Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O vapor on GaN surfaces
O vapor on GaN surfacesSumiya, Masatomo*; Sumita, Masato*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Sakamoto, Tetsuya; Sang, L.*; Harada, Yoshitomo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 23(1), p.189 - 198, 2022/00
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:51.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)GaN is an attracting material for power-electronic devices. Understanding the oxidation at GaN surface is important for improving metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices. In this study, the oxidation at GaN surfaces depending on the GaN crystal planes (+c, -c, and m-plane) was investigated by real time XPS and DFT-MD simulation. We found that H O vapor has the highest reactivity due to the spin interaction between H
O vapor has the highest reactivity due to the spin interaction between H O and GaN surfaces. The bond length between the Ga and N on the -c GaN surface was increased by OH attacking the back side of three-fold Ga atom. The chemisorption on the m-plane was dominant. The intense reactions of oxidation and Al
O and GaN surfaces. The bond length between the Ga and N on the -c GaN surface was increased by OH attacking the back side of three-fold Ga atom. The chemisorption on the m-plane was dominant. The intense reactions of oxidation and Al Ga
Ga N formation for p-GaN were observed at the interface of the Al
N formation for p-GaN were observed at the interface of the Al O
O layer deposited by ALD using H
layer deposited by ALD using H O vapor. This study suggests that an oxidant gas other than H
O vapor. This study suggests that an oxidant gas other than H O and O
O and O should be used to avoid unintentional oxidation during Al
should be used to avoid unintentional oxidation during Al Ga
Ga N atomi layer deposition.
N atomi layer deposition.
 molecule adsorption on polar and
molecule adsorption on polar and  -plane surfaces of GaN
-plane surfaces of GaNSumiya, Masatomo*; Sumita, Masato*; Asai, Yuya*; Tamura, Ryo*; Uedono, Akira*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 124(46), p.25282 - 25290, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:40.15(Chemistry, Physical)The initial oxidation of different GaN surfaces [the polar Ga-face (+c) and N-face (-c) and the nonpolar (10 0) (
0) ( )plane] under O
)plane] under O molecular beam irradiation was studied by real-time synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and DFT molecular dynamics calculation. The results predict that triplet O
molecular beam irradiation was studied by real-time synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and DFT molecular dynamics calculation. The results predict that triplet O either dissociates or chemisorbs at the bridge position on the +c-surface, while on N-terminated -c-surface the O
either dissociates or chemisorbs at the bridge position on the +c-surface, while on N-terminated -c-surface the O 2 molecule only undergoes dissociative chemisorption. On the
2 molecule only undergoes dissociative chemisorption. On the  -GaN surface, although the dissociation of O
-GaN surface, although the dissociation of O is dominant, the bond length and angle were found to fluctuate from those of O
is dominant, the bond length and angle were found to fluctuate from those of O molecules adsorbed on the polar surfaces. The computational model including both the surface spin and polarity of GaN is useful for understanding the interface between GaN and oxide layers in metal-oxide electronic.
molecules adsorbed on the polar surfaces. The computational model including both the surface spin and polarity of GaN is useful for understanding the interface between GaN and oxide layers in metal-oxide electronic.
Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Sumiya, Masato; Kida, Takashi; Kokusen, Junya; Uchida, Shoji; Kaminaga, Jota; Oki, Keiichi; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Sono, Hiroki
JAEA-Technology 2016-025, 42 Pages, 2016/11
A preliminary test on MOX fuel dissolution for the STACY critical experiments had been conducted in 2000 through 2003 at Nuclear Science Research Institute of JAEA. Accordingly, the uranyl / plutonium nitrate solution should be reconverted into oxide powder to store the fuel for a long period. For this storage, the moisture content in the oxide powder should be controlled from the viewpoint of criticality safety. The stabilization of uranium / plutonium solution was carried out under a precipitation process using ammonia or oxalic acid solution, and a calcination process using a sintering furnace. As a result of the stabilization operation, recovery rate was 95.6% for uranium and 95.0% for plutonium. Further, the recovered oxide powder was calcined again in nitrogen atmosphere and sealed immediately with a plastic bag to keep its moisture content low and to prevent from reabsorbing atmospheric moisture.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Miyagawa, Naoto; Nakano, Masanao; Nakada, Akira; Fujita, Hiroki; Takeyasu, Masanori; Isozaki, Tokuju; Morisawa, Masato; Mizutani, Tomoko; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-056, 181 Pages, 2014/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2012 to March 2013. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant of Tokyo Electric Power Co. in March 2011.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Takeyasu, Masanori; Nakada, Akira; Fujita, Hiroki; Isozaki, Tokuju; Morisawa, Masato; Mizutani, Tomoko; Nagaoka, Mika; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-009, 195 Pages, 2013/06
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2011 to March 2012. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant on Tokyo Electric Power Co. in March 2011.
Kokusen, Junya; Sumiya, Masato; Seki, Masakazu; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Ishii, Junichi; Umeda, Miki
JAEA-Technology 2012-041, 32 Pages, 2013/02
Uranyl nitrate solution fuel used in the STACY and the TRACY is adjusted in the Fuel Treatment System, in which such parameters are varied as concentration of uranium, free nitric acid, soluble neutron poison, and so on. Operations for concentration and denitration of the solution fuel were carried out with an evaporator from JFY 2004 to JFY 2008 in order to adjust the fuel to the experimental condition of the STACY and the TRACY. In parallel, the solution fuel in which some kinds of soluble neutron poison were doped was also adjusted in JFY 2005 and JFY 2006 for the purpose of the STACY experiments to determine neutron absorption effects brought by fission products, etc. After these experiments in the STACY, a part of the solution fuel including the soluble neutron poison was purified by the solvent extraction method with mixer-settlers in JFY 2006 and JFY 2007. This report summarizes operation data of the Fuel Treatment System from JFY 2004 to JFY 2008.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Takeyasu, Masanori; Nakada, Akira; Fujita, Hiroki; Isozaki, Tokuju; Morisawa, Masato; Mizutani, Tomoko; Kokubun, Yuji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2012-015, 166 Pages, 2012/05
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2010 to March 2011. In this report, some data include the influence of the accidental release from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant on Tokyo Electric Power Co. in 2011 March. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring program, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes. In addition, the data exceeded the normal range of fluctuation by the accidental release was evaluated in the appendices.
Furuta, Sadaaki; Sumiya, Shuichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Imaizumi, Kenji; Takeyasu, Masanori; Nakada, Akira; Fujita, Hiroki; Mizutani, Tomoko; Morisawa, Masato; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-035, 89 Pages, 2011/08
As a correspondence to the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, the environmental radiation monitoring was performed at the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, JAEA. This report presented the measurement results of ambient radiation dose rate, radioactivity concentration in the air and radioactivity concentration in fallout and meteorological observation result until May 31, 2011. The ambient radiation dose rate increased, with the peak dose rate of several thousand nGy/h at 7 o'clock in March 15, at 5 o'clock in March 16, and at 4 o'clock in March 21. The variation on the radioactivity concentration in the air and in fallout showed the almost same tendency as that of the dose rate. The concentration ratio of I-131/Cs-137 in the air increased to about 100. The dose was estimated resulting from internal exposure due to inhalation.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Matsuura, Kenichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Takeyasu, Masanori; Fujita, Hiroki; Isozaki, Tokuju; Morisawa, Masato; Mizutani, Tomoko; Kokubun, Yuji; et al.
JAEA-Review 2011-004, 161 Pages, 2011/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV - Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2009 to March 2010. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring program, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes.
 -ray dose rate around the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, JAEA
-ray dose rate around the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, JAEAMizutani, Tomoko; Onuma, Toshimitsu; Sugai, Masamitsu*; Watanabe, Hajime*; Morisawa, Masato; Takeyasu, Masanori; Sumiya, Shuichi
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 1, p.380 - 383, 2011/02
The Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories (NCL), JAEA operates the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP), plutonium fuel fabrication facilities and the supplemental facilities. In the terrestrial environment, environmental  -ray dose rate was measured continuously using an energy-thermo-compensation-type NaI(Tl) scintillation counter. The data of environmental dose rate measured in 5 monitoring stations and 8 monitoring posts were collected and analyzed to monitor on real-time. This paper summarizes the monitoring data of environmental dose rate around the NCL during the past 10 year (fiscal 1998-2007). The monthly average of the environmental dose rate for all monitoring stations and posts were in the range of 31-48 nGy h
-ray dose rate was measured continuously using an energy-thermo-compensation-type NaI(Tl) scintillation counter. The data of environmental dose rate measured in 5 monitoring stations and 8 monitoring posts were collected and analyzed to monitor on real-time. This paper summarizes the monitoring data of environmental dose rate around the NCL during the past 10 year (fiscal 1998-2007). The monthly average of the environmental dose rate for all monitoring stations and posts were in the range of 31-48 nGy h , except the value influenced by the criticality accident at the JCO in 1999. The long-term variation in the environmental dose rate was not found. The cases of the short-term increases occurred by the operations of the facilities in the NCL were concluded by the discharges of
, except the value influenced by the criticality accident at the JCO in 1999. The long-term variation in the environmental dose rate was not found. The cases of the short-term increases occurred by the operations of the facilities in the NCL were concluded by the discharges of  Kr from the TRP, transportation of MOX fuels or radioactive solid wastes, X-ray generator to calibrate the radiation monitoring instruments. The other cases to affect the change of the environmental dose rate were the scavenging of the airborne natural radionuclides, a patient cured by the radiation therapy and the shield effect by cars.
Kr from the TRP, transportation of MOX fuels or radioactive solid wastes, X-ray generator to calibrate the radiation monitoring instruments. The other cases to affect the change of the environmental dose rate were the scavenging of the airborne natural radionuclides, a patient cured by the radiation therapy and the shield effect by cars.
Ishii, Junichi; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Uchida, Shoji; Sumiya, Masato; Kida, Takashi; Shirahashi, Koichi; Umeda, Miki; Sakuraba, Koichi
JAEA-Technology 2009-068, 20 Pages, 2010/03
At Nuclear Fuel Cycle Safety Engineering Research Facility, the cerium mediated electrolytic oxidation method which is a decontamination technique to decrease the radioactivity of TRU wastes to the clearance-level has been developed for the effective reduction of TRU wastes generated from the decommissioning of a nuclear fuel reprocessing facility and so on. This method corrodes the oxide layer and the surface of metallic TRU metal wastes by the strong oxidation power of Ce in nitric acid. In this study, parameter tests were conducted to optimize the solution condition of Ce
in nitric acid. In this study, parameter tests were conducted to optimize the solution condition of Ce initial concentrations and nitric acid concentrations. The target corrosion rate of metallic TRU wastes set to be 2
initial concentrations and nitric acid concentrations. The target corrosion rate of metallic TRU wastes set to be 2 4
4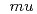 m/h for the practical use of this method. Under the optimized solution condition, a dissolution test of stainless steel simulating wastes was carried out. From the result of the dissolution test, the average corrosion rate was 3.3
m/h for the practical use of this method. Under the optimized solution condition, a dissolution test of stainless steel simulating wastes was carried out. From the result of the dissolution test, the average corrosion rate was 3.3  m/h during the test time of 90 hours. Based on the supposition that the corrosion depth of metallic TRU wastes was 20
m/h during the test time of 90 hours. Based on the supposition that the corrosion depth of metallic TRU wastes was 20  m enough to achieve the clearance-level, the treatment time for the decontamination was about 6 hours. It was confirmed from the result that the decontamination could be performed within one day and the decontamination solution could repeatedly reuse 15 times.
m enough to achieve the clearance-level, the treatment time for the decontamination was about 6 hours. It was confirmed from the result that the decontamination could be performed within one day and the decontamination solution could repeatedly reuse 15 times.
Sumiya, Shuichi; Matsuura, Kenichi; Nakano, Masanao; Takeyasu, Masanori; Morisawa, Masato; Onuma, Toshimitsu; Fujita, Hiroki; Mizutani, Tomoko; Watanabe, Hajime*; Sugai, Masamitsu*
JAEA-Review 2009-064, 166 Pages, 2010/03
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been conducted by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of JAEA, Chapter IV; Environmental monitoring" and Environmental Radiation Monitoring Program decided by the Ibaraki prefectural government. The radiation monitoring installations and equipments were also prepared for emergency. This manual describes; (1) the installations of radiological measurement, (2) the installations of meteorological observation, and (3) environmental data processing system for executing the terrestrial environmental monitoring by Environmental Protection Section, Radiation Protection Department. The environmental monitoring has been operated through the manual published in 1993 (PNC TN8520 93-001). Then the whole articles were revised because the partially of installations and equipments having been updated in recent years.
Takeishi, Minoru; Sumiya, Shuichi; Matsuura, Kenichi; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Nakano, Masanao; Takeyasu, Masanori; Isozaki, Hisaaki*; Isozaki, Tokuju; Morisawa, Masato; Fujita, Hiroki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-048, 177 Pages, 2009/12
Environmental radiation monitoring around the Tokai Reprocessing Plant has been performed by the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories, based on "Safety Regulations for the Reprocessing Plant of Japan Atomic Energy Agency, Chapter IV; Environmental Monitoring". This annual report presents the results of the environmental monitoring and the dose estimation to the hypothetical inhabitant due to the radioactivity discharged from the plant to the atmosphere and the sea during April 2008 to March 2009. Appendices present comprehensive information, such as monitoring program, monitoring methods, monitoring results and their trends, meteorological data and discharged radioactive wastes.
Ishii, Junichi; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Uchida, Shoji; Sumiya, Masato; Umeda, Miki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray dose rate around TRP
-ray dose rate around TRPMizutani, Tomoko; Onuma, Toshimitsu; Morisawa, Masato; Watanabe, Hajime*; Sugai, Masamitsu*; Nakada, Akira; Sumiya, Shuichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Umeda, Miki; Sumiya, Masato; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Sono, Hiroki; Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sumiya, Masato; Ikeda, Koki; Sonoda, Takashi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Mikake, Shinichiro; Abe, Hironobu; Inoue, Makoto; Eguchi, Kazutoshi; Kozawa, Masachiyo; Terunuma, Akihiro; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Aoki, Isao; Asazuma, Shinichiro; Sudo, Tomoyuki; Komiya, Tomokazu; Nakamura, Masahiko; Uchida, Shinichi; Kozawa, Masachiyo; Sonoda, Takashi; Mikake, Shinichiro; Ikeda, Koki; et al.
no journal, ,
JAEAs technical experiences and lessons learned for environmental remediationof Fukushima. (Technical supports for local governments)
Kobayashi, Fuyumi; Sumiya, Masato; Kida, Takashi; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Ogawa, Kazuhiko
no journal, ,
Towards the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Stations (1F), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has designed fabrication equipment of a pseudo fuel debris for the evaluation of the criticality characteristics of 1F fuel debris. In order to confirm the feasibility of the fabrication-method in designing, some fuel pellets mixed with uranium oxide and structural materials (iron, silicon, zirconium, etc.) were manufactured. The properties such as pressing and sintering condition were obtained by the prototyped fuel debris. The pseudo fuel debris fabricating equipment reflecting these properties is designed in 2016 and now constructed. The equipment will be installed in 2018 to start the fabrication.
Maekawa, Tomoyuki; Seki, Masakazu; Sumiya, Masato; Araki, Shohei; Murakami, Takahiko; Hasegawa, Kenta; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Mori, Takashi*; Ishii, Junichi; Kobayashi, Fuyumi; et al.
no journal, ,
As previously reported, to clarify critical characteristics of fuel debris, the Static Experiment Critical Facility (STACY) is being converted to the heterogenous thermal system using fuel rods and light water moderator from the homogenous system using solution fuel. Seismic reinforcement of the support structure of the core tank started in 2022. This report presents progress on manufacture and construction of the modified STACY in 2021 and 2022.