Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Goto, Yuichi; Suzuki, Yoshimasa; Horigome, Kazushi; Miyamoto, Toshihiko*; Usui, Masato*; Mori, Eito*; Kuno, Takehiko
JAEA-Technology 2022-005, 42 Pages, 2022/07
Radioactive wastes were generated and stored in the hot cell of Operation Testing Laboratory of Tokai Reprocessing Plant due to the experiments related to the reprocessing technology development from 1974 to 2014. Waste removal work was strengthened by the shift work in the past, however another wastes were generated by the equipment dismantling. From 2006, an improved waste removal method was established by using bag-out technique and wastes were taken from the glove-box connected to the hot cell. The removal period, estimated from the conventional method using Cask No. 10, was reduced from 14 to 5 years. From 2016, upgrade of worker's awareness including related departments was performed by various software and hardware improvements. Also, the worker's skills were improved and equipment in Cask No.10 was checked for preventive maintenance. The prevention measures for past troubles were discussed with Radiation Control Department. In addition, transportation schedule including safety operation with Transportation Department and Waste Receiving Department was optimized to maintain the waste removal cycle. The removal period was reduced from 5 to 3 years by the above efforts. Finally, the work was completed in March 2020.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Tsukahara, Takehiko*; Saga, Kaname*; Suzuki, Hideya*; Matsumura, Tatsuro
Kurin Tekunoroji, 29(12), p.4 - 7, 2019/12
no abstracts in English
 -isopropylacrylamide) with diglycolamide-typed ligands
-isopropylacrylamide) with diglycolamide-typed ligandsSaga, Kaname*; Suzuki, Hideya; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Tsukahara, Takehiko*
Analytical Sciences, 35(4), p.461 - 464, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:7.76(Chemistry, Analytical)The phase transition-based gelification phenomenon of poly- -isopropylacrylamide (PNIPAAm) in aqueous solutions has a great potential in developing new waste-free extraction processes of metal ions. By using hydrophobic diglycolamide-typed ligands in gelification extraction, a one-step complete extraction of all the RE ions from a nitric acid solution was successfully realized.
-isopropylacrylamide (PNIPAAm) in aqueous solutions has a great potential in developing new waste-free extraction processes of metal ions. By using hydrophobic diglycolamide-typed ligands in gelification extraction, a one-step complete extraction of all the RE ions from a nitric acid solution was successfully realized.
Tsukahara, Takehiko*; Suzuki, Hideya*; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Saga, Kaname*
Bunri Gijutsu, 49(4), p.221 - 225, 2019/04
no abstracts in English
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:259 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Suzuki, Yoshimasa; Tanaka, Naoki; Goto, Yuichi; Inada, Satoshi; Kuno, Takehiko
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-14-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.385 - 389, 2017/08
Greenhouse is used in order to prevent diffusion of radioactive materials on the maintenance of machineries and decomposition of the analytical equipment such as glove box in Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP). The specifications of the greenhouse change depending on a risk of the radiation exposure, operation and environment. Design and application of original greenhouses in the analytical laboratory of TRP is summarized.
 2015.12
2015.12Horigome, Kazushi; Suzuki, Hisanori; Suzuki, Yoshimasa; Ishibashi, Atsushi; Taguchi, Shigeo; Inada, Satoshi; Kuno, Takehiko; Surugaya, Naoki
JAEA-Technology 2016-026, 21 Pages, 2016/12
In order to mitigate potential hazards of storage plutonium in solution such as hydrogen generation, conversion of plutonium solution into MOX powder has been carried out since 2014 in the Plutonium Conversion Development Facility. With respect to the samples taken from the conversion process, about 3500 items of plutonium/uranium solutions and MOX powders have been analyzed for the operation control in the related analytical laboratories at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant. This paper describes the reports on analytical activities and related maintenance works in the analytical laboratories conducted from April 2014 to December 2015.
Takahashi, Naoki; Yoshinaka, Kazuyuki; Harada, Akio; Yamanaka, Atsushi; Ueno, Takashi; Kurihara, Ryoichi; Suzuki, Soju; Takamatsu, Misao; Maeda, Shigetaka; Iseki, Atsushi; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Homu Peji (Internet), 64 Pages, 2016/00
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Akifumi; Suzuki, Takehiko; Takahashi, Masa; Nakata, Toru; Murayama, Takashi; Tsunoda, Masahiko
JAEA-Technology 2014-049, 19 Pages, 2015/03
Optically Stimulated Luminescence, OSL, dosimeters have been used as individual dosimeters for external radiation in Nuclear Science Research Institute and so on since October, 2014 as successor of the RPL glass dosimeters. Characteristics of the OSL dosimeters such as dose linearity, energy response, angular dependence, fading characteristics and responses at mixed irradiation fields were examined prior to the start of use. As a result, it was found that the OSL dosimeters met the performances that the national standard (JIS Z 4339) determined. The characteristics of OSL dosimeters were comparable with those of the RPL glass dosimeters. In conclusion, it was confirmed the OSL dosimeters had sufficient performances for the practical use on individual monitoring. This report shows the testing methods and the results for the characteristics of OSL dosimeters.
Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hoashi, Eiji*; Fukada, Satoshi*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Yagi, Juro*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of Plasma Conference 2014 (PLASMA 2014) (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2014/11
In the IFMIF/EVEDA (International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility/ Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activity), the validation tests of the EVEDA lithium test loop with the world's highest flow rate of 3000 L/min was succeeded in generating a 100 mm-wide and 25 mm-thick free-surface lithium flow steadily under the IFMIF operation condition of a high-speed of 15 m/s at 250 C in a vacuum of 10
C in a vacuum of 10  Pa. Some excellent results of the recent engineering validations including lithium purification, lithium safety, and remote handling technique were obtained, and the engineering design of lithium facility was also evaluated. These results will advance greatly the development of an accelerator-based neutron source to simulate the fusion reactor materials irradiation environment as an important key technology for the development of fusion reactor materials.
Pa. Some excellent results of the recent engineering validations including lithium purification, lithium safety, and remote handling technique were obtained, and the engineering design of lithium facility was also evaluated. These results will advance greatly the development of an accelerator-based neutron source to simulate the fusion reactor materials irradiation environment as an important key technology for the development of fusion reactor materials.
 -methyltyrosine (FAMT) uptake on PET in patients with oesophageal cancer
-methyltyrosine (FAMT) uptake on PET in patients with oesophageal cancerSuzuki, Shigemasa*; Kaira, Kyoichi*; Ohshima, Yasuhiro; Ishioka, Noriko; Soda, Makoto*; Yokobori, Takehiko*; Miyazaki, Tatsuya*; Oriuchi, Noboru*; Tominaga, Hideyuki*; Kanai, Yoshikatsu*; et al.
British Journal of Cancer, 110(8), p.1985 - 1991, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:60.43(Oncology)
Sakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Shimozawa, Yoko; Fukamoto, Kana*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sora, Sakura*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
Biological Sciences in Space, 26, p.21 - 25, 2012/10
High linear energy transfer (LET) radiation is important cosmic rays that has neurobiological effects: it is known to induce conditioned taste aversion, and suppress neurogenesis that may underlie cognitive impairment. However, the impact of high-LET radiation on other learning effects remains largely unknown. Here, we focus on kinetics of the radiation response for the salt chemotaxis learning (SCL) behavior in the nameatode,  , because the SCL during the learning conditioning was modulated after low-LET
, because the SCL during the learning conditioning was modulated after low-LET  -irradiation. Firstly, the SCL ability was examined following high-LET irradiation (
-irradiation. Firstly, the SCL ability was examined following high-LET irradiation ( C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/
C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/ m), revealing its dose-dependent decrease after high- and low-LET exposure. Next, we demonstrate that the SCL at the early phase of the learning conditioning is greatly affected by high- and low-LET irradiation, and interestingly, the magnitude of these effects by high-LET radiation was smaller than that by low-LET one. Moreover, the analysis of
m), revealing its dose-dependent decrease after high- and low-LET exposure. Next, we demonstrate that the SCL at the early phase of the learning conditioning is greatly affected by high- and low-LET irradiation, and interestingly, the magnitude of these effects by high-LET radiation was smaller than that by low-LET one. Moreover, the analysis of 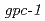 mutant showed that the G-protein
mutant showed that the G-protein  subunit, GPC-1 is responsible for such early phase response. This study is the first to provide the evidence for the kinetics of changes in SCL after high-LET irradiation of C.
subunit, GPC-1 is responsible for such early phase response. This study is the first to provide the evidence for the kinetics of changes in SCL after high-LET irradiation of C. 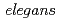 .
.
 against high-LET radiation exposure
against high-LET radiation exposureSakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Shimozawa, Yoko; Fukamoto, Kana*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sora, Sakura*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
Biological Sciences in Space, 26, p.7 - 11, 2012/07
Here, we investigated the resistance to high-LET radiation exposure for two behaviors of the nematode,  , which is known as a model organism for the nervous system. Tested behaviors were locomotion and chemotaxis to NaCl. In addition, egg hatchability was examined as an indicator of high-LET radiation sensitivity. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of high-LET radiation (
, which is known as a model organism for the nervous system. Tested behaviors were locomotion and chemotaxis to NaCl. In addition, egg hatchability was examined as an indicator of high-LET radiation sensitivity. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) of high-LET radiation ( C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/
C, 18.3 MeV/u, LET = 113 keV/ m) relative to low-LET radiation for hatchability was 4.5, whereas RBEs for locomotion and chemotaxis were 1.4 and 1.1, respectively. This study shows that the behavioral system for locomotion and chemotaxis of
m) relative to low-LET radiation for hatchability was 4.5, whereas RBEs for locomotion and chemotaxis were 1.4 and 1.1, respectively. This study shows that the behavioral system for locomotion and chemotaxis of  is highly resistant to high-LET radiation exposure.
is highly resistant to high-LET radiation exposure.
Arima, Hiroshi; Hattori, Takanori; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Abe, Jun; Utsumi, Wataru; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Suzuki, Akio*; Suzuya, Kentaro; Kamiyama, Takashi; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 215(1), p.012025_1 - 012025_6, 2010/03
The powder diffractometer dedicated to high-pressure experiments (PLANET) is now being constructed on BL11 at the spallation neutron source of J-PARC. PLANET aims to study structures of hydrogen-bearing materials including dense hydrous minerals of the Earth's deep interior, magmas and light element liquids. The instrument will realize diffraction and radiography experiments for powder and liquid/glass samples at high pressures up to 20 GPa and 2000 K. It covers d spacing from 0.2  to 4.1
to 4.1  at 90
at 90 bank within the first frame.
bank within the first frame.
Arima, Hiroshi*; Hattori, Takanori; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Abe, Jun; Utsumi, Wataru; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Suzuki, Akio*; Suzuya, Kentaro; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 215(1), p.012025_1 - 012025_6, 2010/03
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:96.3(Instruments & Instrumentation)The powder diffractometer dedicated to high-pressure experiments (PLANET) is now being constructed on BL11 at the spallation neutron source of J-PARC. PLANET aims to study structures of hydrogen-bearing materials including dense hydrous minerals of the Earth's deep interior, magmas and light element liquids. The instrument will realize diffraction and radiography experiments for powder and liquid/glass samples at high pressures up to 20 GPa and 2000 K. It covers  spacing from 0.2
spacing from 0.2 to 4.1
to 4.1 at 90
at 90 bank within the first frame. The design and performance of PLANET have been evaluated using Monte Carlo simulations.
bank within the first frame. The design and performance of PLANET have been evaluated using Monte Carlo simulations.
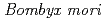 , induces the somatic mutation
, induces the somatic mutationFurusawa, Toshiharu*; Fukamoto, Kana*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Eiko*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Funayama, Tomoo; Suzuki, Hiromi*; Ishioka, Noriaki*; Wada, Seiichi*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 50(4), p.371 - 375, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:32.08(Biology)Using heavy-ion microbeam, we report target irradiation of selected compartments within the diapause-terminated egg and its mutational consequences in the silkworm, 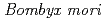 . On one hand, carbon-ion exposure of embryo to 0.5 - 6 Gy increased the somatic mutation frequency, suggesting targeted radiation effects. On the other, such increases were not observed when yolk was targeted, suggesting a lack of nontargeted bystander effect.
. On one hand, carbon-ion exposure of embryo to 0.5 - 6 Gy increased the somatic mutation frequency, suggesting targeted radiation effects. On the other, such increases were not observed when yolk was targeted, suggesting a lack of nontargeted bystander effect.
Nakamura, Takehiko; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Sasajima, Hideo; Ogiyanagi, Jin; Nakamura, Jinichi; Suzuki, Masahide; Kawamura, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
In order to maintain and enhance safety of light water reactors in long-term and up-graded operations, proper understanding of irradiation behavior of fuels and materials is essentially important. Japanese government and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency have decided to refurbish the JMTR and to install new tests rigs, in order to play an active role for solving irradiation related issues on plant aging and high-duty uses of the current LWRs and on development of next-generation reactors. New tests on fuel integrity under simulated abnormal transients and high-duty irradiation conditions are planned in the JMTR. Power ramp tests of new design fuel rods will also be performed in the first stage of the program, which is expected to start in year 2011 after refurbishment of the JMTR. Combination of the JMTR tests with simulated reactivity initiated accident tests in the NSRR and loss of coolant accident tests in hot laboratories would serve as the integrated fuel safety research on the high performance fuels at extended burnups, covering from the normal to the accident conditions, including abnormal transients. For the materials irradiation, fracture toughness of reactor vessel steels and stress corrosion cracking behavior of stainless steels are being studied in addition to basic irradiation behavior of nuclear materials such as hafnium. The irradiation studies would contribute not only to solve the current problems but also to identify possible seeds of troubles and to make proactive responses.
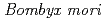
Furusawa, Toshiharu*; Suzuki, Eiko*; Nagaoka, Shunji*; Suzuki, Hiromi*; Ishioka, Noriaki*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 115, 2008/03
Using heavy ion microbeam, we investigated the somatic mutation arising on the larvae in embyro and yolk in the egg of silkworm, 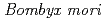 . The incidence of the somatic mutation was 12%, and the same level of mutation following the microbeam irradiation at the center of the egg. However, the microbeam irradiation to the abdomen of the silkworm larvae induced the increase of somatic mutation, 63% (3 Gy) and 80% (6 Gy).
. The incidence of the somatic mutation was 12%, and the same level of mutation following the microbeam irradiation at the center of the egg. However, the microbeam irradiation to the abdomen of the silkworm larvae induced the increase of somatic mutation, 63% (3 Gy) and 80% (6 Gy).
 to high-LET carbon ion beam irradiation
to high-LET carbon ion beam irradiationSakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 111, 2008/03
We investigated the high LET carbon ions induced response of salt chamotaxis learning in  . The performance of the salt chemotaxis learning was normal even after the exposure at the dose of 100 - 500 Gy. Also, the normal chemotaxis to benzaldehyde was normal, whereas the salt chemotaxis learning was affected by carbon irradiation. These results suggest the specific effect of carbon ions on the neuron network in
. The performance of the salt chemotaxis learning was normal even after the exposure at the dose of 100 - 500 Gy. Also, the normal chemotaxis to benzaldehyde was normal, whereas the salt chemotaxis learning was affected by carbon irradiation. These results suggest the specific effect of carbon ions on the neuron network in  .
.