Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
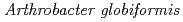 ; Assignment of bound diatomic molecules as O
; Assignment of bound diatomic molecules as O
Murakawa, Takeshi*; Hayashi, Hideyuki*; Sunami, Tomoko; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota; Suzuki, Mamoru*; Tanizawa, Katsuyuki*; Okajima, Toshihide*
Acta Crystallographica Section D, 69(12), p.2483 - 2494, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:67.31(Biochemical Research Methods)The crystal structure of a Cu amine oxidase from 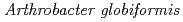 was determined at 1.08
was determined at 1.08  resolution with the use of low-molecular-weight polyethylene glycol (LMW PEG; average molecular weight
resolution with the use of low-molecular-weight polyethylene glycol (LMW PEG; average molecular weight  200) as a cryoprotectant. The final crystallographic
200) as a cryoprotectant. The final crystallographic  -factor and
-factor and 
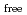 value are 13.0% and 15.0%, respectively. Several molecules of LMW PEG were found to occupy cavities in the protein interior including the active site, which resulted in the marked reduction of the overall
value are 13.0% and 15.0%, respectively. Several molecules of LMW PEG were found to occupy cavities in the protein interior including the active site, which resulted in the marked reduction of the overall 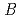 factor and consequently led to a sub-atomic resolution structure for a relatively large protein with a monomer molecular weight of
factor and consequently led to a sub-atomic resolution structure for a relatively large protein with a monomer molecular weight of  70,000. About 40% of all the presumed hydrogen atoms were observed as clear electron densities in the
70,000. About 40% of all the presumed hydrogen atoms were observed as clear electron densities in the 
 -
- 
 difference map. Multiple minor conformers were also identified for many residues. Anisotropic displacement fluctuations were evaluated in the active site that contains a post-translationally derived quinone cofactor and a Cu atom. Furthermore, diatomic molecules, most likely molecular oxygen, are bound to the protein, one of which is located in the region that has been previously proposed as an entry route for the substrate dioxygen from the central cavity of the dimer interface to the active site.
difference map. Multiple minor conformers were also identified for many residues. Anisotropic displacement fluctuations were evaluated in the active site that contains a post-translationally derived quinone cofactor and a Cu atom. Furthermore, diatomic molecules, most likely molecular oxygen, are bound to the protein, one of which is located in the region that has been previously proposed as an entry route for the substrate dioxygen from the central cavity of the dimer interface to the active site.
 and CaCl
and CaCl
Chatake, Toshiyuki*; Sunami, Tomoko
Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 124, p.15 - 25, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:58.01(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Sunami, Tomoko; Kono, Hidetoshi
PLOS ONE (Internet), 8(2), p.e56080_1 - e56080_12, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:28.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Adachi, Motoyasu; Sunami, Tomoko; Kuroki, Ryota
Koso Riyo Gijutsu Taikei, p.34 - 37, 2010/04
no abstracts in English
 -Lactamase TOHO-1 determined by combined high-resolution neutron and X-ray crystallography
-Lactamase TOHO-1 determined by combined high-resolution neutron and X-ray crystallographyKurihara, Kazuo; Sunami, Tomoko; Yamada, Mitsugu; Nitanai, Yasushi*; Okazaki, Nobuo; Adachi, Motoyasu; Tamada, Taro; Shimamura, Tatsuro*; Miyano, Masashi*; Ishii, Yoshikazu*; et al.
no journal, ,
To help resolve questions regarding the catalytic activity of  -lactamase, the crystal structure of an unliganded form of the
-lactamase, the crystal structure of an unliganded form of the  -lactamase Toho-1 with double mutation R274N/R276N (Toho-1/NN) has been determined by the use of high-resolution neutron and X-ray diffraction data. A large single crystal of Toho-1/NN with a dimension of 2.6
-lactamase Toho-1 with double mutation R274N/R276N (Toho-1/NN) has been determined by the use of high-resolution neutron and X-ray diffraction data. A large single crystal of Toho-1/NN with a dimension of 2.6  2.5
2.5  1.3 mm
1.3 mm was used to collect 100 K neutron diffraction data to 1.5
was used to collect 100 K neutron diffraction data to 1.5  resolution and X-ray diffraction data to 1.4
resolution and X-ray diffraction data to 1.4  resolution. The structural model of Toho-1/NN was refined to an R-factor of 19.7% using a program PHENIX. The structure showed that Glu166, a catalytic residue of Toho-1, was protonated even at pH 7 nonetheless for the close location to the positively charged side chain amino group (-NH3
resolution. The structural model of Toho-1/NN was refined to an R-factor of 19.7% using a program PHENIX. The structure showed that Glu166, a catalytic residue of Toho-1, was protonated even at pH 7 nonetheless for the close location to the positively charged side chain amino group (-NH3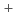 ) of Lys73. It is also found that there is a hydration water network bridging between the protonated Glu166 and the oxyanion hole comprising two main chain nitrogen atoms of Ser70 and Ser237. The neutron structure analysis also revealed the clear configuration of the proposed catalytic water molecule bridging Glu166 and Ser70. These observations are important to understand the catalytic action of
) of Lys73. It is also found that there is a hydration water network bridging between the protonated Glu166 and the oxyanion hole comprising two main chain nitrogen atoms of Ser70 and Ser237. The neutron structure analysis also revealed the clear configuration of the proposed catalytic water molecule bridging Glu166 and Ser70. These observations are important to understand the catalytic action of  -lactamase Toho-1.
-lactamase Toho-1.
Sunami, Tomoko; Kono, Hidetoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sunami, Tomoko; Kono, Hidetoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sunami, Tomoko; Kono, Hidetoshi
no journal, ,
Sunami, Tomoko; Kono, Hidetoshi
no journal, ,
Sunami, Tomoko; Kono, Hidetoshi
no journal, ,
DNA-protein interaction plays a key role in many cellular functions such as transcription and replication. Understanding the mechanisms by which the protein recognizes DNA sequences is necessary. With increased amount of crystal structures, conformational changes of proteins in DNA interfaces are suggested to be one of important factors in DNA recognition. To better understand a role of the deformation of the proteins, we carried out quantitative analyses of local conformational changes observed in DNA interfaces using pre-defined 4-residue-length 7-letter structural-codes. We found (1) larger number of fragments in DNA interface undergo conformational change upon DNA binding, (2) conformational variation in DNA interface is high in DNA-unbound state and less in DNA-bound state, (3) amino acid composition of conformationally variable regions in DNA interfaces is different from that in other region, but structural characteristics of DNA interface are similar to that of other region.
Sunami, Tomoko; Kono, Hidetoshi
no journal, ,
Sunami, Tomoko; Kono, Hidetoshi
no journal, ,