Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 based on experimental data and density functional theory calculation result
based on experimental data and density functional theory calculation resultWatanabe, Masashi; Nakamura, Hiroki; Suzuki, Kiichi; Machida, Masahiko; Kato, Masato
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 105(3), p.2248 - 2257, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Materials Science, Ceramics)Properties of CeO were evaluated by DFT simulation to determine band gap, Frenkel defect formation energy and defect migration energy. Band gap and Frenkel defect formation energy were used to analyze defect equilibria. Oxygen partial pressure dependence of defect equilibria was evaluated based on oxygen potential experimental data and DFT calculation, and a Brouwer diagram was derived. The defect formation energies, including Frenkel defect, electron-hole pair and so on, were determined and used to evaluate the properties, including oxygen diffusion coefficients, electrical conduction, heat capacity and thermal conductivity. Mechanisms of various properties were discussed for a deeper understanding based on defect chemistry, and the relationship among properties were systematically described.
were evaluated by DFT simulation to determine band gap, Frenkel defect formation energy and defect migration energy. Band gap and Frenkel defect formation energy were used to analyze defect equilibria. Oxygen partial pressure dependence of defect equilibria was evaluated based on oxygen potential experimental data and DFT calculation, and a Brouwer diagram was derived. The defect formation energies, including Frenkel defect, electron-hole pair and so on, were determined and used to evaluate the properties, including oxygen diffusion coefficients, electrical conduction, heat capacity and thermal conductivity. Mechanisms of various properties were discussed for a deeper understanding based on defect chemistry, and the relationship among properties were systematically described.

Suzuki, Kiichi; Kato, Masato; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Uno, Hiroki*; Carvajal-Nunez, U.*; Nelson, A. T.*; McClellan, K. J.*
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 102(4), p.1994 - 2008, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:90.42(Materials Science, Ceramics)The fundamental properties of CeO were assessed using a range of experimental techniques. The oxygen potential of CeO
were assessed using a range of experimental techniques. The oxygen potential of CeO was measured by the thermogravimetric technique, and a numerical fit for the oxygen potential of CeO
was measured by the thermogravimetric technique, and a numerical fit for the oxygen potential of CeO is derived based on defect chemistry. Mechanical properties of CeO
is derived based on defect chemistry. Mechanical properties of CeO were obtained using sound velocity measurement, resonant ultrasound spectroscopy and nanoindentation. The obtained mechanical properties of CeO
were obtained using sound velocity measurement, resonant ultrasound spectroscopy and nanoindentation. The obtained mechanical properties of CeO are then used to evaluate the Debye temperature and Gruneisen constant. The heat capacity and thermal conductivity of CeO
are then used to evaluate the Debye temperature and Gruneisen constant. The heat capacity and thermal conductivity of CeO were also calculated using the Debye temperature and the Gruneisen constant. Finally, the thermal conductivity was calculated based upon laser flash analysis measurements. This result demonstrates that the thermal conductivity has strong dependence upon material purity.
were also calculated using the Debye temperature and the Gruneisen constant. Finally, the thermal conductivity was calculated based upon laser flash analysis measurements. This result demonstrates that the thermal conductivity has strong dependence upon material purity.
Suzuki, Kiichi; Okita, Takatoshi; Aono, Shigenori
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Next Generation Nuclear Systems for Sustainable Development (FR-17) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2017/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed mixed plutonium-uranium oxide (MOX) fuel fabrication technologies in large-scale and fabricated MOX fuel assemblies for experimental fast reactor "JOYO" and prototype fast reactor "MONJU" at Plutonium Fuel Production Facility (PFPF) since 1988. Low density pellet is adopted as MONJU fuel. For the low density pellet fabrication in large-scale, various challenges were encountered. In order to resolve these challenges, countermeasures such as new pore former with high softening temperature and improved granulation method for MOX powder were considered. In this presentation, accumulated MOX fuel fabrication technologies as mentioned above and recent R&D activity such as new pelletizing method, or die wall lubrication pelletizing, for low-decontaminated TRU fuel fabrication will be discussed.
 N
N films
filmsMorita, Yosuke*; Nakajima, Kaoru*; Suzuki, Motofumi*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Saito, Yuichi; Ishikawa, Norito; Hojo, Kiichi; Tsujimoto, Masahiko*; Isoda, Shoji*; Kimura, Kenji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 315, p.142 - 145, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:69.61(Instruments & Instrumentation)Takato, Kiyoto; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Suzuki, Kiichi; Shibanuma, Kimikazu; Hatanaka, Nobuhiro; Yamaguchi, Bungo; Tobita, Yoshimasa; Shinozaki, Masaru; Iimura, Naoto; Okita, Takatoshi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2013-026, 42 Pages, 2013/10
In order to cope with making a commercial fast reactor fuel burn-up higher, oxygen-to-metal (O/M) ratio in the fuel specification is designed to 1.95. As the test for the fabrication of such low O/M ratio pellets, two kinds of O/M ratio preparation tests of different reduction mechanism were done. In the first test, we evaluated the technology to prepare the O/M ratio low by annealing the sintered pellets in production scale. In addition, we know from past experience that O/M ratio of the sintered pellets can be reduced by residual carbon when the de-waxed pellets with high carbon content are sintered. Thus, in another test, the green pellets containing a large amount of organic additives were sintered and we evaluated the technology to produce the low O/M ratio sintered pellets by the reduction due to residual carbon. From the first test results, we found a tendency that the higher annealing temperature or the longer annealing time resulted in the lower O/M ratio. However, the amount of O/M ratio reduction was small and it is estimated that a substantial annealing time is necessary to prepare the O/M ratio to 1.95. It is considered that reducing O/M ratio by annealing was difficult because atmosphere gas containing oxygen released from pellets remained and the O/M ratio was changed to the value equilibrated with the gas having high oxygen potential. From another test results, it was confirmed that O/M ratio was reduced by the reduction due to residual carbon. We found that it was important to manage an oxygen potential of atmosphere gas in a sintering furnace low to reduce the O/M ratio effectively.
Hirooka, Shun; Kato, Masato; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Nelson, A. T.*; McClellan, K. J.*; Suzuki, Kiichi
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Safe Technologies and Sustainable Scenarios (FR-13) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2013/03
As research and development activities for MOX fuel pellet production, oxidation and reduction behaviors of MOX powders were investigated by thermogravimetry and X-ray diffraction measurements. It was observed that the oxidation limit decreased with oxidizing temperature and Pu content. The MOX powders showed a two-step oxidation and kinetic stability under non-stoichiometry. The oxidation rates were evaluated from the isothermal oxidation tests. It was found that the reduction temperature of M O
O + M
+ M O
O was higher than that of M
was higher than that of M O
O . This indicated that the reduction of M
. This indicated that the reduction of M O
O was prevented by the existence of M
was prevented by the existence of M O
O . Activation energy of the reduction was derived from the non-isothermal reduction tests. The data are expected to contribute to establishing a control technique for O/M ratio during MOX powder storage and pellet production.
. Activation energy of the reduction was derived from the non-isothermal reduction tests. The data are expected to contribute to establishing a control technique for O/M ratio during MOX powder storage and pellet production.
 N
N by TEM
by TEMNakajima, Kaoru*; Morita, Yosuke*; Suzuki, Motofumi*; Narumi, Kazumasa; Saito, Yuichi; Ishikawa, Norito; Hojo, Kiichi; Tsujimoto, Masahiko*; Isoda, Shoji*; Kimura, Kenji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 291, p.12 - 16, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:73.47(Instruments & Instrumentation)Thin films of amorphous Si N
N (thickness 20 nm) were irradiated with 120-720 keV C
(thickness 20 nm) were irradiated with 120-720 keV C
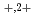 ions and observed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The ion track produced in an amorphous material was directly observed by TEM. For quantitative analysis, the ion tracks were also observed using high-angle annular dark field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM). The observed ion track consists of a low density core (radius
ions and observed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The ion track produced in an amorphous material was directly observed by TEM. For quantitative analysis, the ion tracks were also observed using high-angle annular dark field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM). The observed ion track consists of a low density core (radius  2.5 nm) and a high density shell (width
2.5 nm) and a high density shell (width  2.5 nm), which is very similar to the ion tracks in amorphous SiO
2.5 nm), which is very similar to the ion tracks in amorphous SiO irradiated with high energy heavy ions observed by small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). Although the observed ion tracks may be affected by surface effects, the present result indicates that TEM and HAADF-STEM have potential to observe directly the fine structures of ion tracks in amorphous materials.
irradiated with high energy heavy ions observed by small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). Although the observed ion tracks may be affected by surface effects, the present result indicates that TEM and HAADF-STEM have potential to observe directly the fine structures of ion tracks in amorphous materials.
Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato; Suzuki, Kiichi; Uno, Hiroki*
Proceedings of 2010 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '10) (CD-ROM), p.1859 - 1865, 2010/06
The sintering behavior of the de-waxed pellets containing about 3000 ppm of carbon was analyzed during the sintering process using thermal gravimetry and dilatometer measurements as a parameter of the ratio of hydrogen partial pressure-to-moisture partial pressure (H /H
/H O) in the sintering atmosphere. The attained O/M ratio and the shrinkage rate increased with decreasing H
O) in the sintering atmosphere. The attained O/M ratio and the shrinkage rate increased with decreasing H /H
/H O ratio in the sintering atmosphere. As a result, it is considered that a carbothermic reduction caused the significant decrease of the O/M ratio in the case of the sintering in the atmosphere of high H
O ratio in the sintering atmosphere. As a result, it is considered that a carbothermic reduction caused the significant decrease of the O/M ratio in the case of the sintering in the atmosphere of high H /H
/H O ratio. In contrast, decrement of O/M ratio could be inhibited by keeping the oxygen potential of the atmosphere high in the case of the sintering in the atmosphere of lower H
O ratio. In contrast, decrement of O/M ratio could be inhibited by keeping the oxygen potential of the atmosphere high in the case of the sintering in the atmosphere of lower H /H
/H O ratio.
O ratio.
Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Suzuki, Kiichi; Hatanaka, Nobuhiro; Hanawa, Yukio; Shinozaki, Masaru; Murakami, Shinichi; Tobita, Yoshimasa; Kawasaki, Takeshi; Kobayashi, Yoshihito; Iimura, Naoto; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2008-017, 97 Pages, 2008/03
Low density MOX pellets for FBR "MONJU" have not been fabricated in Plutonium Fuel Fabricating Facility (PFPF) for these 9 years since completion of the first reload fuel for "MONJU" in 1995. In this period, about 60 % of machines in the pellet fabrication process of PFPF have been replaced with new ones, and fabrication of MOX pellets for "JOYO" has been continued using these machines. Concerning the feed MOX powders for "MONJU", the amount of decay heat has been increased with increase of accumulated Am-241 in this period. In addition, powder characteristic of recycled MOX powder which is one of feed powders, MH-MOX powder, UO powder and recycled MOX powder, was significantly changed by replacing former processing machine used for scrap recycling with improved one. Using MOX powder with increased decay heat and recycled MOX powder processed by new machine, a series of low density MOX pellet fabrication tests were conducted to confirm pellet fabrication conditions for current pellet fabrication machines from October in 2004 to August in 2006. As a conclusion, it was confirmed that low density MOX pellets could be fabricated using these feed powders and replaced machines by adjusting pellet fabrication conditions adequately. This report summarizes the results of a series of low density MOX pellet fabrication tests.
powder and recycled MOX powder, was significantly changed by replacing former processing machine used for scrap recycling with improved one. Using MOX powder with increased decay heat and recycled MOX powder processed by new machine, a series of low density MOX pellet fabrication tests were conducted to confirm pellet fabrication conditions for current pellet fabrication machines from October in 2004 to August in 2006. As a conclusion, it was confirmed that low density MOX pellets could be fabricated using these feed powders and replaced machines by adjusting pellet fabrication conditions adequately. This report summarizes the results of a series of low density MOX pellet fabrication tests.
 Pu
Pu )O
)O with two fcc phases
with two fcc phasesSuzuki, Kiichi; Kato, Masato; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Aono, Shigenori; Kashimura, Motoaki
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 444-445, p.590 - 593, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.98(Chemistry, Physical)It was reported that sintered MOX pellet of hypostoichiometric composition was oxidized at room temperature in an atmosphere of inert gas and air. The region of two fcc phases exist at room temperature in the (U,Pu)O with Pu content of greater than 20%. In this study, the oxidation rate of (U
with Pu content of greater than 20%. In this study, the oxidation rate of (U Pu
Pu )O
)O with two fcc phases was investigated to contribute to understanding of the oxidation behavior using thermogravimetric technique. The sintered pellets of (U
with two fcc phases was investigated to contribute to understanding of the oxidation behavior using thermogravimetric technique. The sintered pellets of (U Pu
Pu )O
)O were prepared by mechanical blending method and were sliced into disc-like sample with about 1 mm thick and 85-93% theoretical density. The oxidation rate of the samples were measured at 60, 125 and 150
were prepared by mechanical blending method and were sliced into disc-like sample with about 1 mm thick and 85-93% theoretical density. The oxidation rate of the samples were measured at 60, 125 and 150 C in an atmosphere of Air, N
C in an atmosphere of Air, N and Air/N
and Air/N gas mixture containing moisture of 1 - 700ppm using thermal gravity and differential thermal analysis. The curve of the isothermal oxidation was analyzed by the model of diffusion in a system consisting of two phases. The diffusion model can represent the oxidation curve as a function of time and temperature. In the results of X-ray diffraction measurement, fcc phase with O/M
gas mixture containing moisture of 1 - 700ppm using thermal gravity and differential thermal analysis. The curve of the isothermal oxidation was analyzed by the model of diffusion in a system consisting of two phases. The diffusion model can represent the oxidation curve as a function of time and temperature. In the results of X-ray diffraction measurement, fcc phase with O/M  2.00 was observed to increase by oxidation of sample. These results indicate that the oxidation of the (U
2.00 was observed to increase by oxidation of sample. These results indicate that the oxidation of the (U Pu
Pu )O
)O with two fcc phases proceeds by diffusion of the phase with O/M
with two fcc phases proceeds by diffusion of the phase with O/M  2.00 which is formed on the sample surface.
2.00 which is formed on the sample surface.
Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Suzuki, Kiichi; Aono, Shigenori
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.891 - 896, 2007/09
no abstracts in English
Ito, Takashi; Asano, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Takatoshi; Yamazaki, Yoshishige; Naito, Fujio*; Takasaki, Eiichi*; Yoshino, Kazuo*; Tanaka, Hirokazu*; Kato, Takao*; Kabeya, Zenzaburo*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2006) (CD-ROM), p.782 - 784, 2007/00
Three DTL tanks and 32 SDTL tanks for the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) were assembled at KEK site. After the assembling, the high-power conditioning of the DTL1 and 12 SDTL tanks and the beam acceleration test for the DTL1 ware carried out. And then all the DTL and SDTL tanks have to be transported form KEK to JAEA. In order to confirm the effect of the transportation to the drift tube alignment, we measured the displacement of the drift tube positions before and after the transportation by using a prototype cavity. As a result of the test, the measured displacement of the drift tubes by the transportation was less than 0.02mm which is consistent in the measurement accuracy. Based on this result, all the DTL and SDTL tanks were transported form KEK to JAEA.
Hojo, Kiichi; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Suzuki, Masahide; Hamada, Shozo; Hishinuma, Akimichi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 179-181, p.496 - 499, 1991/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:19.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 O
O in magnetic fields
in magnetic fieldsKatano, Susumu; Tsunoda, Yorihiko*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Shiratori, Kiichi*; Kay, Kohn*; Kita, Eiji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Suzuki, Kiichi; Aono, Shigenori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Kiichi; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Aono, Shigenori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Pu
Pu )O
)O
Suzuki, Kiichi; Kato, Masato; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Uno, Hiroki*; Kashimura, Motoaki; Aono, Shigenori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato; Suzuki, Kiichi; Uno, Hiroki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Kiichi; Takeuchi, Kentaro; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato; Uno, Hiroki*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Suzuki, Kiichi; Shibanuma, Kimikazu; Aono, Shigenori
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English