Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kotegawa, Hisashi*; Nakamura, Akira*; Huyen, V. T. N.*; Arai, Yuki*; To, Hideki*; Sugawara, Hitoshi*; Hayashi, Junichi*; Takeda, Keiki*; Tabata, Chihiro; Kaneko, Koji; et al.
Physical Review B, 110(21), p.214417_1 - 214417_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Sr
Sr CoO
CoO at initial electrochemical process in an alkaline solution
at initial electrochemical process in an alkaline solutionMatsuzaki, Akira*; Hirayama, Masaaki*; Oguchi, Shoya*; Komo, Mamoru*; Ikezawa, Atsunori*; Suzuki, Kota*; Tamura, Kazuhisa; Arai, Hajime*; Kanno, Ryoji*
Electrochemistry (Internet), 90(10), p.107001_1 - 107001_8, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Electrochemistry)Oxygen reduction and evolution reactions (ORR and OER) of perovskite-type La Sr
Sr CoO
CoO were characterized using two-dimensional model electrodes with different reaction planes. Synthesized by pulsed laser deposition, these thin and flat electrodes can reveal the reaction plane dependence of the ORR activity. From steady-state polarization measurements in KOH (aq.), the ORR activity was the highest on the (001) film during the first ORR/OER cycle, and it decreased significantly during the second cycle. In-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction clarified crystal structure changes in the bulk and surface regions of La
were characterized using two-dimensional model electrodes with different reaction planes. Synthesized by pulsed laser deposition, these thin and flat electrodes can reveal the reaction plane dependence of the ORR activity. From steady-state polarization measurements in KOH (aq.), the ORR activity was the highest on the (001) film during the first ORR/OER cycle, and it decreased significantly during the second cycle. In-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction clarified crystal structure changes in the bulk and surface regions of La Sr
Sr CoO
CoO , and these changes are associated with forming oxygen defects during the initial electrochemical process. Furthermore, the La
, and these changes are associated with forming oxygen defects during the initial electrochemical process. Furthermore, the La Sr
Sr CoO
CoO surface partially decomposed upon reacting. Therefore, the interfacial structures formed in the electrochemical reaction field is important for enhancing ORR and OER activities.
surface partially decomposed upon reacting. Therefore, the interfacial structures formed in the electrochemical reaction field is important for enhancing ORR and OER activities.
Shiba, Tomooki; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Nomi, Takayoshi; Suzuki, Risa; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Nauchi, Yasushi*; Takada, Akira*; Nagatani, Taketeru; Okumura, Keisuke
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/10
Nauchi, Yasushi*; Nomi, Takayoshi; Suzuki, Risa; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Shiba, Tomooki; Takada, Akira*; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Okumura, Keisuke
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
 Cs concentrations in coastal sediments off Fukushima
Cs concentrations in coastal sediments off FukushimaSuzuki, Shotaro*; Amano, Yosuke*; Enomoto, Masahiro*; Matsumoto, Akira*; Morioka, Yoshiaki*; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Kaeriyama, Hideki*; Miura, Hikaru*; Tsumune, Daisuke*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 831, p.154670_1 - 154670_15, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.53(Environmental Sciences)Toyoda, Satoshi*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*
Hoshako, 35(3), p.200 - 206, 2022/05
The present status of spatiotemporal depth profiling analysis of the multilayer stacked film interface based on Ambient Pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (APXPS) is presented. To begin with, depth profiles of the multilayer stacked film interfaces have been achieved by time-division Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved PhotoEmission Spectroscopy data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division angle resolved AP-XPS data including spatial resolution, which enables us to realize spatiotemporal depth profiles of the interfaces under reaction conditions such as oxidation and reduction. In addition, it is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
Takahashi, Atsushi*; Chiba, Mirei*; Tanahara, Akira*; Aida, Jun*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; Murakami, Shinobu*; Koarai, Kazuma; Ono, Takumi*; Oka, Toshitaka; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.10355_1 - 10355_11, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:40.51(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:96.23(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
 measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPS
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPSToyoda, Satoshi*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*; Ohashi, Yuji*; et al.
Vacuum and Surface Science, 64(2), p.86 - 91, 2021/02
We have developed  measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
Nagae, Daisuke*; Abe, Yasushi*; Okada, Shunsuke*; Omika, Shuichiro*; Wakayama, Kiyoshi*; Hosoi, Shun*; Suzuki, Shinji*; Moriguchi, Tetsuro*; Amano, Masamichi*; Kamioka, Daiki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 986, p.164713_1 - 164713_7, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:72.28(Instruments & Instrumentation)Matsuura, Yuto*; Hayano, Akira; Itakura, Kenichi*; Suzuki, Yukinori*
Applied Soft Computing, 84, p.105737_1 - 105737_9, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:28.37(Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence)LiDAR (laser imaging detection and ranging) has been developed to obtain a high-resolution point cloud data indicating the detailed 3D shapes of an object. To identify discontinuities in a rock mass of a tunnel gallery wall, it is necessary to approximate the rock mass surface with small planes. Normal vectors of the planes are important to identify discontinuities. We developed an algorithm for estimation of planes based on multi-dimensional particle swarm optimization (MD PSO) from point cloud data. Point cloud data were segmented into bounding boxes and grouped into clusters by MD PSO. Planes were estimated using the least squares method for point cloud data in the respective clusters. The newly developed MD PSO algorithm was evaluated using point cloud data obtained from a gallery wall. Evaluation was carried out in comparison with the previous developed variable-box segmentation (VBS) algorithm. The MD PSO-based algorithm showed a 7% higher accuracy than that of the VBS algorithm.
Iwasaki, Toshiki*; Sekiyama, Tsuyoshi*; Nakajima, Teruyuki*; Watanabe, Akira*; Suzuki, Yasushi*; Kondo, Hiroaki*; Morino, Yu*; Terada, Hiroaki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Takigawa, Masayuki*; et al.
Atmospheric Environment, 214, p.116830_1 - 116830_11, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.69(Environmental Sciences)The utilization of numerical atmospheric dispersion prediction (NDP) models for accidental discharge of radioactive substances was recommended by a working group of the Meteorological Society of Japan. This paper is to validate the recommendation through NDP model intercomparison in the accidental release from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2011. Emission intensity is assumed to be constant during the whole forecast period for the worst-case scenario unless time sequence of emission is available. We expect to utilize forecasts of surface air contaminations for preventions of inhalations of radioactive substances, and column-integrated amounts for mitigation of radiation exposure associated with wet deposition. Although NDP forecasts have ensemble spread, they commonly figure out relative risk in space and time. They are of great benefit to disseminating effective warnings to public without failure. The multi-model ensemble technique may be effective to improve the reliability.
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc generator by (n,
Tc generator by (n, ) method
) methodFujita, Yoshitaka; Seki, Misaki; Namekawa, Yoji*; Nishikata, Kaori; Kimura, Akihiro; Shibata, Akira; Sayato, Natsuki; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Sano, Tadafumi*; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; et al.
KURNS Progress Report 2018, P. 155, 2019/08
no abstracts in English
Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:156 Percentile:99.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:298 Percentile:99.68(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Nakayoshi, Akira; Suzuki, Seiya; Okamura, Nobuo; Watanabe, Masayuki; Koizumi, Kenji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(10), p.1119 - 1129, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)Matsukawa, Shun*; Itakura, Kenichi*; Hayano, Akira; Suzuki, Yukinori*
Journal of MMIJ, 133(11), p.256 - 263, 2017/11
LIDAR detects a rock mass surface configurations as a point cloud. DiAna (Discontinuity Analysis) is a Matlab tool which was developed for geo-structural analysis of rock mass discontinuities. DiAna segments a point cloud into bounding boxes to estimate the surface of a rock mass. However, an expert's skills necessary to determine the appropriate size of the bounding boxes for DiAna. We developed the VBS (Variable-Box Segmentation) algorithm to determine the appropriate box size depending on the location of the point cloud and to estimate the surface of a rock mass. The performance of the VBS algorithms was evaluated by comparison with the DiAna algorithm. The results of comparison showed that the VBS algorithm estimated planes more accurately for the reference planes than the DiAna algorithm. Therefore, the VBS algorithm determines appropriate box sizes automatically depending on the location of the point cloud and estimates the surface appropriately.
 =28 and
=28 and  =50; Spectroscopy of
=50; Spectroscopy of 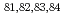 Zn
ZnShand, C. M.*; Podoly k, Zs.*; G
k, Zs.*; G rska, M.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Otsuka, T.*; Sieja, K.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Tsunoda, T.*; et al.
rska, M.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Otsuka, T.*; Sieja, K.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Tsunoda, T.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 773, p.492 - 497, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:87.72(Astronomy & Astrophysics) pellets for Mo-99 production, 3
pellets for Mo-99 production, 3Ishida, Takuya; Suzuki, Yoshitaka; Nishikata, Kaori; Yonekawa, Minoru; Kato, Yoshiaki; Shibata, Akira; Kimura, Akihiro; Matsui, Yoshinori; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Sano, Tadafumi*; et al.
KURRI Progress Report 2015, P. 64, 2016/08
no abstracts in English
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc solution, 1
Tc solution, 1Suzuki, Yumi*; Nakano, Hiroko; Suzuki, Yoshitaka; Ishida, Takuya; Shibata, Akira; Kato, Yoshiaki; Kawamata, Kazuo; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
JAEA-Technology 2015-031, 58 Pages, 2015/11
Technetium-99m ( Tc) is one of the most commonly used radioisotopes in the field of nuclear medicine. In the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), the research and development (R&D) have been carried out for production of molybdenum-99 (
Tc) is one of the most commonly used radioisotopes in the field of nuclear medicine. In the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), the research and development (R&D) have been carried out for production of molybdenum-99 ( Mo) by (n,
Mo) by (n,  ) method, a parent nuclide of
) method, a parent nuclide of  Tc, with the Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR). On the other hand, the new project as "Domestic Production of Medical Radioisotope (Technetium preparation) in Japan" was adopted in the Tsukuba International Strategic Zone on October, 2013 and the demonstration tests will be planned for the domestic production of
Tc, with the Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR). On the other hand, the new project as "Domestic Production of Medical Radioisotope (Technetium preparation) in Japan" was adopted in the Tsukuba International Strategic Zone on October, 2013 and the demonstration tests will be planned for the domestic production of  Mo/
Mo/ Tc with the JMTR. Thus, new facilities and analysis devices were equipped in the JMTR Hot Laboratory in 2014 as the part of this project. As the part of the analytical device equipment, the
Tc with the JMTR. Thus, new facilities and analysis devices were equipped in the JMTR Hot Laboratory in 2014 as the part of this project. As the part of the analytical device equipment, the  -TLC analyzer and the radiation detector connected with the High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) were installed for quality inspection of the
-TLC analyzer and the radiation detector connected with the High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) were installed for quality inspection of the  Mo/
Mo/ Tc solution and the extracted
Tc solution and the extracted  Tc solution in the JMTR Hot Laboratory. The performance tests of these devices such as detection sensitivity, resolution, linearity and selectivity of energy range were carried out with
Tc solution in the JMTR Hot Laboratory. The performance tests of these devices such as detection sensitivity, resolution, linearity and selectivity of energy range were carried out with  Cs and
Cs and  Eu as alternative radionuclides of
Eu as alternative radionuclides of  Mo and
Mo and  Tc, respectively. In the results, bright prospects were obtained concerning the quality inspection of the
Tc, respectively. In the results, bright prospects were obtained concerning the quality inspection of the  Mo/
Mo/ Tc and
Tc and  Tc solutions using these devices. This report describes the results of those performance tests.
Tc solutions using these devices. This report describes the results of those performance tests.