Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Rh
Rh Sn
Sn
Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Suyama, Kazuya*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Raymond, S.*; Steffens, P.*; Yamada, Akira*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Aoki, Yuji*; Kawasaki, Ikuto; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:66.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Katsuyama, Jinya; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Uno, Shumpei*; Li, Y.; Yoshimura, Shinobu*
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 142(2), p.021205_1 - 021205_10, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:15.42(Engineering, Mechanical)no abstracts in English
Katsuyama, Jinya; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Uno, Shumpei; Li, Y.; Yoshimura, Shinobu*
Proceedings of 2017 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2017) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2017/07
A structural integrity assessment methodology based on probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) is a rational methodology in evaluating failure frequency of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) by considering the probabilistic distributions of various influence factors related to the aged degradation. We have developed a PFM analysis code PASCAL to evaluate the failure frequency of RPVs considering the neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events. We have also developed a guideline on the structural integrity assessment of RPVs based on PFM to improve the applicability of PFM in Japan and to be able to perform the PFM analyses and evaluate through-wall cracking frequency of RPVs. The technical basis for PFM analysis is provided and the latest knowledge is included in the guideline. In this paper, an overview of the guideline and some typical analysis results obtained based on the guideline and Japanese database related to PTS evaluation are presented.
Masaki, Koichi; Miyamoto, Yuhei*; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Uno, Shumpei*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 2017 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2017) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2017/07
A probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL has been developed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). PASCAL can evaluate failure frequencies of Japanese reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) during pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events based on domestic structural integrity assessment models and data of influence factors. In order to improve the engineering applicability of PFM to Japanese RPVs, we have performed verification of the PASCAL. In general, PFM code consists of many functions such as fracture mechanics evaluation functions, probabilistic evaluation functions including random variables sampling modules and probabilistic evaluation models, and so on. The verification of PFM code is basically difficult because it is impossible to confirm such functions through the comparison with experiments. When a PFM code is applied for evaluating failure frequencies of RPVs, verification methodology of the code should be clarified and it is important that verification results including the region and process of the verification of the code are indicated. In this paper, our activities of verification for PASCAL are presented. We firstly represent the overview and methodology of verification of PFM code, and then, some verification examples are provided. Through the verification activities, the applicability of PASCAL in structural integrity assessments for Japanese RPVs was confirmed with great confidence.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Uno, Shumpei; Li, Y.
JAEA-Research 2016-022, 40 Pages, 2017/02
For reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) in the light water reactors, the fracture toughness decreases due to the neutron irradiation embrittlement with operating years. In Japan, to prevent RPVs from a nil-ductile fracture, deterministic fracture mechanics methods in accordance with the codes provided by the Japan Electric Association are performed for assessing the structural integrity of RPVs under the pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events by taking the neutron irradiation embrittlement into account. On the other hand, in recent years, probabilistic methodologies for PTS evaluation are introduced into regulations in Europe and the United States. For example, in the United States, a PTS screening criterion related to the reference temperature derived by the probabilistic method is stipulated. If the screening criterion is not satisfied, it is approved to perform the evaluation based on the probabilistic method by calculating numerical index such as through-wall crack frequency (TWCF). To reach the objectives that persons who have knowledge on the fracture mechanics can carry out the PFM analyses and obtain TWCF for a domestic RPVs by referring to this report, we develop the guideline on a structural integrity assessment method based on PFM by reflecting the latest knowledge and expertise.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Onoe, Hironori; Sato, Toshinori; Fujita, Tomoo; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Takeda, Masaki; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-014, 274 Pages, 2016/08
We synthesized the research results from the Mizunami/Horonobe Underground Research Laboratories (URLs) and geo-stability projects in the second midterm research phase. This report can be used as a technical basis for the Nuclear Waste Management Organization of Japan/Regulator at each decision point from siting to beginning of disposal (Principal Investigation to Detailed Investigation Phase).
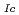 and K
and K for Japanese RPV steels
for Japanese RPV steelsKatsuyama, Jinya; Katsumata, Genshichiro; Onizawa, Kunio; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*
Proceedings of 2015 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2015) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/07
Probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL3 has been developed to apply the PFM analysis to the structural integrity assessment of domestic RPVs. In this paper, probabilistic evaluation models of fracture toughness KIc and KIa which have the largest scatter among the associated factors based on the database of Japanese RPV steels are presented. We developed probabilistic evaluation models for KIc and KIa based on the Weibull and lognormal distributions, respectively. The models are compared with the existing lower bound of fracture toughness in the Japanese code and probabilistic model in USA. As the results, the models established in present work satisfy lower bounds of fracture toughness in the Japanese code. The comparison in the models between present work and US showed significant differences that may have an influence on fracture probability of RPV.
Osakabe, Kazuya*; Masaki, Koichi*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Katsumata, Genshichiro; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimura, Shinobu*
Proceedings of 2015 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2015) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2015/07
A probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis method for pressure boundary components is useful to evaluate the structural integrity in a quantitative way. This is because the uncertainties related to influence parameters can be rationally incorporated in PFM analysis. From this viewpoint, the probabilistic approach evaluating through-wall cracking frequencies (TWCFs) of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) has already been adopted as the regulation on fracture toughness requirements against PTS events in the U.S. As a study of applying PFM analysis to the integrity assessment of domestic RPVs, JAEA has been preparing input data and analysis models to calculate TWCFs using PFM analysis code PASCAL3. In this paper, activities have been introduced such as preparing input data and models for domestic RPVs, verification of PASCAL3, and formulating guideline on general procedures of PFM analysis for the purpose of utilizing PASCAL3. In addition, TWCFs for a model RPV evaluated by PASCAL3 are presented.
Osakabe, Kazuya*; Masaki, Koichi*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Katsumata, Genshichiro; Onizawa, Kunio
Proceedings of 2014 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2014) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2014/07
The structural integrity of reactor pressure vessel (RPV) during pressurized thermal shock events is judged to be maintained unless the stress intensity factors at the crack tip is smaller than fracture toughness 
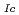 based on deterministic approach in the current Japanese code. Application of a probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis method for the structural reliability assessment of RPVs has become attractive recently, because uncertainties of several parameters can be incorporated rationally. According to the PFM analysis method in the U.S., through-wall cracking frequencies (TWCFs) are estimated. In this study, in order to identify the conservatism in the current code, PFM analyses on TWCF have been performed for certain model of RPVs. The result shows that the current assumption in JEAC 4206-2007 is conservative as compared with realistic conditions. Effects of variation of PTS transients on crack initiation frequency and TWCF have been also discussed.
based on deterministic approach in the current Japanese code. Application of a probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis method for the structural reliability assessment of RPVs has become attractive recently, because uncertainties of several parameters can be incorporated rationally. According to the PFM analysis method in the U.S., through-wall cracking frequencies (TWCFs) are estimated. In this study, in order to identify the conservatism in the current code, PFM analyses on TWCF have been performed for certain model of RPVs. The result shows that the current assumption in JEAC 4206-2007 is conservative as compared with realistic conditions. Effects of variation of PTS transients on crack initiation frequency and TWCF have been also discussed.
Li, Y.; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Katsumata, Genshichiro; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimura, Shinobu*
Proceedings of 2014 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2014) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2014/07
Multiple cracks in the same welded joints have been detected in piping systems of nuclear power plants. Therefore, structural integrity assessments considering multiple cracks and crack initiation in aged piping have been important. Probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) is a rational methodology in structural integrity assessment of aged piping in nuclear power plants. Two PFM codes, PASCAL-SP and PRAISE-JNES, have been improved or developed in Japan for the structural integrity assessment considering the age related degradation mechanisms of pipes. In this paper, a benchmark analysis was conducted considering multiple cracks and crack initiation, in order to confirm their reliability and applicability. Based on the numerical investigation in consideration of important influence factors such as crack number, crack location, crack distribution and crack detection probability of in-service inspection, it was concluded that the analysis results of these two codes are in good agreement.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Ito, Hiroto*; Li, Y.*; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimura, Shinobu*
International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 117-118, p.56 - 63, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:58.56(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Several probabilistic fracture mechanical (PFM) analysis codes have been improved or developed in Japan, such as PASCAL-SP developed at JAEA, and PRAISE-JNES developed at JNES for structural integrity assessment of aged piping in nuclear power plants. Although they were developed for different purposes, they have similar functions. In this paper, in order to confirm the reliability and applicability of two PFM analysis codes, PASCAL-SP and PRAISE-JNES, benchmark analyses on piping failure probability have been carried out considering typical aging mechanisms, such as fatigue crack growth for piping materials in BWR plants Moreover, a criterion is proposed to judge whether the differences between the analysis results from two codes can be acceptable. Based on the proposed criterion, it is concluded that the analysis results of these two codes are in good agreements.
Onizawa, Kunio; Masaki, Koichi; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-9-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.374 - 379, 2012/07
To assure the structural integrity of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) is known as one of the critical issues to maintain the safe long-term operation of a nuclear power plant. In Japan, the assessment methods for RPV integrity, stipulated in the codes and standards, have been endorsed by the regulatory body. Authors have initiated extensive research on the improvement of structural integrity assessment methods of RPVs. In this paper, we describe some research results obtained from the first-year activity. These include the study on revisiting the technical background of the methods, such as loading conditions, postulated crack definition, the other evaluation methods. In addition, studies on probabilistic methods for the applicability to the current rules and the standardization of the probabilistic analysis methods have been presented.
Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Goto, Nobuhisa*; Suzuki, Hirokazu*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
Mizuho Joho Soken Giho (Internet), 4(1), 5 Pages, 2012/03
Stainless steel with 5 mm thickness is weld-overlay cladded on the inner surface reactor pressure vessels for protecting the vessel walls against the corrosion. Residual stress which corresponds to yield stress is generated near the cladding layer due to the weld-overlay cladding. However, there is no specific provision in the codes related to the cladding. Therefore, in order to confirm how the residual stress affects on the structural integrity of RPVs during pressurize thermal shock events, we evaluate the residual stress caused by the weld-overlay cladding and effects of the stress on the structural integrity. In this paper, the analysis method of welding residual stress of RPVs using finite element method and that of fracture mechanics considering postulated crack are introduced.
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki; Inoue, Tomio*; Hayakawa, Kazushige*; Shiotari, Harutaka*; Nakamura, Yoshihide*; Matsuyama, Kazuya*; Nagasawa, Kiyoshi*
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 67(7-8), p.1387 - 1391, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.63(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Economic scale of radioisotopes (RI) in Japan is studied in the field of medicine, agriculture and a part of industry. (1) RI is used during medical examination with economic scale by 1.7M (million) dollars in 1997 and 0.4M dollars in 2005. (2) Economic scale of RI utilization in agriculture is 4M dollars for R&D, 127M dollars for environmental protection and 1M dollars for chronology. A total sum is 132M dollars for 2005 and 24M dollars for 1997. RI usage in agriculture is increased 5 times due to needs at environmental technology lasted after the Kyoto protocol. (3) Indirect economic scale of RI ( Kr,
Kr, 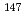 Pm,
Pm,  Cr) usage in paper fabrication field in Japan for 2006 is 8,432M dollars.
Cr) usage in paper fabrication field in Japan for 2006 is 8,432M dollars.
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki; Inoue, Tomio*; Hayakawa, Kazushige*; Shiotari, Harutaka*; Nakamura, Yoshihide*; Matsuyama, Kazuya*; Nagasawa, Kiyoshi*
Proceedings of 4th International Symposium on Radiation Education (ISRE 2008), p.3_16 - 3_20, 2008/12
The economic scale of radiological technologies applied to medical reimbursement is 14 billion dollars in 2005, which is larger by a factor of 17% than that of 1997. The value corresponds to about 4 to 8% (4.4% for medicine and 0.4% for dentistry) of the national health expenditure (301 billion dollars). The economic scale of radiation application at FDGPET and the charged particle therapy is 74 million dollars and 24 million dollars in 2005. In 1997 it was only 2 million dollars for the former and zero for the latter. The radiation technologies in these fields are rapidly developing. FDGPET enhanced the survival of 50,558 patients. Charged particle therapy enhanced the survival of 927 patients at 4 specified hospitals and 5,229 patients at the Proton Medical Research Center University of Tsukuba. Radiological technology is quite beneficial for the improvement of Japanese people's quality of life (QOL).
Funaki, Hironori; Tokiwa, Tetsuya; Ishii, Eiichi; Hatsuyama, Yoshihiro*; Matsuo, Shigeaki*; Tsuda, Kazuyasu*; Koizumi, Akira*; Ishikawa, Taiki*; Daijo, Yuichi*; Sugiyama, Kazutoshi*
JAEA-Data/Code 2008-013, 65 Pages, 2008/08
We conducted geological investigation of the pilot borehole of the ventilation shaft in Horonobe during October 2007 and March 2008. This report describes the field operations (core description, core photograph, and core sampling) and laboratory measurements (modal analysis and X-ray diffraction analysis), equipments as well as processing procedures, and shows the obtained results. The information obtained from this investigation will be reflected in spring water control plan on shaft excavation and additional plan of drainage treatment facilities.
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki; Inoue, Tomio*; Hayakawa, Kazushige*; Shiotari, Harutaka*; Nakamura, Yoshihide*; Matsuyama, Kazuya*; Nagasawa, Kiyoshi*
no journal, ,
Our economic study performed in 1997 revealed that the use of radiological technology in medicine was tended to spread. A reimbursement of medicine was about 10 billion dollars corresponding to about 4% of the national health expenditures (240 billion dollars) or to an average expenditure of 1,900 dollars a year for the Japanese. In 2005 it was about 13 billion dollars. An increasing rate was 17%. One of main cause of this increase is a significant advancement of medical devices represented by digital-X ray, multi-slice CT, PET and PET-CT.
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki; Inoue, Tomio*; Hayakawa, Kazushige*; Shiotari, Harutaka*; Nakamura, Yoshihide*; Matsuyama, Kazuya*; Nagasawa, Kiyoshi*
no journal, ,
The economic scale of radiological technology in medicine/dentistry in 2005 was about 13 billion dollars. Economic scale of medical/dental cares in 2005 was large to the magnitude of 17% than that in 1997. It is worthy of mentioning that almost radiological items used in medical/dental cares were increased except a radioisotope examination in medical care. Namely, radioisotope examination was 1.7 million dollars in 1997 but was 0.4 million dollars in 2005. No radioisotopes were used in the examination of dentist.
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki; Inoue, Tomio*; Hayakawa, Kazushige*; Shiotari, Harutaka*; Nakamura, Yoshihide*; Matsuyama, Kazuya*; Nagasawa, Kiyoshi*
no journal, ,
For Japan, application of radiation in nuclear medicine is prominently used for the diagnosis, the radiotherapy and the examination by radioisotopes (RI). They addressed to FDG-PET, charged particle therapy and BNCT at the specified hospitals. Incomes are reimbursed by a national health insurance. In 2005, reimbursed incomes at those hospitals were studied as an economic scale as a commissioned work from the Cabinet Office, Government of Japan. Results were directly compared with those from previous work done in 1997. The economic scale of the application of radiation to all medical reimbursement in our country is 14 billion dollars, which is larger by a factor of 17% than that of 1997. The value corresponds to about 4.8% of the national health expenditure (301billion dollars), consisting of 4.4% for medicine and 0.4% for dentistry.
Katsuyama, Jinya; Ito, Hiroto*; Li, Y.*; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimura, Shinobu*
no journal, ,
Several probabilistic fracture mechanical (PFM) analysis codes have been improved or developed in Japan, such as PASCAL-SP developed at JAEA, and PRAISE-JNES developed at JNES for structural integrity assessment of aged piping in nuclear power plants. Although they were developed for different purposes, they have similar functions. In this paper, in order to confirm the reliability and applicability of two PFM analysis codes, PASCAL-SP and PRAISE-JNES, benchmark analyses on piping failure probability have been carried out considering typical aging mechanisms, such as fatigue crack growth for piping materials in BWR plants Moreover, a criterion is proposed to judge whether the differences between the analysis results from two codes can be acceptable. Based on the proposed criterion, it is concluded that the analysis results of these two codes are in good agreements.