Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kotegawa, Hisashi*; Nakamura, Akira*; Huyen, V. T. N.*; Arai, Yuki*; To, Hideki*; Sugawara, Hitoshi*; Hayashi, Junichi*; Takeda, Keiki*; Tabata, Chihiro; Kaneko, Koji; et al.
Physical Review B, 110(21), p.214417_1 - 214417_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Entani, Shiro*; Sato, Shinichiro*; Honda, Mitsunori; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Oshima, Takeshi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 199, p.110369_1 - 110369_7, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.04(Chemistry, Physical)Ni silicide synthesis by Ni ion beam irradiation into Si attracts attention due to its advantages including the ability of formation of local structures, the controllability of ion beams, the formability of silicide without heat treatment and the high reproducibility of the resulting specimen. In this work, we investigate the local atomic structure of Si implanted with 3.0 MeV Ni ions. Analysis of Ni K-edge fluorescent-yield extended X-ray absorption fine structure reveals that Ni atoms have mixed structure of metallic-like face-centered cubic Ni and NiSi
ions. Analysis of Ni K-edge fluorescent-yield extended X-ray absorption fine structure reveals that Ni atoms have mixed structure of metallic-like face-centered cubic Ni and NiSi phases at the initial stage of the irradiation and the formation of NiSi
phases at the initial stage of the irradiation and the formation of NiSi promotes significantly with the ion fluence above 10
promotes significantly with the ion fluence above 10  ions cm
ions cm . With consideration of the agreement between the ion fluence threshold for the structural transition and the critical Si-amorphization fluence, it is concluded that the amorphization of Si plays an important role in the synthesis of the NiSi
. With consideration of the agreement between the ion fluence threshold for the structural transition and the critical Si-amorphization fluence, it is concluded that the amorphization of Si plays an important role in the synthesis of the NiSi phase in Ni
phase in Ni -irradiated Si.
-irradiated Si.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:73.20(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Xu, P. G.; Takamura, Masato*; Iwamoto, Chihiro*; Hakoyama, Tomoyuki*; Otake, Yoshie*; Suzuki, Hiroshi
Isotope News, (774), p.7 - 10, 2021/04
no abstracts in English
Nemoto, Fumiya*; Kofu, Maiko; Nagao, Michihiro*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Takata, Shinichi; Suzuki, Junichi*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Ueki, Takeshi*; Kitazawa, Yuzo*; et al.
Journal of Chemical Physics, 149(5), p.054502_1 - 054502_11, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:74.13(Chemistry, Physical)Yoshida, Kensuke*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; Higashiguchi, Takeshi*; Ugomori, Teruyuki*; Tanaka, Nozomi*; Kawasaki, Masato*; Suzuki, Yuhei*; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Tomita, Kentaro*; Hirose, Ryoichi*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 106(12), p.121109_1 - 121109_5, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:53.60(Physics, Applied)Yoshida, Kensuke*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; Higashiguchi, Takeshi*; Ugomori, Teruyuki*; Tanaka, Nozomi*; Ohashi, Hayato*; Kawasaki, Masato*; Suzuki, Yuhei*; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Tomita, Kentaro*; et al.
Applied Physics Express, 7(8), p.086202_1 - 086202_4, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:74.22(Physics, Applied)We demonstrate high conversion efficiency for extreme ultraviolet (EUV) emission at 6.5-6.7 nm from multiple laser beam-produced one-dimensional spherical plasmas. Multiply charged-state ions produce strong resonance emission lines, which combine to yield intense unresolved transition arrays in Gd, Tb, and Mo. The maximum in-band EUV conversion efficiency was observed to be 0.8%, which is one of the highest values ever reported due to the reduction of plasma expansion loss.
Koike, Fumihiro*; Funaba, Hisamichi*; Goto, Motoshi*; Kato, Daiji*; Kato, Takako*; Morita, Shigeru*; Murakami, Izumi*; Sakaue, Hiroyuki*; Sudo, Shigeru*; Suzuki, Chihiro*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1545, p.202 - 211, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:82.30(Physics, Applied)Atomic ionic states and transition properties of elements with atomic numbers Z ranging from 50 to 80 are discussed as these are important to the understanding of plasmas containing such heavy elements. As such, data productions and the current status of theoretical calculations in this field are discussed. Further, recent spectroscopic measurements and respective theoretical analyses for W, Gd, and Nd are provided.
Shimada, Taihei; Nomura, Masahiro; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Omori, Chihiro*; Toda, Makoto*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Schnase, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of 4th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '13) (Internet), p.2750 - 2752, 2013/06
no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Kensaku; Ida, Katsumi*; Yoshinuma, Mikiro*; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; LHD Experimental Group*
Nuclear Fusion, 53(1), p.013003_1 - 013003_9, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:59.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper provides and proposes a new technique to determine the location of the LCFS that is based on a characterization of the 
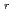 structure derived from CXS measurements in the LHD. We found that the spatial derivative in the
structure derived from CXS measurements in the LHD. We found that the spatial derivative in the 
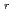 structure had the local maximum value at the region very near, or possibly outside the vacuum LCFS location of vacuum magnetic field at the outer midplane in the low
structure had the local maximum value at the region very near, or possibly outside the vacuum LCFS location of vacuum magnetic field at the outer midplane in the low  plasma.
plasma.
Shimada, Taihei; Suzuki, Hiromitsu; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Schnase, A.; Toda, Makoto*; Omori, Chihiro*; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Nomura, Masahiro; Tamura, Fumihiko; et al.
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1143 - 1145, 2012/08
The RF cavities of J-PARC 3 GeV synchrotron use 198 MA cores. Buckling occurred in some cores since the operation starting on the October of 2007. We have measured the inner diameters of the cores as a part of the investigation to determine the cause of the buckling when the cavities were disassembled for maintenance. We noticed that deformations of the inner shapes of the cores related to its manufacturing process and that inner diameters change over year were not measured in the most of the cores without buckled cores. Furthermore, the effective manufacturing process of cores to avoid the buckling has be established. We are going to replace old type cores with new type cores in shutdown periods in summer every year.
Usui, Toshihide; Mikami, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Makoto; Nakayama, Naoto; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Tani, Kotaro*; Yamasaki, Keizo*; Misawa, Tsuyoshi*
KURRI Progress Report 2010, P. 209, 2011/10
no abstracts in English
Ochiai, Kentaro; Kondo, Keitaro; Onishi, Seiki; Takakura, Kosuke; Sato, Satoshi; Abe, Yuichi; Konno, Chikara; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Yagi, Takahiro*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(2), p.1953 - 1956, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.71(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Lead is an important candidate material as multiplier of nuclear fusion reactor. Few DT neutron integral benchmark experiments were performed for lead so far. Therefore, we have carried out an integral benchmark experiment on lead at the DT neutron source facility of JAEA, FNS. A cubic lead assembly on a side of 45.3 cm was set up and was irradiated with the DT neutron source. Reaction rates of the  Al(n,
Al(n, )
) Na,
Na,  Nb(n,2n)
Nb(n,2n)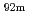 Nb,
Nb,  Zr(n,2n)
Zr(n,2n)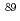 Zr and
Zr and  In(n,n')
In(n,n')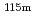 In reactions were measured as fast neutron spectrum indices in the assembly. A small NE213 spectrometer was also used for measurement of neutron spectra in the assembly. A Monte Carlo calculation code, MCNP5, was adopted to calculate the above neutron spectra and activation reaction rates. Nuclear data libraries, JENDL-3.3, ENDF/B-VII.0, JEFF-3.1 and FENDL-2.1, were used in the calculation. The calculation results of the three libraries except for JENDL-3.3 agreed with the measuring ones. In case of JENDL-3.3, some remarkable disagreements were found. From our investigations, it was pointed out that the inappropriate evaluation of the (n,2n) and inelastic cross sections of lead in JENDL-3.3 caused such disagreement.
In reactions were measured as fast neutron spectrum indices in the assembly. A small NE213 spectrometer was also used for measurement of neutron spectra in the assembly. A Monte Carlo calculation code, MCNP5, was adopted to calculate the above neutron spectra and activation reaction rates. Nuclear data libraries, JENDL-3.3, ENDF/B-VII.0, JEFF-3.1 and FENDL-2.1, were used in the calculation. The calculation results of the three libraries except for JENDL-3.3 agreed with the measuring ones. In case of JENDL-3.3, some remarkable disagreements were found. From our investigations, it was pointed out that the inappropriate evaluation of the (n,2n) and inelastic cross sections of lead in JENDL-3.3 caused such disagreement.
Nomura, Masahiro; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Schnase, A.; Shimada, Taihei; Suzuki, Hiromitsu; Tamura, Fumihiko; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Omori, Chihiro*; Toda, Makoto*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 623(3), p.903 - 909, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.18(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have been operating ten RF cavities loaded with magnetic alloy cores in J-PARC 3 GeV RCS since September 2007. During 3 years operation, we detected three times the impedance reductions of RF cavities resulting from the buckling of MA cores. To find out the origin of the MA core buckling, we evaluated the thermal stress inside the MA cores in operation and studied the relationship between the MA core buckling and core structure. We figured out that the MA core buckling was caused by the thermal stress that was enhanced due to the impregnation with low viscosity epoxy resin.
Ogino, Haruyuki*; Kono, Takahiko; Yamasoto, Kotaro; Fujiwara, Keiko*; Suzuki, Chihiro*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 52(8), p.458 - 461, 2010/08
, 52(8), p.458 - 461, 2010/08
no abstracts in English
Shimada, Taihei; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Nomura, Masahiro; Schnase, A.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Omori, Chihiro*; Toda, Makoto*; Suzuki, Hiromitsu; et al.
Proceedings of 7th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (DVD-ROM), p.549 - 551, 2010/08
The beam pipes of the RF acceleration section in the J-PARC RCS have a large aperture (247 mm) in order to handle a high power proton beam of 1 MW with acceptable loss. When we disassemble and later reassemble the test cavity in between the high power test runs for the MA cores, it is quite hard work to take out, and reinstall the beam pipe. Therefore, instead of using an original beam pipe, risking that it becomes unusable for accelerator operation due to scratches or discharges, we developed a light weight dummy beam pipe and dedicated copper connection parts for the acceleration gaps, which are easy to take apart and to assemble. Accordingly, the copper parts, which are used to connect the acceleration gaps to the cavity tanks for the installed cavity systems were redesigned, so that the time required for assembly or disassembly is reduced. This is especially important, as the cavities in the accelerator tunnel are in a high radiation environment caused by high power RCS operation.
Nomura, Masahiro; Schnase, A.; Shimada, Taihei; Suzuki, Hiromitsu; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Ezura, Eiji*; Omori, Chihiro*; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.3723 - 3725, 2010/05
We have been operating the RF cavities loaded with MA cores with a high field gradient of more than 20 kV/m since October 2007. We have been measuring the RF cavity impedance at the shutdown periods, and we detected the impedance reductions of RCS RF cavities on January and June 2009. Taking out the RF cavities from the beam line and opening them, we found that many of cores showed a buckling at the inner radius. We report the detail of condition of MA cores and the relation between the impedance reduction and core condition.
Shimada, Taihei; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Nomura, Masahiro; Schnase, A.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Omori, Chihiro*; Toda, Makoto*; Yoshii, Masahito*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.3717 - 3719, 2010/05
Several magnetic alloy cores of the RF cavities, which are installed in the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) of J-PARC have shown buckling after about two years operation. To find the reason, why the local deformation happened, we made a test setup. There we heat up MA cores in air by 500 kHz RF and measure the thermal deformation in order to collect information about the buckling process. The results obtained by comparing the expansion of cores made by different production methods are reported.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Schnase, A.; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Nomura, Masahiro; Toda, Makoto*; Suzuki, Hiromitsu; Shimada, Taihei; Hara, Keigo*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.1443 - 1445, 2010/05
The wide-band RF cavities in the J-PARC RCS are operated in the dual-harmonic operation, in which each single cavity is driven by a superposition of the fundamental and the second harmonic RF signals. By the dual-harmonic operation large amplitude second harmonic signals for the bunch shape manipulation are generated without extra cavities. The phase control of the second harmonic RF is a key for the bunch shape manipulation. The fundamental RF signal is controlled by the phase feedback loop to damp the dipole oscillation. The second harmonic is locked to the phase of the vector-sum phase of the fundamental RF signals. We present the system detail and the performance in the beam operation of the RCS.
Schnase, A.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Koseki, Tadashi*; Tomizawa, Masahito*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Nomura, Masahiro; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Toda, Makoto*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.1446 - 1448, 2010/05