Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sueoka, Shigeru; Kawakami, Tetsuo*; Suzuki, Kota*; Kagami, Saya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Shibazaki, Bunichiro*; Nagata, Mitsuhiro; Yamazaki, Ayu*; Higashino, Fumiko*; King, G. E.*; et al.
Fisshion, Torakku Nyusureta, (36), p.1 - 3, 2023/12
no abstracts in English
Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Tsuzuki, Takayuki*; Murai, Tetsuro*
JAEA-Technology 2022-023, 128 Pages, 2022/11
In a mercury target of the J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex), pulsed proton beams repeatedly bombard the flowing mercury which is confined in a stainless-steel vessel (target vessel). Cavitation damage caused by the propagation of the pressure waves is a factor of the life of the target vessel. As a measure to reduce damages, we developed a bubbler to inject the gas microbubbles into the flowing mercury, which can reduce the pressure waves. To operate the mercury target vessel stably with the 1 MW high-intensity proton beams, further reduction of the damage is required. The bubbler setting position should be closer to the beam window to increase the bubble population, which could enhance the reduction effect on the pressure waves and damage. However, the space at the beam window of the target vessel is restricted. The bubbler design and setting position as well as the vane design for the mercury flowing pattern are optimized by means of a machine learning technique to get more suitable bubble distribution, increasing in bubble population and optimizing bubble size nearby the beam window of the target vessel. The results of CFD analyses performed with 1000 cases were used for machine learning. Since the flow rate of mercury affects the temperature of the target vessel, this was used for the constraint condition. As a result, we found a design of mercury target vessel that can increase the bubble population by ca. 20% higher than the current design.
Suzuki, Gen*; Ishikawa, Tetsuo*; Oba, Takashi*; Hasegawa, Arifumi*; Nagai, Haruyasu; Miyatake, Hirokazu*; Yoshizawa, Nobuaki*
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 63(6), p.796 - 804, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:44.25(Biology)To elucidate the association between radiation dose and thyroid cancer after the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident, it is essential to estimate individual thyroid equivalent doses (TEDs) to children. In a previous study, we reported a methodology for reconstructing TEDs from inhalation based on individual behavioural survey sheets combined with a spatiotemporal radionuclides database constructed by an atmospheric transport, diffusion, and deposition model (ATDM). In the present study, we further refined our methodology and estimated the combined TEDs from inhalation and ingestion among children in 16 municipalities around the nuclear power station utilizing 3,256 individual whereabouts questionnaire survey sheets. Distributions of estimated TEDs were similar to estimates based on direct thyroid measurements in 1080 children in Iwaki City, Kawamata Town, Iitate Village, and Minamisoma City. Mean TEDs in 1-year-old children ranged from 1.3 mSv in Date City to 14.9 mSv in Odaka Ward in Minamisoma City, and the 95th percentiles varied from 2.3 mSv in Date City to 28.8 mSv in Namie Town. In the future, this methodology can be useful for a case-control study of thyroid cancer after the FDNPS accident.
Suzuki, Kota*; Kawakami, Tetsuo*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yamazaki, Ayu*; Kagami, Saya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Tagami, Takahiro*
Island Arc, 31(1), p.e12462_1 - e12462_15, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:15.73(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)G tz, M.*; Yakushev, A.*; G
tz, M.*; Yakushev, A.*; G tz, S.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D
tz, S.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Asai, Masato; Kindler, B.*; Krier, J.*; Lommel, B.*; Nagame, Yuichiro*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Asai, Masato; Kindler, B.*; Krier, J.*; Lommel, B.*; Nagame, Yuichiro*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 110(2), p.75 - 86, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.55(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The study of volatile superheavy element carbonyl complexes requires more efficient methods because the yield of transactinide elements decreases with increasing atomic number. This is achieved by using a newly developed double chamber system to separate the recoil chamber and the reaction one, thereby avoiding the decomposition of reactive molecules by the projectile ion beam, which hinders the synthesis of carbonyl complexes. The feasibility of this method was verified by synthesizing 5d metal short-lived isotopes as homologous element isotopes of the light transactinide elements Sg, Bh, Hs, and Mt at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency tandem accelerator and conducting model experiments.

Chiera, N. M.*; Sato, Tetsuya; Eichler, R.*; Tomitsuka, Tomohiro; Asai, Masato; Adachi, Sadia*; Dressler, R.*; Hirose, Kentaro; Inoue, Hiroki*; Ito, Yuta; et al.
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 60(33), p.17871 - 17874, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.19(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The formation and the chemical characterization of single atoms of dubnium (Db, element 105), in the form of its volatile oxychloride, was investigated using the on-line gas phase chromatography technique, in the temperature range 350 - 600  C. Under the exact same chemical conditions, comparative studies with the lighter homologs of group-5 in the Periodic Table clearly indicate the volatility sequence being NbOCl
C. Under the exact same chemical conditions, comparative studies with the lighter homologs of group-5 in the Periodic Table clearly indicate the volatility sequence being NbOCl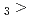 TaOCl
TaOCl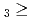 DbOCl
DbOCl . From the obtained experimental results, thermochemical data for DbOCl
. From the obtained experimental results, thermochemical data for DbOCl were derived. The present study delivers reliable experimental information for theoretical calculations on the chemical properties of transactinides.
were derived. The present study delivers reliable experimental information for theoretical calculations on the chemical properties of transactinides.
Harada, Masahide; Sekijima, Mitsuaki*; Morikawa, Noriyuki*; Masuda, Shiho; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Sakai, Kenji; Kai, Tetsuya; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Muto, Giichi*; Suzuki, Akio*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011099_1 - 011099_6, 2021/03
In MLF at J-PARC, a unified mercury radioactivity monitor (UHAM) is installed to find an indication of failure of the mercury target and loop system by detecting radioactive materials leaked from the system with a  -ray energy analysis with Germanium semi-conductor detectors (Ge detectors). It is composed of three units of sampling port and radiation monitors: (1) HAM for interstitial helium gas layer between the mercury vessel and surrounding water shroud of the mercury target, (2) CAM for atmosphere in the hot cell where the target loop is operated and (3) VAM for helium gas in the helium vessel where the target vessel is installed. Once any leakages of radioactive materials are detected, an alarm signal is issued immediately to the accelerator control system to stop beam operation. Software and hardware have been upgraded yearly. For example, two Ge detectors are used for HAM for redundancy, NaI Scintillation detectors are also used as supplemental for the Ge detector to keep availability of the system for high counting rate event. In April 2015, the UHAM activated when a small water coolant leakage from the water shroud of the mercury target occurred. VAM detected an abnormal increase of the counting rate in the helium vessel. It was also indicated that the measured radioactive nuclides were generated from the activation of the coolant (water) in the water shroud and not from the mercury.
-ray energy analysis with Germanium semi-conductor detectors (Ge detectors). It is composed of three units of sampling port and radiation monitors: (1) HAM for interstitial helium gas layer between the mercury vessel and surrounding water shroud of the mercury target, (2) CAM for atmosphere in the hot cell where the target loop is operated and (3) VAM for helium gas in the helium vessel where the target vessel is installed. Once any leakages of radioactive materials are detected, an alarm signal is issued immediately to the accelerator control system to stop beam operation. Software and hardware have been upgraded yearly. For example, two Ge detectors are used for HAM for redundancy, NaI Scintillation detectors are also used as supplemental for the Ge detector to keep availability of the system for high counting rate event. In April 2015, the UHAM activated when a small water coolant leakage from the water shroud of the mercury target occurred. VAM detected an abnormal increase of the counting rate in the helium vessel. It was also indicated that the measured radioactive nuclides were generated from the activation of the coolant (water) in the water shroud and not from the mercury.
Nagae, Daisuke*; Abe, Yasushi*; Okada, Shunsuke*; Omika, Shuichiro*; Wakayama, Kiyoshi*; Hosoi, Shun*; Suzuki, Shinji*; Moriguchi, Tetsuro*; Amano, Masamichi*; Kamioka, Daiki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 986, p.164713_1 - 164713_7, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:64.12(Instruments & Instrumentation)Hosoda, Masahiro*; Nugraha, E. D.*; Akata, Naofumi*; Yamada, Ryohei; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Sasaki, Michiya*; Kelleher, K.*; Yoshinaga, Shinji*; Suzuki, Takahito*; Rattanapongs, C. P.*; et al.
Science of the Total Environment, 750, p.142346_1 - 142346_11, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:85.26(Environmental Sciences)The biological effects of low dose-rate radiation exposures on humans remains unknown. In fact, the Japanese nation still struggles with this issue after the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Recently, we have found a unique area in Indonesia where naturally high radiation levels are present, resulting in chronic low dose-rate radiation exposures. We aimed to estimate the comprehensive dose due to internal and external exposures at the particularly high natural radiation area, and to discuss the enhancement mechanism of radon. A car-borne survey was conducted to estimate the external doses from terrestrial radiation. Indoor radon measurements were made in 47 dwellings over three to five months, covering the two typical seasons, to estimate the internal doses. Atmospheric radon gases were simultaneously collected at several heights to evaluate the vertical distribution. The absorbed dose rates in air in the study area vary widely between 50 nGy h and 1109 nGy h
and 1109 nGy h . Indoor radon concentrations ranged from 124 Bq m
. Indoor radon concentrations ranged from 124 Bq m to 1015 Bq m
to 1015 Bq m . That is, the indoor radon concentrations measured exceed the reference levels of 100 Bq m
. That is, the indoor radon concentrations measured exceed the reference levels of 100 Bq m recommended by the World Health Organization. Furthermore, the outdoor radon concentrations measured were comparable to the high indoor radon concentrations. The annual effective dose due to external and internal exposures in the study area was estimated to be 27 mSv using the median values. It was found that many residents are receiving radiation exposure from natural radionuclides over the dose limit for occupational exposure to radiation workers. This enhanced outdoor radon concentration might be as a result of the stable atmospheric conditions generated at an exceptionally low altitude. Our findings suggest that this area provides a unique opportunity to conduct an epidemiological study related to health effects due to chronic low dose-rate radiation exposure.
recommended by the World Health Organization. Furthermore, the outdoor radon concentrations measured were comparable to the high indoor radon concentrations. The annual effective dose due to external and internal exposures in the study area was estimated to be 27 mSv using the median values. It was found that many residents are receiving radiation exposure from natural radionuclides over the dose limit for occupational exposure to radiation workers. This enhanced outdoor radon concentration might be as a result of the stable atmospheric conditions generated at an exceptionally low altitude. Our findings suggest that this area provides a unique opportunity to conduct an epidemiological study related to health effects due to chronic low dose-rate radiation exposure.
Maruoka, Teruyuki*; Nishio, Yoshiro*; Kogiso, Tetsu*; Suzuki, Katsuhiko*; Osawa, Takahito; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Terada, Yasuko*
GSA Bulletin, 132(9-10), p.2055 - 2066, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.75(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary) F from
F from  O
O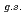 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:73.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 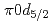 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O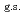 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
Bae, S.*; Jee, H.*; Suh, H.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Machida, Akihiko*; Watanuki, Tetsu*; Shobu, Takahisa; Morooka, Satoshi; Geng, G.*; et al.
Construction and Building Materials, 237, p.117714_1 - 117714_10, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:66.13(Construction & Building Technology)Takahashi, Osamu*; Shibui, Yohei*; Xu, P. G.; Harjo, S.; Suzuki, Tetsuya*; Tomota, Yo*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(1), p.16_1 - 16_15, 2020/03
 He
He
 excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron-
excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron- He absorption reaction
He absorption reactionSonnenschein, V.*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kokuryu, Shoma*; Kubo, Wataru*; Suzuki, So*; Tomita, Hideki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Matsushita, Taku*; Wada, Nobuo*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(3), p.033318_1 - 033318_12, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Instruments & Instrumentation)Oba, Takashi*; Ishikawa, Tetsuo*; Nagai, Haruyasu; Tokonami, Shinji*; Hasegawa, Arifumi*; Suzuki, Gen*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10(1), p.3639_1 - 3639_11, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:84.26(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Internal doses of residents after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident have been reconstructed. In total 896 behaviour records in the Fukushima Health Management Survey were analysed to estimate thyroid doses via inhalation, using a spatiotemporal radionuclides concentration database constructed by atmospheric dispersion simulations. After a decontamination factor for sheltering and a modifying factor for the dose coefficient were applied, estimated thyroid doses were close to those estimated on the basis of direct thyroid measurement. The median and 95th percentile of thyroid doses of 1-year-old children ranged from 1.2 to 15 mSv and from 7.5 to 30 mSv, respectively.
Shoji, Eita*; Isogai, Shosei*; Suzuki, Rikuto*; Kubo, Masaki*; Tsukada, Takao*; Kai, Tetsuya; Shinohara, Takenao; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 175, p.29 - 32, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:77.41(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) F and comparison of the structure among perovskite-type oxyfluorides
F and comparison of the structure among perovskite-type oxyfluoridesKatsumata, Tetsuhiro*; Suzuki, Ryo*; Sato, Naoto*; Suzuki, Shumpei*; Nakashima, Mamoru*; Inaguma, Yoshiyuki*; Mori, Daisuke*; Aimi, Akihisa*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro
Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 279, p.120919_1 - 120919_8, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:47.15(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Sonoda, Tetsu*; Katayama, Ichiro*; Wada, Michiharu*; Iimura, Hideki; Sonnenschein, V.*; Iimura, Shun*; Takamine, Aiko*; Rosenbusch, M.*; Kojima, Takao*; Ahn, D. S.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(11), p.113D02_1 - 113D02_12, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.4(Physics, Multidisciplinary)An in-flight separator, BigRIPS, at RIBF in RIKEN provides each experiment with specific nuclides separated from many nuclides produced by projectile fragmentation or in-flight fission. In this process, nuclides other than separated ones are discarded on the slits in BigRIPS, although they include many nuclides interested from the view point of nuclear structure. In order to extract these nuclides for parasitic experiments, we are developing a method using laser ion-source (PALIS). A test experiment with 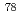 Se beam from RIBF has been performed by using a gas cell set in BigRIPS. Unstable nuclides around
Se beam from RIBF has been performed by using a gas cell set in BigRIPS. Unstable nuclides around  Se were stopped in the gas cell in accordance with a calculation using LISE code. The stopping efficiency has been estimated to be about 30%. As a next step, we will establish the technique for extracting reaction products from the gas cell.
Se were stopped in the gas cell in accordance with a calculation using LISE code. The stopping efficiency has been estimated to be about 30%. As a next step, we will establish the technique for extracting reaction products from the gas cell.
Iwasaki, Sachio; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei*; Yoshida, Tetsuya*
AIP Conference Proceedings 2130, p.050001_1 - 050001_8, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.09(Physics, Nuclear)We find a novel phenomenon induced by the interplay between a strong magnetic field and finite orbital angular momenta in hadronic systems, which is analogous to the Paschen-Back effect observed in the field of atomic physics. This effect allows the wave functions to drastically deform. We discuss anisotropic decay from the deformation as a possibility to measure the strength of the magnetic field in heavy-ion collision at LHC, RHIC and SPS, which has not experimentally been measured. As an example we investigate charmonia with finite orbital angular momentum in a strong magnetic field. We calculate the mass spectra and mixing rate. To obtain anisotropic wave functions, we apply the cylindrical Gaussian expansion method, where the Gaussian bases to expand the wave functions have different widths along transverse and longitudinal directions in the cylindrical coordinate.
Iwasaki, Sachio; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei*; Yoshida, Tetsuya*
International Journal of Modern Physics; Conference Series (Internet), 49, p.1960002_1 - 1960002_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.09(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The hadronic Paschen-Back effects in P-wave charmonia are analyzed using the constituent quark models in strong magnetic field.