Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:259 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Shibata, Yoshihide; Isayama, Akihiko; Matsunaga, Go; Kawano, Yasunori; Miyamoto, Seiji*; Lukash, V.*; Khayrutdinov, R.*; JT-60 Team
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 9(Sp.2), p.3402084_1 - 3402084_5, 2014/06
We performed the disruption simulation using DINA code to investigate the effect of the electron temperature  on the plasma current decay after the initial phase of current quench (CQ). In this calculation, we used the measured
on the plasma current decay after the initial phase of current quench (CQ). In this calculation, we used the measured  profile during the initial phase of CQ. After the initial phase of CQ, we assumed that the
profile during the initial phase of CQ. After the initial phase of CQ, we assumed that the  profile does not change in time and used the value at the end of the initial phase of current quench because
profile does not change in time and used the value at the end of the initial phase of current quench because  profile could not be measured after the initial phase of CQ. From the simulation results, it was found that the time evolution of plasma current calculated by DINA was similar to experimental one in this calculation. However, the time evolution of
profile could not be measured after the initial phase of CQ. From the simulation results, it was found that the time evolution of plasma current calculated by DINA was similar to experimental one in this calculation. However, the time evolution of  profile in this calculation was different from the measured
profile in this calculation was different from the measured  profile because Te after first mini-collapse rapidly decreased until the value below a measurement limit (less than 0.1 keV). Moreover, the time evolution of poloidal cross-section S calculated by DINA code was rapidly decreased although the experimental one was gradually decreased. The plasma current decay during the disruption is determined by various parameters,
profile because Te after first mini-collapse rapidly decreased until the value below a measurement limit (less than 0.1 keV). Moreover, the time evolution of poloidal cross-section S calculated by DINA code was rapidly decreased although the experimental one was gradually decreased. The plasma current decay during the disruption is determined by various parameters, 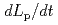 ,
,  and S. It is necessary to evaluate the effect of
and S. It is necessary to evaluate the effect of  profile on the plasma current decay after the initial phase of CQ by using various assumed
profile on the plasma current decay after the initial phase of CQ by using various assumed  model and DINA code.
model and DINA code.
Shibata, Yoshihide; Isayama, Akihiko; Miyamoto, Seiji*; Kawakami, Sho*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Matsunaga, Go; Kawano, Yasunori; Lukash, V.*; Khayrutdinov, R.*; JT-60 Team
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 56(4), p.045008_1 - 045008_8, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.46(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In JT-60U disruption, the plasma current decay during the initial phase of current quench has been calculated by a disruption simulation code (DINA) using the measured electron temperature  profile. In the case of fast plasma current decay,
profile. In the case of fast plasma current decay,  has a peaked profile just after thermal quench and the
has a peaked profile just after thermal quench and the  profile doesn't change significantly during the initial phase of current quench. On the other hand, in the case of the slow plasma current decay, the
profile doesn't change significantly during the initial phase of current quench. On the other hand, in the case of the slow plasma current decay, the  profile is border just after the thermal quench, and the
profile is border just after the thermal quench, and the  profile shrinks. The results of DINA simulation show that plasma internal inductance
profile shrinks. The results of DINA simulation show that plasma internal inductance 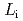 increases during the initial phase of current quench, while plasma external inductance
increases during the initial phase of current quench, while plasma external inductance 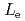 does not change in time. The increase of
does not change in time. The increase of 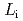 is caused by current diffusion toward the core plasma due to the decrease of
is caused by current diffusion toward the core plasma due to the decrease of  in intermediate and edge regions. It is suggested that an additional heating in the plasma periphery region has the effect of slowing down plasma current decay.
in intermediate and edge regions. It is suggested that an additional heating in the plasma periphery region has the effect of slowing down plasma current decay.
Matsunaga, Takeshi; Nagao, Seiya*; Ueno, Takashi; Takeda, Seiji; Amano, Hikaru; Tkachenko, Y.*
Applied Geochemistry, 19(10), p.1581 - 1599, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:55.27(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The association of dissolved  Sr,
Sr, 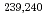 Pu and
Pu and  Am with natural colloids was investigated in surface waters in the Chernobyl nuclear accident area by means of ultrafiltration. Results suggest that Pu and Am isotopes were preferentially associated with dissolved humic substances (HS) of high molecular size. A model calculation of the complexation of Pu and Am with HS also supported the above. This study has expanded our understanding of the general role of natural organic colloids in dictating the chemical form of actinides in the surface aquatic environment.
Am with natural colloids was investigated in surface waters in the Chernobyl nuclear accident area by means of ultrafiltration. Results suggest that Pu and Am isotopes were preferentially associated with dissolved humic substances (HS) of high molecular size. A model calculation of the complexation of Pu and Am with HS also supported the above. This study has expanded our understanding of the general role of natural organic colloids in dictating the chemical form of actinides in the surface aquatic environment.
Matsunaga, Takeshi; Nagao, Seiya*; Takeda, Seiji; Ueno, Takashi; Amano, Hikaru
Dai-43-Kai Kankyo Hoshano Chosa Kenkyu Seika Rombun Shorokushu (Heisei-12-Nendo), p.49 - 50, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Yoshihide; Isayama, Akihiko; Miyamoto, Seiji; Matsunaga, Go; Kawano, Yasunori; Sugihara, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimada, Yoshihiro*; Shibata, Yoshihide; Nakamura, Yuji*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Kawakami, Sho*; Miyamoto, Seiji; Isayama, Akihiko; Matsunaga, Go; Sugihara, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Yoshihide; Isayama, Akihiko; Matsunaga, Go; Kawano, Yasunori; Miyamoto, Seiji*; Lukash, V. E.*; Khayrutdinov, R.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okawa, Kiyotaka*; Hiratsuka, Hajime; Suzuki, Rie*; Maeda, Ikuko*; Sunaga, Seiji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takir, D.*; Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; et al.
no journal, ,
JAXA spacecraft and sample return mission Hayabusa2 has arrived at the near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, which is classified a primitive carbonaceous object. Here we report recent results of near-infrared spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. The observations provide direct measurements of the surface composition of Ryugu and context for the returned samples. NIRS3 has detected a weak and narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micrometer across entire observed surface. This absorption feature is attributed to the presence of OH-bearing minerals. The NIRS3 observations also revealed that Ryugu is the darkest object to be observed up-close by a visiting spacecraft. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are consistent with thermally-and/or shock-metamorphosed, and/or carbon-rich space-weathered primitive and hydrated carbonaceous chondrites.