Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sugiura, Yuki; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Tachi, Yukio
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-017, 58 Pages, 2022/03
Sorption behavior of radionuclides (RNs) in buffer materials (bentonites), rocks and cementitious materials is one of the key processes in a safe geological disposal of radioactive waste because RNs migration in these materials is expected to be retarded by the sorption process. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the sorption process and develop a database compiling reliable data and mechanistic/predictive models so that reliable parameters can be set under a variety of geochemical conditions relevant to a performance assessment (PA). For this purpose, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has developed the database of sorption parameters in bentonites, rocks and cementitious materials. This sorption database (SDB) was firstly developed as an important basis for the H12 PA of a high-level radioactive waste disposal, and have been provided through the Web. JAEA has continued to improve and update the SDB in the view of potential future needs of data focusing on assuring the desired quality level and testing the usefulness of the databases for possible applications to the PA-related parameter setting. This report focuses on updating of the sorption database (JAEA-SDB) as a basis of integrated approach for the PA-related distribution coefficient (Kd) setting and development of mechanistic sorption models. This report also includes an overview of the database structure and contents. Kd data and their quality assurance (QA) results were updated from literature collected with wider ranges. As a result, 8,503 Kd data from 70 references related to the above-mentioned systems were added and the total number of Kd values in JAEA-SDB reached 79,072. The QA/classified Kd data reached about 75.4% for all Kd data in JAEA-SDB. The updated JAEA-SDB is expected to make it possible to give a basis for the next-step PA-related Kd setting.
Sugiura, Yuki; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Tachi, Yukio
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-022, 40 Pages, 2020/03
Sorption behavior of radionuclides (RNs) in buffer materials, rocks and cementitious materials is one of the key processes in a safe geological disposal. This report focuses on updating of JAEA sorption database (JAEA-SDB) as a basis of integrated approach for the performance assessment (PA)-related distribution coefficient (K ) setting and development of mechanistic sorption models. K
) setting and development of mechanistic sorption models. K data and their quality assurance (QA) results were updated by focusing on the following systems as potential needs extracted from our recent activities on the K
data and their quality assurance (QA) results were updated by focusing on the following systems as potential needs extracted from our recent activities on the K setting and development of mechanistic models, i.e., clay minerals, sedimentary rocks and cementitious materials. As a result, 6,702 K
setting and development of mechanistic models, i.e., clay minerals, sedimentary rocks and cementitious materials. As a result, 6,702 K data from 60 references were added and the total number of K
data from 60 references were added and the total number of K values in JAEA-SDB reached 69,679. The QA/classified K
values in JAEA-SDB reached 69,679. The QA/classified K data reached about 72% for all K
data reached about 72% for all K data in JAEA-SDB.
data in JAEA-SDB.
Tachi, Yukio; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Mihara, Morihiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-021, 101 Pages, 2020/03
Sorption of radionuclides in cement and bentonite as engineered barrier materials, and rocks as natural barrier is the one of key processes in the performance assessment of geological disposal of TRU and high-level waste. The magnitude of sorption, expressed normally by a distribution coefficient (K ), needs to be measured and determined taking into account the properties of barrier materials and geochemical conditions and associated uncertainty in the performance assessment. The basic concept for TRU waste disposal contains cementitious materials as an engineered barrier materials, in addition to bentonite and rock. It is therefore needed to consider the effects of the cement degradation and co-existing substances such as nitrates on radionuclide sorption. This report focused on data acquisition of distribution coefficient (K
), needs to be measured and determined taking into account the properties of barrier materials and geochemical conditions and associated uncertainty in the performance assessment. The basic concept for TRU waste disposal contains cementitious materials as an engineered barrier materials, in addition to bentonite and rock. It is therefore needed to consider the effects of the cement degradation and co-existing substances such as nitrates on radionuclide sorption. This report focused on data acquisition of distribution coefficient (K ) by batch sorption experiments for the systems coupling barrier material-chemical condition-radionuclides that are needed to consider for the performance assessment of geological disposal of TRU waste. The barrier materials considered are ordinary Portland cement (OPC), degraded OPC and tuff rock. The chemical conditions are distilled water and synthetic seawater equilibrated with OPC and those containing nitrates and ammonium salts, etc. The radionuclides considered are organic carbon, inorganic carbon, Cl, I, Cs, Ni, Se, Sr, Sn, Nb, Am and Th. Although K
) by batch sorption experiments for the systems coupling barrier material-chemical condition-radionuclides that are needed to consider for the performance assessment of geological disposal of TRU waste. The barrier materials considered are ordinary Portland cement (OPC), degraded OPC and tuff rock. The chemical conditions are distilled water and synthetic seawater equilibrated with OPC and those containing nitrates and ammonium salts, etc. The radionuclides considered are organic carbon, inorganic carbon, Cl, I, Cs, Ni, Se, Sr, Sn, Nb, Am and Th. Although K values have been partly reported previously as RAMDA (Radionuclide Migration Datasets) for the performance assessment in the TRU-2 report, these results and addition K
values have been partly reported previously as RAMDA (Radionuclide Migration Datasets) for the performance assessment in the TRU-2 report, these results and addition K data are reported with the details of experimental methods and conditions.
data are reported with the details of experimental methods and conditions.
Sugiura, Yuki; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Tachi, Yukio
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-016, 54 Pages, 2018/03
Sorption and diffusion of radionuclides in buffer materials (bentonites), rocks and cementitious materials are the key processes in the safe geological disposal of radioactive waste, because migration of radionuclides in these barrier materials is expected to be diffusion-controlled and retarded by sorption processes. It is therefore necessary to understand the sorption and diffusion processes and develop databases compiling reliable data and mechanistic/predictive models, so that reliable parameters can be set under a variety of geochemical conditions relevant to performance assessment (PA). The present report focuses on updating of the sorption database (JAEA-SDB) as basis of integrated approach for PA-related K setting and mechanistic sorption model development. This includes an overview of database structure and contents. K
setting and mechanistic sorption model development. This includes an overview of database structure and contents. K data and their QA results are updated by focusing our recent activities on the K
data and their QA results are updated by focusing our recent activities on the K setting and mechanistic model development. As a result, 4,256 K
setting and mechanistic model development. As a result, 4,256 K data from 30 references were added, total number of K
data from 30 references were added, total number of K values in the JAEA-SDB reached about 63,000. The QA/classified K
values in the JAEA-SDB reached about 63,000. The QA/classified K data reached about 69% for all K
data reached about 69% for all K data in JAEA-SDB. The updated JAEA-SDB is expected to make it possible to obtain quick overview of the available data, and to have suitable access to the respective data for PA-related K
data in JAEA-SDB. The updated JAEA-SDB is expected to make it possible to obtain quick overview of the available data, and to have suitable access to the respective data for PA-related K setting in effective, traceable and transparent manner.
setting in effective, traceable and transparent manner.
Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Matsubara, Ryuta*; Shibutani, Sanae*; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Tachi, Yukio
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-014, 31 Pages, 2018/03
NUMO and JAEA have developed the methodology of post-closure safety assessment for the geological disposal. For this purpose, NUMO and JAEA have conducted a collaborative research project for developing the safety assessment methodology based on international state of the art knowledge. The present report focuses on investigation of sorption and diffusion data reported and their QA evaluation for updating sorption and diffusion database (SDB and DDB) as the collaborative research project between NUMO and JAEA. This report includes sorption and diffusion data for mainly sedimentary rocks and cement materials. As a result, 1,746 sorption data from 19 references and 593 diffusion data from 25 references were extracted and prepared in the datasheet of SDB and DDB.
 setting approaches for rocks for the performance assessment of geological disposal; Application for granitic rocks
setting approaches for rocks for the performance assessment of geological disposal; Application for granitic rocksTachi, Yukio; Suyama, Tadahiro*; Shibutani, Sanae*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 24(2), p.109 - 133, 2017/12
For performance assessment (PA), the distribution coefficient (K ) need to be determined taking into account the specific PA conditions, including geochemical variability or uncertainty. The K
) need to be determined taking into account the specific PA conditions, including geochemical variability or uncertainty. The K setting approach for rocks was developed by integrating three methods; (i) direct use of measured K
setting approach for rocks was developed by integrating three methods; (i) direct use of measured K data extracted from the sorption database, (ii) semi-quantitative estimation by scaling differences between experimental and PA conditions, and (iii) thermodynamic sorption models. This approach was tested for granitic rock by comparing K
data extracted from the sorption database, (ii) semi-quantitative estimation by scaling differences between experimental and PA conditions, and (iii) thermodynamic sorption models. This approach was tested for granitic rock by comparing K values and their uncertainties of Cs and Am. The results indicated that K
values and their uncertainties of Cs and Am. The results indicated that K can be quantitatively evaluated by all approaches when adequate data and models are available. The K
can be quantitatively evaluated by all approaches when adequate data and models are available. The K dataset for safety-relevant 25 radionuclides was developed based on the direct use of measured data, and compared with the recent K
dataset for safety-relevant 25 radionuclides was developed based on the direct use of measured data, and compared with the recent K dataset in European PA projects. This K
dataset in European PA projects. This K setting approaches allowed to estimate the K
setting approaches allowed to estimate the K values and their uncertainties under the expected site conditions.
values and their uncertainties under the expected site conditions.
Tachi, Yukio; Suyama, Tadahiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2015-028, 60 Pages, 2016/03
Sorption and diffusion of radionuclides in buffer materials and rocks are the key processes in the safe geological disposal of radioactive waste, because migration of radionuclides in this barrier is expected to be diffusion-controlled and retarded by sorption processes. For this purpose, Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed databases of sorption and diffusion parameters in buffer materials and rocks. The present report focuses on developing and updating of the sorption database as basis of integrated approach for PA-related Kd setting and mechanistic sorption model development. This includes an overview of database structure, contents and functions including additional data evaluation function focusing on multi-parameter dependence, operating method, PA-related applications of the web-based JAEA-SDB. Kd data and their QA results are updated by focusing our recent activities on the Kd setting and mechanistic model development. As a result, 11,206 Kd data from 81 references are added, total Kd values in the JAEA-SDB are about 58,000. The QA/classified Kd data are about 39% for all Kd data in JAEA-SDB. The updated JAEA-SDB is expected to make it possible to obtain quick overview of the available data, and to have suitable access to the respective data for PA-related Kd setting in effective, traceable and transparent manner.
Tachi, Yukio; Suyama, Tadahiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2015-027, 40 Pages, 2016/03
Sorption and diffusion of radionuclides in buffer materials (bentonite) and rocks are the key processes in the safe geological disposal of radioactive waste, because migration of radionuclides in these barrier materials is expected to be diffusion-controlled and retarded by sorption processes. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has developed databases of sorption and diffusion parameters in bentonites and rocks. The present report focuses on updating of the diffusion database (JAEA-DDB) as basis of PA-related parameter setting. This includes an overview of database structure, contents and functions including additional data evaluation function. The diffusion data are updated by focusing on bentonites, granites and mudstones related to our recent PA activities. As a result, about 3,500 data from 221 references were added, total number of diffusion data in the JAEA-DDB reached about 5,000. The updated JAEA-DDB is expected to make it possible to obtain quick overview of the available data, and to have suitable access to the respective data for PA-related diffusion parameter setting in effective, traceable and transparent manner.
Tachi, Yukio; Suyama, Tadahiro; Yotsuji, Kenji; Ishii, Yasuo; Takahashi, Hiroaki*
CMS Workshop Lectures, Vol.21, p.241 - 250, 2016/00
Sorption and diffusion of radionuclides in argillaceous rocks are key processes in the safe geological disposal. The diffusion and sorption behavior of Ni(II), Am(III) and Se(IV) in mudstone from the Horonobe URL were investigated by experimental and modeling approaches. Effective diffusivities obtained by the through-diffusion experiments were in the sequence of Cs , Ni
, Ni , HTO, I
, HTO, I , Se(SeO
, Se(SeO
 ), Am(Am(CO
), Am(Am(CO )
) ) by comparison with the previous study. The distribution coefficient values were consistent with those obtained by batch sorption tests. These results were interpreted by the clay-based modeling approach coupling the thermodynamic sorption model assuming key contributions of clays (smectite and illite) and the diffusion model assuming the electrical double layer theory and the simplified pore model with size distribution. This clay-based model could provide reasonable account of observed trends and could be basically applicable for various radionuclides.
) by comparison with the previous study. The distribution coefficient values were consistent with those obtained by batch sorption tests. These results were interpreted by the clay-based modeling approach coupling the thermodynamic sorption model assuming key contributions of clays (smectite and illite) and the diffusion model assuming the electrical double layer theory and the simplified pore model with size distribution. This clay-based model could provide reasonable account of observed trends and could be basically applicable for various radionuclides.
Shibata, Masahiro; Sawada, Atsushi; Tachi, Yukio; Makino, Hitoshi; Wakasugi, Keiichiro; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Kitamura, Akira; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Oda, Chie; Ishidera, Takamitsu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2014-030, 457 Pages, 2015/03
JAEA and NUMO have conducted a collaborative research work which is designed to enhance the methodology of repository design and post-closure performance assessment in preliminary investigation stage. With regard to (1) study on rock suitability in terms of hydrology, based on some examples of developing method of hydro-geological structure model, acquired knowledge are arranged using the tree diagram, and model uncertainty and its influence on the evaluation items were discussed. With regard to (2) study on scenario development, the developed approach for "defining conditions" has been reevaluated and improved from practical viewpoints. In addition, the uncertainty evaluation for the effect of use of cementitious material, as well as glass dissolution model, was conducted with analytical evaluation. With regard to (3) study on setting radionuclide migration parameters, based on survey of precedent procedures, multiple-approach for distribution coefficient of rocks was established, and the adequacy of the approach was confirmed though its application to sedimentary rock and granitic rock. Besides, an approach for solubility setting was developed including the procedure of selection of solubility limiting solid phase. The adequacy of the approach was confirmed though its application to key radionuclides.
Tachi, Yukio; Ochs, M.*; Suyama, Tadahiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(10), p.1177 - 1190, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:66.60(Nuclear Science & Technology)The integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD) model for bentonite was developed to predict the long-term migration of radionuclides (RNs). The basic premise in the ISD model was to consistently use the same simple model design and parameters for describing RNs sorption as well as the clay surface chemistry. A 1-site non-electrostatic surface complexation model in combinations with 1-site ion exchange model was selected to keep model characteristics relatively robust when applied to compacted systems. Fundamental model parameters were evaluated from titration data for purified montmorillonite. The resulting model was then parameterized on the basis of selected sorption datasets for Np(V), Am(III) and U(VI), which cover key geochemical conditions such as pH, ionic strength and carbonate. The sorption trends for these RNs can be quantitatively described by the model considering a full suite of surface species including carbonate species which are consistent with aqueous RNs speciation.
Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji; Suyama, Tadahiro; Ochs, M.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(10), p.1191 - 1204, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:83.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)The integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD) model for compacted bentonites was developed based on the consistent combination of (1) the porewater chemistry model, (2) the thermodynamic sorption model (TSM), and (3) the diffusion model based on the electrical double layer (EDL) theory. This ISD model was successfully tested for various actinides with a complex chemistry (Np(V), Am(III), U(VI) under conditions where carbonate complexes are formed), by using published diffusion and sorption data (
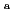 ,
, 
 ,
, 
 ) as a function of partial montmorillonite density. Quantitative agreements were observed as same as monovalent cations (Cs
) as a function of partial montmorillonite density. Quantitative agreements were observed as same as monovalent cations (Cs , Na
, Na ), anions (Cl
), anions (Cl , I
, I , TcO
, TcO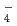 ) previously reported. The ISD model could be therefore seen to be able to predict sorption and diffusion behavior of various complex radionuclides in compacted bentonites.
) previously reported. The ISD model could be therefore seen to be able to predict sorption and diffusion behavior of various complex radionuclides in compacted bentonites.
 setting approach through semi-quantitative estimation procedures and thermodynamic sorption models; A Case study for Horonobe URL conditions
setting approach through semi-quantitative estimation procedures and thermodynamic sorption models; A Case study for Horonobe URL conditionsTachi, Yukio; Ochs, M.*; Suyama, Tadahiro; Trudel, D.*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1665, p.149 - 155, 2014/09
Sorption of radionuclides (K ) in host rocks depends critically on relevant geochemical conditions, need to correspond to the specific performance assessment (PA) conditions. The integrated approaches for site-specific K
) in host rocks depends critically on relevant geochemical conditions, need to correspond to the specific performance assessment (PA) conditions. The integrated approaches for site-specific K setting have been developed focusing two transferring procedures, semi-quantitative estimation procedures and thermodynamic sorption models. The present paper focused on illustrating the derivation of K
setting have been developed focusing two transferring procedures, semi-quantitative estimation procedures and thermodynamic sorption models. The present paper focused on illustrating the derivation of K values and their uncertainties of Cs, Ni, Am and Th for geochemical conditions from the Horonobe URL. These K
values and their uncertainties of Cs, Ni, Am and Th for geochemical conditions from the Horonobe URL. These K -setting results were compared with the measured K
-setting results were compared with the measured K values, indicating that the magnitude of sorption can be quantitatively evaluated when adequate data and models were available. These comparative discussions between transferring procedures and measured data are effective to enhance the reliability of K
values, indicating that the magnitude of sorption can be quantitatively evaluated when adequate data and models were available. These comparative discussions between transferring procedures and measured data are effective to enhance the reliability of K setting, and the careful selections from transferred results are needed according to the situation in the existing data and process understanding.
setting, and the careful selections from transferred results are needed according to the situation in the existing data and process understanding.
Ochs, M.*; Tachi, Yukio; Trudel, D.*; Suyama, Tadahiro*
JAEA-Research 2012-044, 130 Pages, 2013/03
JAEA has developed the setting approaches of sorption parameter (Kd) for site-specific conditions, to derive reliable parameter for performance assessment (PA) of geological disposal. These approaches include any transferring procedures from experimental conditions to PA conditions through expert judgments, semi-quantitative estimation procedures and thermodynamic sorption models (TSMs). The present report focused on illustrating a range of example calculations regarding the derivation of Kd values and their uncertainties based on semi-quantitative estimation procedures and TSMs. The Kd values of four key radionuclides, Cs, Ni, Am and Th were derived for Horonobe mudstone systems. These Kd-setting exercises allowed to estimate the magnitude of sorption under the site-specific conditions, and to identify some critical gaps in the existing data and process understanding. The possibilities of extending such approaches to further rock types including granitic rocks were also discussed.
Suyama, Tadahiro; Tachi, Yukio
JAEA-Data/Code 2011-022, 34 Pages, 2012/03
The present report focuses on updating of the sorption database (JAEA-SDB) by adding Kd data for various systems including soil and cement systems, to apply JAEA-SDB for the PA-related Kd setting for disposal of low level radioactive wastes including TRU wastes and the evaluation of radionuclide transport in surface soil systems. The updated data includes Kd data for soil and cement systems extracted from mainly previous published database, and Kd data related to our recent activities on the Kd setting and mechanistic model development. As a result, 16,000 Kd data from 334 references are added, total Kd values in the JAEA-SDB are about 46,000. The updated JAEA-SDB is expected to make it possible to obtain quick overview of the available data, and to have suitable access to the respective data for the performance assessment of various types of radioactive waste.
Tachi, Yukio; Suyama, Tadahiro; Ochs, M.*; Ganter, C.*
JAEA-Data/Code 2010-031, 168 Pages, 2011/03
JAEA has developed sorption database (SDB) compiling Kd data in buffer material and rock, which is key parameter for performance assessment (PA) of the geological disposal. The present report focuses on developing and updating of the JAEA-SDB as basis of integrated approach for PA-related Kd setting. This includes an overview of database structure, contents and functions including additional data evaluation function focusing on multi-parameter dependence, operating method, PA-related applications of the web-based SDB. Kd data and their QA results are updated by focusing our recent activities on the Kd setting and mechanistic model development. As a result, total Kd values in the SDB are about 28,540, and QA/classified Kd data are about 39 % for all Kd data. The updated JAEA-SDB is expected to make it possible to obtain quick overview of the available data, and to have suitable access to the respective data for PA-related Kd setting in effective, traceable and transparent manner.
Ochs, M.*; Tachi, Yukio; Ganter, C.*; Suyama, Tadahiro; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Research 2010-052, 59 Pages, 2011/02
For reliable parameter setting in performance assessment of geological disposal, JAEA has developed the integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD) model/database in bentonite systems. The main goal of the mechanistic model/database development is to provide a tool for a consistent explanation, prediction, and uncertainty assessment. This report focuses on developing the thermodynamic sorption model (TSM) including selection of model design and surface species, and on the quantification and handling of model uncertainties, based on illustrating by example of Ni sorption on montmorillonite/bentonite. Two fundamentally different approaches are presented and compared for representing TSM uncertainties: (1) TSM parameter uncertainties based on optimization routines and statistical procedure, (2) overall error estimated by direct comparison of modeled and experimental Kd values. The overall error in Kd is viewed as the best representation of model uncertainty in ISD model/database development.
Suyama, Tadahiro; Ganter, C.*; Kunze, S.*; Tachi, Yukio; Ochs, M.*
JAEA-Data/Code 2010-026, 72 Pages, 2011/02
Sorption of radionuclides in bentonites and rocks is one of the key processes in the safe geological disposal of radioactive waste. JAEA has developed sorption database (JAEA-SDB) which includes extensive compilation of sorption Kd data. JAEA has been continuing to update the SDB in view of potential future data needs, focusing on assuring the quality level and practical applications to Kd-setting for the geological environment. In this report, the QA/classification of selected entries in the JAEA-SDB, focusing on key radionuclides (Th, Np, Am, Se and Cs) sorption on tuff existing widely in geological environment, was done following the approach/guideline defined in our previous report. As a result, the reliability of 560 Kd values was evaluated and classified. This classification scheme is expected to make it possible to obtain quick overview of the available data from the SDB, and to have suitable access to the respective data for Kd-setting in PA.
Tachi, Yukio; Nakazawa, Toshiyuki*; Ochs, M.*; Yotsuji, Kenji; Suyama, Tadahiro; Seida, Yoshimi; Yamada, Norikazu*; Yui, Mikazu
Radiochimica Acta, 98(9-11), p.711 - 718, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:85.98(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Diffusion and sorption of radionuclides in compacted bentonite are the key processes in the safe geological disposal. The effects of carbonate and salinity on Np(V) diffusion and sorption in compacted montmorillonite were investigated by experimental and modeling approaches. Effective diffusion coefficients (
 ) and distribution coefficients (
) and distribution coefficients (
 ) of Np in montmorillonite compacted to dry density of 800 kg/m
) of Np in montmorillonite compacted to dry density of 800 kg/m were measured under four conditions with different salinities (0.05/0.5 M NaCl) and carbonate concentrations (0/0.01 M NaHCO
were measured under four conditions with different salinities (0.05/0.5 M NaCl) and carbonate concentrations (0/0.01 M NaHCO ). The
). The 
 for carbonate-free conditions decreased as salinity increased, and those for carbonate conditions showed the opposite dependency. The
for carbonate-free conditions decreased as salinity increased, and those for carbonate conditions showed the opposite dependency. The 
 decreased by one order of magnitude under high carbonate condition. Diffusion and sorption behaviors were interpreted by coupling the thermodynamic aqueous speciation, the thermodynamic sorption model based on ion exchange and surface complexation, and the diffusion model based on electrical double layer theory in narrow pores. The mechanistic model could be useful in predicting the sorption and diffusion behavior of complex species in compacted systems.
decreased by one order of magnitude under high carbonate condition. Diffusion and sorption behaviors were interpreted by coupling the thermodynamic aqueous speciation, the thermodynamic sorption model based on ion exchange and surface complexation, and the diffusion model based on electrical double layer theory in narrow pores. The mechanistic model could be useful in predicting the sorption and diffusion behavior of complex species in compacted systems.
Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji; Suyama, Tadahiro; Ochs, M.*; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Research 2009-069, 83 Pages, 2010/03
This report presents the prototype model/database for integrated sorption and diffusion (ISD2009) in bentonite systems as basis for performance assessment (PA) of geological disposal. The sorption model is based on a relatively simple 1-site surface complexation/diffuse layer model in combination with 1-site ion exchange model. The model parameters for surface chemistry/sorption are evaluated based on existing datasets for Na-montmorillonite, which covers key geochemical conditions, in consistent way. The diffusion model based on homogeneous pore structure and electrical double layer theory was developed and coupled with batch-based sorption model, then was validated by using data in compacted montmorillonite. The sorption and diffusion models were also tested by applying data in bentonite systems. The model and related parameters developed for key radionuclides such as Cs, Np(V), Ni, Am, etc. are integrated to ISD2009 database, which could be useful in future PA exercise.