Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Demachi, Kazuyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(5), p.559 - 567, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.74(Nuclear Science & Technology)Facility design of nuclear power plant for a sabotage protection is investigated and an effect of the design change for damage control on reduction of sabotage risk is shown using the vital area identification methodology. The loss of offsite power leading to the station blackout is assumed to be a typical example for further evaluation. In this study, the vulnerability of target set is defined as the multiplication of the accessibility, the distribution of target and the degree of adversary's interference. The built-in measures for damage control are of vital importance in case of the existence of adversary's interference until neutralization. It is confirmed that not only the physical protection system but also the facility design play an important role in the effective and efficient sabotage protection. It is very important to introduce a security by design approach in an initial stage of the NPP construction while considering the interface between safety and security.
Kikuchi, Masahiro*; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi
Wiley StatsRef; Statistics Reference Online (Internet), 7 Pages, 2018/03
A near-real-time accountancy (NRTA) as a timely statistical test method for nuclear material inventory verification in international safeguards has a unique feature and development history, and it has been maintained and updated in large nuclear facilities in Japan. A recent discussion on approaches of measurement uncertainty may have impacted on the decision criteria of NRTA because its development origin dates back to the 1970's and derived from the conventional random and systematic error model. In this article, we will show the overview associated with this issue.
Suzuki, Mitsutoshi
Risk Assessment, p.133 - 151, 2018/02
A integrated risk assessment could be developed to promote synergism between safety, security, and safeguards (3S). One of the synergies of the integrated 3S risk assessment is a 3S by Design approach for new nuclear facilities. In safety, the classical probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) has been developed to estimate the frequency of severe accident using the basic event frequency. Because of recent concern about nuclear security, a vital area identification method based on the ETs/FTs has been explored to protect vital areas of nuclear power plants against sabotage. The different difficulty in applying risk assessment to safeguards is determining the initiation of diversion of nuclear material and misuse, because the diversion of nuclear material and misuse of technology are induced by the motivation of states and intentional acts of facility operation. In this chapter, a balance among 3S risk would be explored to pursue an optimal and a cost-effective management.
Yamamura, Tsukasa; Suda, Kazunori; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Kuno, Yusuke; Mochiji, Toshiro
JAEA-Review 2014-011, 74 Pages, 2014/03
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency held "International Forum on Peaceful Use of Nuclear Energy, Nuclear Non-proliferation and Nuclear Security; Ensuring Nuclear Non-Proliferation and Nuclear Security of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Options in consideration of the Accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station" on 3 and 4 December 2013. Keynote speakers from Japan, the United States, France and International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), respectively explained their efforts. In two panel discussions, entitled "Nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security measures of nuclear fuel cycle options in consideration of the Accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station" and "Roles of safeguards and technical measures for ensuring nuclear non-proliferation for nuclear fuel cycle options", active discussions were made. This report includes abstracts of keynote speeches, summaries of two panel discussions and materials of the presentations in the forum.
Terao, Norichika; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi
Journal of Physical Security, 7(2), p.12 - 29, 2014/03
The probability of an adversary's interruption, 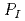 , in a specific scenario can be evaluated using a calculation code, Estimate of Adversary Sequence Interruption (EASI). The purpose of this study is to devise a quantification method of
, in a specific scenario can be evaluated using a calculation code, Estimate of Adversary Sequence Interruption (EASI). The purpose of this study is to devise a quantification method of 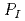 by considering the influence of uncertainty and variability. Specifically, we attempt to devise a new calculation method of three components of
by considering the influence of uncertainty and variability. Specifically, we attempt to devise a new calculation method of three components of 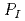 :
: 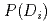 ,
, 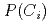 , and
, and 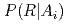 . In addition, we seek to design a hypothetical nuclear facility and an adversary's assault scenario and to assess the
. In addition, we seek to design a hypothetical nuclear facility and an adversary's assault scenario and to assess the 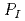 value using our new method. We set the performance data of the facility as temporary values without a real performance test. We attempt to express the uncertainty and variability of each element of the facility using the Monte Carlo method.
value using our new method. We set the performance data of the facility as temporary values without a real performance test. We attempt to express the uncertainty and variability of each element of the facility using the Monte Carlo method.
Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Terao, Norichika
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
Nuclear security risk assessment with the Markov model applied to random events is performed to explore an evaluation methodology for physical protection in nuclear facilities. Because the security incidences are initiated by malicious and intentional acts, expert judgement and Bayes updating are used to estimate scenario and initiation likelihood, and it is assumed that the Markov model can be applied to incidence sequence
Terao, Norichika; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-34-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2013/10
An equation for risk assessment in physical protection is shown by a probability of an adversary attack during a period time, 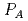 , a probability of system effectiveness,
, a probability of system effectiveness, 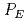 , and consequence value,
, and consequence value, 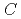 . In addition,
. In addition, 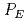 is shown as the multiplication of a probability of interruption of the facility,
is shown as the multiplication of a probability of interruption of the facility, 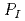 , by a probability of neutralization by response force,
, by a probability of neutralization by response force, 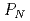 . In this study, it is assumed that an adversary assaults a hypothetical nuclear facility. The new quantification method about
. In this study, it is assumed that an adversary assaults a hypothetical nuclear facility. The new quantification method about 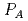 and
and 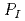 in risk evaluation formula is devised, and risk assessment is attempted. In case of
in risk evaluation formula is devised, and risk assessment is attempted. In case of 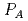 , the possibility of assaults against a nuclear facility is discussed by using terrorism data written in the open source database of terrorism, Global Terrorism database (GTD), summarized by University of Maryland. In addition, it is discussed about
, the possibility of assaults against a nuclear facility is discussed by using terrorism data written in the open source database of terrorism, Global Terrorism database (GTD), summarized by University of Maryland. In addition, it is discussed about 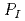 by using the way of thinking of a risk assessment tool, EASI, developed by the Sandia National Laboratories (SNL). In the hypothetical nuclear facility, the performance of response force, sensors, and communication is expressed quantitatively by probability distribution based on some assumptions.
by using the way of thinking of a risk assessment tool, EASI, developed by the Sandia National Laboratories (SNL). In the hypothetical nuclear facility, the performance of response force, sensors, and communication is expressed quantitatively by probability distribution based on some assumptions.
Terao, Norichika; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi
Proceedings of INMM 54th Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2013/07
As a new trial on probabilistic risk assessment in nuclear security field, system effectiveness of physical protection is evaluated in terms of interruption probability considering variation of detection and communication performance. Although the Estimate of Adversary Sequence Interruption (EASI) developed by Sandia National Laboratory has been used worldwide, actual and realistic effect due to fluctuation of signals from sensors and monitoring cameras is not taken into account. Probability distribution of detection and communication variables is introduced into the EASI method to calculate the overall performance of interruption, and system effectiveness is investigated by using a hypothetical model of nuclear facility. Distribution of interruption probability is numerically calculated through detection and communication probabilities with a Monte Carlo method using the normal random number.
Tazaki, Makiko; Yamamura, Tsukasa; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Kuno, Yusuke; Mochiji, Toshiro
JAEA-Review 2013-001, 76 Pages, 2013/03
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency held "International Forum on Nuclear Energy, Nuclear Non-proliferation and Nuclear Security; Measures to ensure nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security for the back end of nuclear fuel cycle and regional cooperation in Asia" on 12 and 13 December 2012. In the forum, 5 keynote speakers respectively explained their views and efforts regarding challenges for peaceful use of nuclear energy and nuclear non-proliferation. In two panel discussions, entitled "Measures to ensure nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security of nuclear fuel cycle back end" and "Measures to ensure nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security for nuclear energy use in the Asian region and a multilateral cooperative framework", active discussions were initiated among panelists. This report includes abstracts of keynote speeches, summaries of two panel discussions and materials of the presentations in the forum.
Kuno, Yusuke; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Yamamura, Tsukasa; Tazaki, Makiko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 55(2), p.111 - 116, 2013/02
, 55(2), p.111 - 116, 2013/02
This article discusses issues on direct disposal of spent fuel and recovered plutonium from reprocessing, and described the international communities' concerns at Japanese nuclear policy change. Some options to be studied for SF and plutonium handling are also discussed.
Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Iwabuchi, Junichi*; Kasai, Yoshimitsu*; Kuno, Yusuke; Mochiji, Toshiro
JAEA-Review 2012-044, 109 Pages, 2013/01
JAEA has worked for the contribution to the world disarmament and nonproliferation through the United States and Russia cooperation on the excess weapon plutonium disposition from Russian as well as to acquire the basic data of the post irradiation test with the BN-600 and the vibropack MOX fuel fabrication technologies. To support the initiative of Japan government, JAEA has started the joint research activities with some of the Russian national laboratories under the MINATOM in 1999. Since then, JAEA has been involved into the demonstration experiment for the vibropack fuel irradiation with the BN-600 that was managed by the PESCO corp. under the contract with MEXT. The joint researches with Russian national laboratories and the demonstration studies on vibropac MOX fuel assemblies from 1999 to 2011 are surmmarized in this document.
Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Terao, Norichika
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, 2013, p.590684_1 - 590684_10, 2013/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Solution monitoring (SM) has been used in a nuclear reprocessing plant as an additional measure to provide assurance that the plant is operated as declared. Recently safety, safeguards, and security by design (3SBD) is proposed to promote an efficient and effective generation of nuclear energy. In 3SBD, proliferation risk assessment has the potential to consider likelihood of the incidence and proliferation risk in safeguards. In this study, risk assessment methodologies for safeguards and security are discussed and several mathematical methods are presented to investigate risk notion applied to intentional acts of facility misuse in an uncertainty environment. Proliferation risk analysis with the Markov model, deterrence effect with the game model, and SBD with fuzzy optimization are shown in feasibility studies to investigate the potential application of the risk and uncertainty analyses in safeguards.
Tazaki, Makiko; Suda, Kazunori; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Kuno, Yusuke; Mochiji, Toshiro
JAEA-Review 2012-021, 83 Pages, 2012/06
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) held "2011 International Forum on the Peaceful Use of Nuclear Energy and Nuclear Security; Taking the lessons learned from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident to the 2012 Seoul Nuclear Security Summit" on 8 and 9 December, 2011. It intended to articulate effective strategies and measures for strengthening nuclear security using lessons learned from the Fukushima nuclear accident. Moreover, it was expected to explore comprehensive approaches which could contribute to enhancing both nuclear safety and security in order to support sustainable and appropriate development of the peaceful use of nuclear energy. This report includes abstracts of keynote speeches, summary of panel discussions and materials of the presentations in the forum.
Suda, Kazunori; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Mochiji, Toshiro
AIP Conference Proceedings 1448, p.16 - 21, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japan, a non-nuclear weapons state, has established a commercial nuclear fuel cycle including LWRs, and now is developing a fast neutron reactor fuel cycle as part of the next generation nuclear energy system, with commercial operation targeted for 2050. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is the independent administrative agency for conducting comprehensive nuclear R&D in Japan after the merger of Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) and Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC). JAEA and its predecessors have extensive experience in R&D, facility operations, and safeguards development and implementation for new types of nuclear facilities for the peaceful use of nuclear energy. As the operator of various nuclear fuel cycle facilities and numerous nuclear materials, JAEA makes international contributions to strengthen nuclear non-proliferation. This paper provides an overview of JAEA's development of nuclear non-proliferation and safeguards technologies, including remote monitoring of nuclear facilities, environmental sample analysis methods and new efforts since the 2010 Nuclear Security Summit in Washington D.C.
Permana, S.; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Zaki, S.*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1448, p.119 - 125, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nuclear fuel materials from spent fuel of light water reactors have a potential to be used for destructive devices with very huge energy release or in the same time, it can be utilized as a peaceful energy or civil applications, for generating electricity, desalination of water, medical application and others applications. Several research activities showed some recycled spent fuel can be used as additional fuel loading for increasing fuel breeding capability as well as improving intrinsic aspect of nuclear non-proliferation. The present investigation intends to evaluate the composition of heavy metals inventories and fuel breeding capability in the FBR design based on the loaded fuel of light water reactor (LWR) spent fuel (SF) based on the LWR SF composition of 33 GWd/t with 5 years cooling time by adopting depletion code of ORIGEN.
Shimizu, Ryo; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Sakurai, Satoshi; Tamai, Hiroshi; Yamamura, Tsukasa; Naoi, Yosuke; Kuno, Yusuke
JAEA-Review 2011-038, 116 Pages, 2012/02
International forum on peaceful use of nuclear energy and nuclear non-proliferation was held at Gakushi-kaikan, Tokyo on February 2-3, 2011 in cooperation with The Japan Institute of International Affairs (JIIA) and The University of Tokyo Global COE. In our International Forum, we would like to encourage active discussion of international challenges to and solutions for compatibility between peaceful use of nuclear energy and nuclear non-proliferation, and international cooperation for emerging nuclear energy states. It was successfully carried out with as many as 310 participants and a lot of discussions. This report includes abstracts of keynote speeches, summary of panel discussions and materials of the presentations in the forum.
Burr, T.*; Hamada, M. S.*; Howell, J.*; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 49(2), p.209 - 221, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)Solution monitoring (SM) is a type of process monitoring (PM) intended to improve nuclear safeguards in facilities such as reprocessing plants. In SM, volume (V) and mass (M) are monitored in each tank-to-tank transfer and during all wait modes for each tank, resulting in residuals that arise by comparing observations to predictions. The main performance measure is the estimated loss detection probability (DP) for material loss scenarios. This report re-estimates DPs when realistic effects are included in simulated data, such as pump carryover, evaporation, condensation, and mixing/sparging. One challenge involves the need for SM to be part of day-to-day assessment without leading to too many alarms, so we widen the control limits to avoid alarming on innocent process variation effects.
Permana, S.; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Suud, Z.*; Saito, Masaki*
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2011/12
Spent fuel (SF) of light water reactors (LWR) is loaded to increase breeding capability and intrinsic aspect of proliferation resistance. This present study intends to evaluate the effect of different loaded doping materials in the blanket region of FBR to the reactor performance and plutonium proliferation resistance level. Basic reactor operation is adjusted to reach 800 days operation by adopting 4 fuel batches systems of Japan Sodium Fast Reactor (JSFR) design. LWR plutonium compositions of Isotopic  Pu and
Pu and  Pu show more sensitive to the decay time due to it shorter half-life which affect to the vector composition of plutonium as well as minor actinide (MA) as a function of decay time.
Pu show more sensitive to the decay time due to it shorter half-life which affect to the vector composition of plutonium as well as minor actinide (MA) as a function of decay time.
Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Demuth, S.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Toward and Over the Fukushima Daiichi Accident (GLOBAL 2011) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/12
Proliferation risk assessment has been investigated to develop a performance-based approach in which the likelihood of diversion incidence, as well as the uncertainty of nuclear material accounting, is simultaneously considered to install intrinsic and extrinsic countermeasures in a conceptual design of a future reprocessing facility. A simulation and modeling approach has been applied to evaluate safeguards performance in a facility-level and diversion pathway analysis, which is demonstrated to detect more efficiently a small, protracted diversion that is usually investigated by trend analysis.
Permana, S.; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Saito, Masaki*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2011/10
Trans-uranium (TRU) compositions of LWR and multi-cycle FBR have been loaded in the FBR design by adopting 4 fuel batches system. 800 days of cycle length was used to investigate the proliferation resistance of plutonium as well as core performance, during reactor operation. Different compositions of TRU as initial fuel composition affect to the fuel behavior, criticality condition and fuel breeding capability. It shows less excess reactivity and better fuel breeding for MA doping in the core. High decay heat (DH) and spontaneous fission neutron (SFN) compositions of plutonium which is mainly caused by high production of even mass of plutonium isotopes will be compared from both typical trans-uranium compositions of LWR and FBR.