solidification by the copper matrix was proposed as one of the previous controlled release technology by JNC. The release rate of I-129 from the waste package solidified by the copper matrix was estimated. The corrosion rate of copper matrix was estimated as the sum of those both in the oxdizing and reducing conditions. The rates and periods of I-129 release were estimated under the assumption of congruent release of I-129 with corrosion of the copper matrix. The total release rate and period in the FRHP groundwater case were 3.11X10
in the reducing condition such as the condition of deep underground. Therefore Iodine can migrate in barrier system easily and strongly contribute to the peak of dose in the performance assessment of TRU waste disposal. An effective measure for reducing the dose peak is the controlled release of Iodine from the waste package in the low flux. The solidification by the copper matrix was proposed as one of the previous controlled release technology by JNC. The release rate of I-129 from the waste package solidified by the copper matrix was estimated. The corrosion rate of copper matrix was estimated as the sum of those both in the oxdizing and reducing conditions. The rates and periods of I-129 release were estimated under the assumption of congruent release of I-129 with corrosion of the copper matrix. The total release rate and period in the FRHP groundwater case were 3.11X10 Bq y
Bq y and 1.64x10
and 1.64x10 y(Initiated at 10
y(Initiated at 10 y and finalized at 1.64x10
y and finalized at 1.64x10 y) respectively. The total release rate and period in the SRHP groundwater case were 9.03x10
y) respectively. The total release rate and period in the SRHP groundwater case were 9.03x10 Bq y
Bq y and 5.66x10
and 5.66x10 y(Initiated at 10
y(Initiated at 10 y and finalized at 5.76x10
y and finalized at 5.76x10 y).
y).
Suguro, Toshiyasu; Notoya, Shin; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Nakamura, Ryosuke*; Shibutani, Tomoki; Kuroha, Mitsuhiko; Kamei, Gento
JNC TN8430 2004-004, 27 Pages, 2005/01
In terms of safety assessment of TRU waste disposal, data on plutonium sorption on cementitious materials have been obtained by means of a static batch-type experiment. Because the repository condition will be reducing and be affected by considerable amount of nitrate, the authors carried out the experiments using ordinary portland cement (OPC) under the reducing (Na S
S O
O as added as reductant) and anoxic condition (O
as added as reductant) and anoxic condition (O
 1ppm) and solution of 0 to 0.5 M NaNO
1ppm) and solution of 0 to 0.5 M NaNO . Other experimental conditions are : liquid/solid (L/S) ratios ; 100 and 1000 mL g
. Other experimental conditions are : liquid/solid (L/S) ratios ; 100 and 1000 mL g , Initially aaded plutonium; 2.84
, Initially aaded plutonium; 2.84 10
10 M, Temperature; 25
M, Temperature; 25 5
5 C and Reaction times; 7, 14 and 28 days. The experimental results suggest that distribution coefficient (
C and Reaction times; 7, 14 and 28 days. The experimental results suggest that distribution coefficient (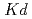 ) ranges 50 to 1000 mL g
) ranges 50 to 1000 mL g in case of L/S=100mL g
in case of L/S=100mL g . Similarly the
. Similarly the 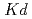 ranges, 100 to 10000 mL g
ranges, 100 to 10000 mL g at L/S=1000mL g
at L/S=1000mL g . These
. These 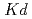 values tend to increase with lapsing reaction time. On the basis of these results, we recommend 50mL g
values tend to increase with lapsing reaction time. On the basis of these results, we recommend 50mL g as a conservative
as a conservative 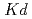 value of plutonium on OPC in a TRU waste repository condition.
value of plutonium on OPC in a TRU waste repository condition.
Muto, K.; Koakutsu, Masayuki; Nakazawa, Osamu; Suguro, Toshiyasu; Kato, Hiroshi
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (24), 71 Pages, 2004/00
Focusing on the cover layer materials (as the Radon Barrier Materials), which could have the effect to restrain the radon from scattering into the air and the effect of the radiation shielding, we produced the radon barrier materials with crude bentonite on an experimental basis, using the rotary type comprehensive unit for grinding and mixing, through which we carried out the evaluation of the characteristics thereof.
Katsumi, Muto,; Koakutsu, Masayuki; Nakazawa, Osamu; Suguro, Toshiyasu; Kato, Hiroshi
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (22), 103 Pages, 2004/00
None
Katsumi, Muto,; Koakutsu, Masayuki; Nakazawa, Osamu; Suguro, Toshiyasu; Kato, Hiroshi
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (23), 119- Pages, 2004/00
The application of the fluoride volatility process in the reprocessing of fuel from the fast breeder reactor is regarded as one of the economical methods. Plutonium hexafluoride (PuF6), however, reacting with fluorine (F2) and plutonium dioxide (PuO2) as the raw material, is in an unstable condition and tends to remain as a solid compound in the process after decomposing into plutonium tetrafluoride (PuF4). Suitable conditions should be established for the practical use of this process. One of them is to enhance the stability of PuF6. The behaviour of plutonium fluorination and relevant chemical reactions were investigated by referring to sundry literature and by thermodynamic calculation. It was then compared with recent data from laboratory scale experiments for this paper. Results from the theoretical analysis agreed with experimental observation that PuF6 could be formed stably under a high temperature condition (approx.1000 K) with over supply of figher concentration of F2.
None; Koakutsu, Masayuki; Nakazawa, Osamu; Suguro, Toshiyasu; Kato, Hiroshi
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (21), P. 126, 2003/00
None
Kagawa, Akio; Suguro, Toshiyasu; Fukumoto, Masahiro; Miyamoto, Yoichi; Nakahishi, Yoshio
PNC TN8410 95-202, 108 Pages, 1995/06
None
Kagawa, Akio; Suguro, Toshiyasu; Fukumoto, Masahiro; Miyamoto, Yoichi; Nakahishi, Yoshio
PNC TN8410 94-281, 60 Pages, 1994/08
None
Yamamoto, Keisuke; Nakagawa, Takuya; Matsuo, Kazuomi; Suguro, Toshiyasu
no journal, ,
Wastewater Treatment Area was constructed to treat radioactive liquid waste generated at the uranium enrichment facilities. The interior equipment installed in this facility was to be dismantled and removed by 2023. After that, contamination inspection for cancellation the controlled area was conducted, and it was confirmed that there was no contamination in the targeted area. In addition, to reduce the amount of radioactive waste, contamination inspection and investigation of building usage history for confirmation of non-radioactive waste was performed on concrete and other building materials, and the results were found to be below the lower detection limit. This presentation shows the findings obtained through the work related to contamination inspection for cancellation the controlled area.
Nakanishi, Yoshiki; Owada, Mitsuhiro; Aoyama, Yoshio; Suguro, Toshiyasu
no journal, ,
The uranium enrichment facilities at the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) were constructed sequentially to develop uranium enrichment technologies with centrifugal separation method and consisted of several facilities for R&D objectives. These developed technologies were transferred to Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited by 2001 and the initial goal was achieved. Wastewater Treatment Area, which was constructed treat radioactive liquid waste generated at the facilities, was to be decommissioned for the role of end and deterioration over time. Decommissioning of the facility included dismantling and removal of interior facilities and radiation measurements from 2003 to 2023 in preparation for cancellation the controlled area. This presentation is summary of the Wastewater Treatment Area decommissioning.
Suguro, Toshiyasu; Kagawa, Akio; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Watahiki, Takashi*; Mihara, Morihiro; Iijima, Kazuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Chinone, Makoto; Yasu, Hideto; Aoyama, Yoshio; Suguro, Toshiyasu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nakagawa, Takuya; Yamamoto, Keisuke; Suguro, Toshiyasu; Sone, Tomoyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Owada, Mitsuhiro; Nakanishi, Yoshiki; Aoyama, Yoshio; Suguro, Toshiyasu
no journal, ,
As a decommissioning measure of the Wastewater Treatment Area, which was constructed treat radioactive liquid waste generated at the uranium enrichment facilities, dismantling and removal of the interior equipment was conducted from November 2021 to August 2023 in preparation for cancellation the controlled area. During the dismantling and removal work, all potentially contaminated equipment and other items were removed in order to perform contamination inspection for cancellation the controlled area. This presentation shows the findings obtained through the work related to dismantling and removal of interior equipment for decommissioning.