Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamashita, Takuya; Honda, Takeshi*; Mizokami, Masato*; Nozaki, Kenichiro*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Pellegrini, M.*; Sakai, Takeshi*; Sato, Ikken; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Technology, 209(6), p.902 - 927, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:90.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)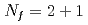 lattice QCD with chiral fermions
lattice QCD with chiral fermionsAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Kanamori, Issaku*; Kaneko, Takashi*; Nakamura, Yoshifumi*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 396, p.332_1 - 332_7, 2022/07
The axial U(1) anomaly in high-temperature QCD plays an important role to understand the phase diagram of QCD. The previous works by JLQCD Collaboration studied high-temperature QCD using 2-flavor dynamical chiral fermions such as the domain-wall fermion and reweighted overlap fermion. We extend our simulations to QCD with 2+1-flavor dynamical quarks, where the masses of the up, down, and strange quarks are near the physical point, and the temperatures are close to or higher than the pseudocritical temperature. In this talk, we will present the results for the Dirac spectrum, topological susceptibility, axial U(1) susceptibility, and hadronic collelators.
Aoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 396, p.050_1 - 050_9, 2022/07
In the early days of QCD, the axial  anomaly was considered as a trigger for the breaking of the
anomaly was considered as a trigger for the breaking of the 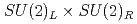 symmetry through topological excitations of gluon fields. However, it has been a challenge for lattice QCD to quantify the effect. In this work, we simulate QCD at high temperatures with chiral fermions. The exact chiral symmetry enables us to separate the contribution from the axial
symmetry through topological excitations of gluon fields. However, it has been a challenge for lattice QCD to quantify the effect. In this work, we simulate QCD at high temperatures with chiral fermions. The exact chiral symmetry enables us to separate the contribution from the axial  breaking from others among the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that the chiral susceptibility, which is conventionally used as a probe for
breaking from others among the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that the chiral susceptibility, which is conventionally used as a probe for 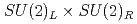 breaking, is actually dominated by the axial
breaking, is actually dominated by the axial  breaking at temperatures
breaking at temperatures 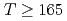 MeV.
MeV.
 anomaly in the chiral susceptibility of QCD at high temperature
anomaly in the chiral susceptibility of QCD at high temperatureAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(2), p.023B05_1 - 023B05_12, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:81.66(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The chiral susceptibility, or the first derivative of the chiral condensate with respect to the quark mass, is often used as a probe for the QCD phase transition since the chiral condensate is an order parameter of 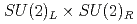 symmetry breaking. However, the chiral condensate also breaks the axial
symmetry breaking. However, the chiral condensate also breaks the axial  symmetry, which is usually not studied as it is already broken by the anomaly and apparently has little impact on the transition. We investigate the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels in order to quantify how much the axial
symmetry, which is usually not studied as it is already broken by the anomaly and apparently has little impact on the transition. We investigate the susceptibilities in the scalar and pseudoscalar channels in order to quantify how much the axial  breaking contributes to the chiral phase transition. Employing a chirally symmetric lattice Dirac operator and its eigenmode decomposition, we separate the axial
breaking contributes to the chiral phase transition. Employing a chirally symmetric lattice Dirac operator and its eigenmode decomposition, we separate the axial  breaking effects from others. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that both of the connected and disconnected chiral susceptibilities are dominated by axial
breaking effects from others. Our result in two-flavor QCD indicates that both of the connected and disconnected chiral susceptibilities are dominated by axial  breaking at temperatures
breaking at temperatures 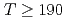 MeV after the quadratically divergent constant is subtracted.
MeV after the quadratically divergent constant is subtracted.
 anomaly at high temperature with lattice chiral fermions
anomaly at high temperature with lattice chiral fermionsAoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Kaneko, Takashi*; Rohrhofer, C.*; Suzuki, Kei
Physical Review D, 103(7), p.074506_1 - 074506_18, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:72(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We investigate the axial  anomaly of two-flavor QCD at temperatures 190-330 MeV. In order to preserve precise chiral symmetry on the lattice, we employ the M
anomaly of two-flavor QCD at temperatures 190-330 MeV. In order to preserve precise chiral symmetry on the lattice, we employ the M bius domain-wall fermion action as well as overlap fermion action implemented with a stochastic reweighting technique. Compared to our previous studies, we reduce the lattice spacing to 0.07 fm, simulate larger multiple volumes to estimate finite size effect, and take more than four quark mass points, including one below physical point to investigate the chiral limit. We measure the topological susceptibility, axial
bius domain-wall fermion action as well as overlap fermion action implemented with a stochastic reweighting technique. Compared to our previous studies, we reduce the lattice spacing to 0.07 fm, simulate larger multiple volumes to estimate finite size effect, and take more than four quark mass points, including one below physical point to investigate the chiral limit. We measure the topological susceptibility, axial  susceptibility, and examine the degeneracy of
susceptibility, and examine the degeneracy of  partners in meson/baryon correlators. All the data above the critical temperature indicate that the axial
partners in meson/baryon correlators. All the data above the critical temperature indicate that the axial  violation is consistent with zero within statistical errors. The quark mass dependence suggests disappearance of the
violation is consistent with zero within statistical errors. The quark mass dependence suggests disappearance of the  anomaly at a rate comparable to that of the
anomaly at a rate comparable to that of the 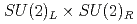 symmetry breaking.
symmetry breaking.
Yamashita, Takuya; Sato, Ikken; Honda, Takeshi*; Nozaki, Kenichiro*; Suzuki, Hiroyuki*; Pellegrini, M.*; Sakai, Takeshi*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Technology, 206(10), p.1517 - 1537, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:86.19(Nuclear Science & Technology)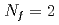 lattice QCD
lattice QCDSuzuki, Kei; Aoki, Shinya*; Aoki, Yasumichi*; Cossu, G.*; Fukaya, Hidenori*; Hashimoto, Shoji*; Rohrhofer, C.*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 363, p.178_1 - 178_7, 2020/08
We investigate the high-temperature phase of QCD using lattice QCD simulations with 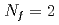 dynamical M
dynamical M bius domain-wall fermions. On generated configurations, we study the axial
bius domain-wall fermions. On generated configurations, we study the axial  symmetry, overlap-Dirac spectra, screening masses from mesonic correlators, and topological susceptibility. We find that some of the observables are quite sensitive to lattice artifacts due to a small violation of the chiral symmetry. For those observables, we reweight the M
symmetry, overlap-Dirac spectra, screening masses from mesonic correlators, and topological susceptibility. We find that some of the observables are quite sensitive to lattice artifacts due to a small violation of the chiral symmetry. For those observables, we reweight the M bius domain-wall fermion determinant by that of the overlap fermion. We also check the volume dependence of observables. Our data near the chiral limit indicates a strong suppression of the axial
bius domain-wall fermion determinant by that of the overlap fermion. We also check the volume dependence of observables. Our data near the chiral limit indicates a strong suppression of the axial  anomaly at temperatures
anomaly at temperatures  220 MeV.
220 MeV.
 Co
Co O
O film
filmHu, W.*; Hayashi, Koichi*; Fukumura, Tomoteru*; Akagi, Kazuto*; Tsukada, Masaru*; Happo, Naohisa*; Hosokawa, Shinya*; Owada, Kenji; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Suzuki, Motohiro*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 106(22), p.222403_1 - 222403_5, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:81.57(Physics, Applied) Mn
Mn Te by X-ray fluorescence holography
Te by X-ray fluorescence holographyHappo, Naohisa*; Tekehara, Yuki*; Fujiwara, Makoto*; Tanaka, Koichi*; Semba, Shinya*; Hosokawa, Shinya*; Hayashi, Koichi*; Hu, W.; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Asada, Hironori*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 9, p.247 - 250, 2011/06
 Mn
Mn Te investigated by X-ray fluorescence holography
Te investigated by X-ray fluorescence holographyHappo, Naohisa*; Tekehara, Yuki*; Fujiwara, Makoto*; Tanaka, Koichi*; Semba, Shinya*; Hosokawa, Shinya*; Hayashi, Koichi*; Hu, W.; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Asada, Hironori*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 50(5), p.05FC11_1 - 05FC11_2, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.4(Physics, Applied) Fe
Fe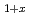 Mo
Mo O
O (0
(0  x
x 1)
1)Yoshida, Koji*; Ikeuchi, Shinya*; Shimizu, Hajime*; Okayasu, Satoru; Suzuki, Takashi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(4), p.044716_1 - 044716_4, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.92(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We studied systematic changes of the structural, electric, and magnetic properties in Sr Fe
Fe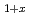 Mo
Mo O
O with 0
with 0  x
x  1, which bridges between a half-metallic double perovskite Sr
1, which bridges between a half-metallic double perovskite Sr FeMoO
FeMoO (x = 0) and an antiferromagnetic metal SrFeO
(x = 0) and an antiferromagnetic metal SrFeO (= Sr
(= Sr Fe
Fe O
O : x = 1). The lattice volume at room temperature linearly decreases with x. The decline steeply enhances around x = 0.5, which is accompanied with a symmetry change from a tetragonal to a cubic crystal structure. In the same composition, we also found changes in the electronic ground state from a metal to an insulator and in the magnetic one from ferromagnetism to paramagnetism. These results indicate the strong correlation among the crystal structure, itinerant electrons and occurrence of ferromagnetic state in the double perovskite. In addition, the value of the critical composition could reflect peculiar physical changes with x.
: x = 1). The lattice volume at room temperature linearly decreases with x. The decline steeply enhances around x = 0.5, which is accompanied with a symmetry change from a tetragonal to a cubic crystal structure. In the same composition, we also found changes in the electronic ground state from a metal to an insulator and in the magnetic one from ferromagnetism to paramagnetism. These results indicate the strong correlation among the crystal structure, itinerant electrons and occurrence of ferromagnetic state in the double perovskite. In addition, the value of the critical composition could reflect peculiar physical changes with x.
 :Mn by X-ray fluorescence holography
:Mn by X-ray fluorescence holographyHayashi, Koichi*; Uchitomi, Naotaka*; Asubar, J. T.*; Happo, Naohisa*; Hu, W.; Hosokawa, Shinya*; Suzuki, Motohiro*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 50(1), p.01BF05_1 - 01BF05_4, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.79(Physics, Applied)Yamamoto, Shinya*; Honda, Makoto*; Sakurai, Hideyuki*; Suzuki, Makoto*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka; Matsui, Hiroya
Proceedings of 14th Annual Conference of the International Association for Mathematical Geosciences (IAMG 2010) (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2010/09
The distribution of groundwater properties is important for understanding of the deep underground hydrogeological environments in the design of the HLW disposal facilities. This study proposes a geostatistical system for modeling the chemical properties of groundwater which have a correlation with the resistivity data obtained from widespread and exhaustive survey. The proposed system is consists of two methodologies (resistivity data integration using Simple Kriging with varying local mean (SKlm) and 3D distribution modeling of hydro-chemical properties of groundwater estimated by SKlm algorithm). 2 types of uncertainty are considered: (1) Aleatory uncertainty; (2) Epistemic uncertainty. As a result, the uncertainties of the proposal model have been estimated lower than other traditional model's.
Honda, Makoto*; Yamamoto, Shinya*; Sakurai, Hideyuki*; Suzuki, Makoto*; Sanada, Hiroyuki; Sugita, Yutaka; Matsui, Hiroya
Doboku Gakkai Rombunshu, C, 66(3), p.609 - 624, 2010/08
This paper proposes a geostatistical system for modeling the groundwater properties which have a correlation with the ground resistivity data obtained from widespread and exhaustive electromagnetic survey. That is, the methodology for the integration of resistivity data measured by various methods and the methodology for modeling the groundwater properties using the integrated resistivity data has been developed. The proposed system has also been validated using the data obtained in the surface-based investigations of the Horonobe URL project. Additionally, the quantification of uncertainties in the estimated model has been tried by numerical simulations based on the data. As a result, the uncertainties of the proposal model have been estimated lower than other traditional model's.
 -ray detection
-ray detectionInoshita, Shinya*; Suzuki, Shogo*; Okada, Yukiko*; Kato, Masahiko*; Hirai, Shoji*; Kimura, Atsushi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Toh, Yosuke; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Oshima, Masumi
Tetsu To Hagane, 94(9), p.345 - 350, 2008/09
"Tatara" is Japanese original steel making method. Steel made by "Tatara" is famous as low alloy and suited to "Kaji" process. By authors' study, it turned out that we could estimate the source region of raw material of Tatara by As and Sb concentration ratio in Tatara sample. But the concentration of these element in Tatara sample is very low (ppm or sub-ppm order), therefore, quantitative analysis is very difficult. In this study, we adopted Neutron Activation Analysis combined with Multiple  -ray detection (NAAMG) to analyze As and Sb in "Tatara" sample (iron lump and sand iron, slag). NAAMG is high sensitive and non-destructive analysis method which combined NAA (Neutron Activation Analysis) and multiple
-ray detection (NAAMG) to analyze As and Sb in "Tatara" sample (iron lump and sand iron, slag). NAAMG is high sensitive and non-destructive analysis method which combined NAA (Neutron Activation Analysis) and multiple  -ray detectors. Each "Tatara" sample (iron lump, sand iron, slag) were irradiated for 1-2 h (for As measurement), 8-17 h (for Sb measurement) in JRR-3M HR irradiation field (thermal neutron flux was about 9.0
-ray detectors. Each "Tatara" sample (iron lump, sand iron, slag) were irradiated for 1-2 h (for As measurement), 8-17 h (for Sb measurement) in JRR-3M HR irradiation field (thermal neutron flux was about 9.0 10
10 n/m
n/m  s
s ). And cooling time was 4-5 days (As), and 19-36 days (Sb). Coincidence
). And cooling time was 4-5 days (As), and 19-36 days (Sb). Coincidence  -rays were measured by
-rays were measured by  -ray detector array, GEMINI-II. Counting time was 1-8 hours (As), and 2-41 hours (Sb). Quantification was made by comparison method. As a result of measurement, the concentration of As and Sb in all "Tatara" samples were determined by NAAMG and these were sub-ppm order. Lower Limit of Determination (LLD) of As was 0.1 ppm order and Sb is 0.01ppm order. From the above-mentioned point, the effectiveness of NAAMG to analyze trace element in "Tatara" sample was confirmed.
-ray detector array, GEMINI-II. Counting time was 1-8 hours (As), and 2-41 hours (Sb). Quantification was made by comparison method. As a result of measurement, the concentration of As and Sb in all "Tatara" samples were determined by NAAMG and these were sub-ppm order. Lower Limit of Determination (LLD) of As was 0.1 ppm order and Sb is 0.01ppm order. From the above-mentioned point, the effectiveness of NAAMG to analyze trace element in "Tatara" sample was confirmed.
Totsuka, Toshiyuki; Suzuki, Yoshio; Sakata, Shinya; Oshima, Takayuki; Iba, Katsuyuki*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(2-3), p.287 - 290, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kawamata, Yoichi; Naito, Osamu; Kiyono, Kimihiro; Itami, Kiyoshi; Totsuka, Toshiyuki; Akasaka, Hiromi; Sueoka, Michiharu; Sato, Tomoki; Oshima, Takayuki; Sakata, Shinya; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(2-3), p.198 - 201, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.55(Nuclear Science & Technology)The design activity of JT-60SA (JT-60 Super Advanced) which is remodeled to a superconducting tokamak device has been starting under the JA-EU collaborative ITER-BA project. For the JT-60SA control system, the existing system should be reused as much as possible from the viewpoint of cost-effectiveness. We have just begun to discuss the configuration of the advanced Supervisory Control System (SVCS) including the following systems: (1) ultimately flexible real-time control system, (2) precise timing system enough to clarify cause and effect, and (3) safety shutdown control system. In this report, we present the design study of the JT-60SA SVCS with focusing on these systems.
Iba, Katsuyuki*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Totsuka, Toshiyuki; Suzuki, Yoshio; Oshima, Takayuki; Sakata, Shinya; Sato, Minoru; Suzuki, Mitsuhiro; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Kiyono, Kimihiro
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(2-3), p.495 - 497, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)Fusion research grid is an environment of collaborative researches using a network that connects scientists far apart and let them collaborate effectively over the difference in time and distance in a nuclear fusion research. Fundamental technology of Fusion research grid has been developed at JAEA in the VizGrid project under the e-Japan project at Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). Remote research environments of experiments, diagnostics, analyses and communications were developed on Fusion research grid. We have developed prototype systems that include a remote experiment system, a remote diagnostics system, and a remote analysis system. All users can access these systems from anywhere because Fusion research grid does not required closed network like Super SINet to maintain security. The prototype systems were verified in experiments at JT-60U and their availability was confirmed.
Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Fujita, Takaaki; Hosoyama, Hiroki; Kamada, Yutaka; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; Oyama, Naoyuki; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 933, p.229 - 236, 2007/10
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Takahiro; Isayama, Akihiko; Ide, Shunsuke; Fujita, Takaaki; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Sakata, Shinya; Sueoka, Michiharu; Hosoyama, Hiroki*; Seki, Masami; JT-60 Team
AIP Conference Proceedings 787, p.279 - 286, 2005/09
A real-time control system of safety factor (q) profile was developed in JT-60. This system, for the first time, enables 1) real time evaluation of q profile using local magnetic pitch angle measurement by motional Stark effect (MSE) diagnostic and 2) control of current drive (CD) location (rhoCD) by adjusting the parallel refractive index 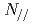 of lower-hybrid (LH) waves through the change of phase difference (dphi) of LH waves between multi-junction launcher modules. The method for q profile evaluation was newly developed, without time-consuming reconstruction of equilibrium, so that the method requires less computational time. The system evaluates q profile within every 10ms, which is much faster than current relaxation time, typically order of 1s. Safety factor profile by the real-time calculation agreed well with that by equilibrium reconstruction with MSE. From temporal evolution of q (or current) profile, we evaluate CD location in real-time, too. The control system controls rhoCD through
of lower-hybrid (LH) waves through the change of phase difference (dphi) of LH waves between multi-junction launcher modules. The method for q profile evaluation was newly developed, without time-consuming reconstruction of equilibrium, so that the method requires less computational time. The system evaluates q profile within every 10ms, which is much faster than current relaxation time, typically order of 1s. Safety factor profile by the real-time calculation agreed well with that by equilibrium reconstruction with MSE. From temporal evolution of q (or current) profile, we evaluate CD location in real-time, too. The control system controls rhoCD through 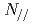 (or directly dphi) in such a way to minimize difference between the real-time evaluated q profile and its reference profile. The real-time control system was applied to positive shear plasmas (
(or directly dphi) in such a way to minimize difference between the real-time evaluated q profile and its reference profile. The real-time control system was applied to positive shear plasmas (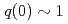 ), having plasma current of 0.6MA, toroidal field of 2.3T, and electron density of
), having plasma current of 0.6MA, toroidal field of 2.3T, and electron density of 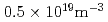 . In order to keep good coupling of LH waves to the plasma, gap between the launcher and the plasma surface was controlled to about 0.1m. The reference q profile was set to q(0)=1.3. The real-time q profile approached to the reference after application of real-time control; the controlled q profile was sustained for 3s, which was limited by injected LH power. RF experiments in JT-60U, such as stabilization of neo-classical tearing modes, plasma startup experiments, etc., are also presented.
. In order to keep good coupling of LH waves to the plasma, gap between the launcher and the plasma surface was controlled to about 0.1m. The reference q profile was set to q(0)=1.3. The real-time q profile approached to the reference after application of real-time control; the controlled q profile was sustained for 3s, which was limited by injected LH power. RF experiments in JT-60U, such as stabilization of neo-classical tearing modes, plasma startup experiments, etc., are also presented.