Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Se from combined conversion-electron and
Se from combined conversion-electron and  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopySmallcombe, J.; Garnsworthy, A. B.*; Korten, W.*; Singh, P.*; Muir, D.*; Pr chniak, L.*; Ali, F. A.*; Andreoiu, C.*; Ansari, S.*; Ball, G. C.*; et al.
chniak, L.*; Ali, F. A.*; Andreoiu, C.*; Ansari, S.*; Ball, G. C.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 110(2), p.024318_1 - 024318_16, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.60(Physics, Nuclear)Soler, J. M.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Havlov
ha, J.*; Havlov , V.*; Trpko
, V.*; Trpko ov
ov , D.*; et al.
, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 209(11), p.1765 - 1784, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:71.02(Nuclear Science & Technology) sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory (Sweden)
Hard Rock Laboratory (Sweden)Soler, J. M.*; Meng, S.*; Moreno, L.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Liu, L.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Vete
ha, J.*; Vete n
n k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
Geologica Acta, 20(7), 32 Pages, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:46.22(Geology)Task 9B of the SKB Task Force on Modelling of Groundwater Flow and Transport of Solutes in fractured rock focused on the modelling of experimental results from the LTDE-SD in situ tracer test performed at the  sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Soler, J. M.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Moreno, L.*; Liu, L.*; Meng, S.*; Svensson, U.*; Iraola, A.*; Ebrahimi, K.*; Trinchero, P.*; Molinero, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 208(6), p.1059 - 1073, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:61.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)The SKB Task Force is an international forum on modelling of groundwater flow and solute transport in fractured rock. The WPDE experiments are matrix diffusion experiments in gneiss performed at the ONKALO underground facility in Finland. Synthetic groundwater containing several conservative and sorbing tracers was injected along a borehole interval. The objective of Task 9A was the predictive modelling of the tracer breakthrough curves from the WPDE experiments. Several teams, using different modelling approaches and codes, participated in this exercise. An important conclusion from this exercise is that the modelling results were very sensitive to the magnitude of dispersion in the borehole opening, which is related to the flow of water. Focusing on the tails of the breakthrough curves, which are more directly related to matrix diffusion and sorption, the results from the different teams were more comparable.
Soler, J. M.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Havlov
ha, J.*; Havlov , V.*; Trpko
, V.*; Trpko ov
ov , D.*; et al.
, D.*; et al.
SKB TR-21-09, 204 Pages, 2021/11
 sp
sp HRL LTDE-SD experiments
HRL LTDE-SD experimentsSoler, J. M.*; Meng, S.*; Moreno, L.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Liu, L.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Vete
ha, J.*; Vete n
n k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
SKB TR-20-17, 71 Pages, 2021/07
Task 9B of the SKB Task Force on Modelling of Groundwater Flow and Transport of Solutes in fractured rock focused on the modelling of experimental results from the LTDE-SD in situ tracer test performed at the  sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Soler, J. M.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Moreno, L.*; Liu, L.*; Meng, S.*; Svensson, U.*; Trinchero, P.*; Iraola, A.*; Ebrahimi, H.*; Molinero, J.*; et al.
SKB R-17-10, 153 Pages, 2019/01
The SKB Task Force is an international forum on modeling of groundwater flow and solute transport in fractured rock. The WPDE experiments are matrix diffusion experiments in gneiss performed at the ONKALO underground facility in Finland. Synthetic groundwater containing several conservative and sorbing tracers was injected along a borehole interval. The objective of Task 9A was the predictive modeling of the tracer breakthrough curves from the WPDE experiments. Several teams, using different modelling approaches, participated in this exercise. An important conclusion from this exercise is that the modeling results were very sensitive to the magnitude of dispersion in the borehole opening, which is related to the flow of water. Focusing on the tails of the breakthrough curves, which are more directly related to matrix diffusion and sorption, the results from the different teams were more comparable. The modeling results have also been finally compared to the measured breakthroughs.
Tobari, Hiroyuki; Inoue, Takashi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Dairaku, Masayuki; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Sakamoto, Keishi; Kuriyama, Masaaki*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(6-8), p.975 - 979, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)The HV bushing, one of the ITER NB components, which is to be procured by JADA, is a multi-conductor feed through composed of five-stage double-layered insulator columns with large brazed ceramic ring and fiber reinforced plastic (FRP) ring. The HV bushing is a bulk head between insulation gas at 0.6 MPa and vacuum. The FRP ring is required to sustain the pressure load, seismic load and dead weight. Brazing area of the ceramic ring with Kovar is required to maintain vacuum leak tightness and pressure tightness against the air filled at 0.6 MPa. To design the HV bushing satisfying the safety factor of  3.5, mechanical analyses were carried out. As for the FRP ring, it was confirmed that isotropic fiber cloth FRP rings should be used for sufficient strength against shear stress. Also, shape and fixation area of the Kovar sleeve were modified to lower the stress at the joint area. As a result, a design of the insulator for the HV bushing was established satisfying the requirement.
3.5, mechanical analyses were carried out. As for the FRP ring, it was confirmed that isotropic fiber cloth FRP rings should be used for sufficient strength against shear stress. Also, shape and fixation area of the Kovar sleeve were modified to lower the stress at the joint area. As a result, a design of the insulator for the HV bushing was established satisfying the requirement.
Son, N. T.*; Trinh, X. T.*; L vile, L. S.*; Svensson, B. G.*; Kawahara, Kotaro*; Suda, Jun*; Kimoto, Tsunenobu*; Umeda, Takahide*; Isoya, Junichi*; Makino, Takahiro; et al.
vile, L. S.*; Svensson, B. G.*; Kawahara, Kotaro*; Suda, Jun*; Kimoto, Tsunenobu*; Umeda, Takahide*; Isoya, Junichi*; Makino, Takahiro; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 109(18), p.187603_1 - 187603_5, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:230 Percentile:98.14(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Tanaka, Masanobu*; Hemsworth, R. S.*; Kuriyama, Masaaki*; Svensson, L.*; Boilson, D.*; Inoue, Takashi; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Umeda, Naotaka; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 39(6), p.1379 - 1385, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:25.98(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In the ITER neutral beam injector (NBI) for plasma heating and current drive, 40 A D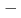 ions are accelerated to 1 MeV with a five-stage electrostatic accelerator. Since the accelerator is immersed in vacuum, vacuum insulation of -1 MV is one of critical issues. In order to sustain high voltage of -1 MV, minimum gap length between the accelerator and the vacuum vessel at ground potential was designed to be more than 900 mm on the basis of previous experimental data. High voltage bushing (HVB) acting as an insulating feed-through supplying electric power and cooling water to the accelerator consists of five stack insulator and each stage is designed to withstand -200 kV. A full-scale and single-stage mockup bushing was manufactured and tested to demonstrate stable voltage holding. As a result, DC -203 kV was sustained stably for 5 hours and the insulation design of HVB has been confirmed.
ions are accelerated to 1 MeV with a five-stage electrostatic accelerator. Since the accelerator is immersed in vacuum, vacuum insulation of -1 MV is one of critical issues. In order to sustain high voltage of -1 MV, minimum gap length between the accelerator and the vacuum vessel at ground potential was designed to be more than 900 mm on the basis of previous experimental data. High voltage bushing (HVB) acting as an insulating feed-through supplying electric power and cooling water to the accelerator consists of five stack insulator and each stage is designed to withstand -200 kV. A full-scale and single-stage mockup bushing was manufactured and tested to demonstrate stable voltage holding. As a result, DC -203 kV was sustained stably for 5 hours and the insulation design of HVB has been confirmed.
DeEsch, H. P. L.*; Svensson, L.*; Inoue, Takashi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Umeda, Naotaka; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Fubiani, G.*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 84(2-6), p.669 - 675, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:63.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Dairaku, Masayuki; DeEsch, H. P. L.*; Grisham, L. R.*; Svensson, L.*; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Umeda, Naotaka; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Sakamoto, Keishi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(6), p.065008_1 - 065008_7, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:64.17(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)At JAEA, a MAMuG (multi-aperture multi-grid) accelerator has been developed to perform required R&D for the ITER neutral beam system. H ion beam current was increased to 0.32 A (the ion current density (J
ion beam current was increased to 0.32 A (the ion current density (J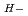 ) of 140 A/m
) of 140 A/m ) at the beam energy(Vb) of 796 keV. After the high power beam operation, pulse length was successfully extended from 0.2 s to 5 s at 550 keV, which yielded 131 mA H
) at the beam energy(Vb) of 796 keV. After the high power beam operation, pulse length was successfully extended from 0.2 s to 5 s at 550 keV, which yielded 131 mA H ion beam as an initial test of the long pulse operation. A test of a SINGAP (single-aperture single-gap) accelerator was performed at JAEA under an ITER R&D task agreement so as to compare the SINGAP and the MAMuG. The MAMuG accelerator was defined as the baseline design for ITER, due to advantages in its better voltage holding and less electron acceleration. In three dimensional beam trajectory analyses, aperture offset was found effective for compensation of beamlet deflection due to their own space charge and beamlet focusing.
ion beam as an initial test of the long pulse operation. A test of a SINGAP (single-aperture single-gap) accelerator was performed at JAEA under an ITER R&D task agreement so as to compare the SINGAP and the MAMuG. The MAMuG accelerator was defined as the baseline design for ITER, due to advantages in its better voltage holding and less electron acceleration. In three dimensional beam trajectory analyses, aperture offset was found effective for compensation of beamlet deflection due to their own space charge and beamlet focusing.
Taniguchi, Masaki; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Dairaku, Masayuki; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Inoue, Takashi; DeEsch, H.*; Svensson, L.*
JAEA-Research 2008-121, 26 Pages, 2009/03
For the ITER NBI, two accelerator concepts have been proposed. One is the SINGAP (single gap single aperture) developed at CEA Cadarache and the other is the MAMuG (Multi aperture multi gap) developed at JAEA. In order to assess the performance of the SINGAP and the MAMuG concepts at the same test facility under the same diagnostics, a collaborative test was performed between JAEA and CEA Cadarache under an ITER task agreement. For this purpose, the SINGAP accelerator was installed at the MTF of JAEA. From the viewpoint of voltage holding, maximum beam current and electron acceleration, the MAMuG showed better performance than the SINGAP, and it has been decided to choose the MAMuG as the baseline accelerator for the ITER NBI.
 accelerator at JAEA for ITER NB
accelerator at JAEA for ITER NBTaniguchi, Masaki; DeEsch, H. P. L.*; Svensson, L.*; Umeda, Naotaka; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Dairaku, Masayuki; Sakamoto, Keishi; Inoue, Takashi
AIP Conference Proceedings 1097, p.335 - 343, 2009/03
DeEsch, H. P. L.*; Svensson, L.*; Inoue, Takashi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Umeda, Naotaka; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Fubiani, G.*
AIP Conference Proceedings 1097, p.353 - 363, 2009/03
CEA Cadarache and JAEA Naka have entered into a collaboration in order to test a SINGAP accelerator at the Megavolt Test Facility (MTF) at Naka, Japan. Whereas at the CEA testbed the acceleration current was limited to 0.1 A, at JAEA 0.5 A is available. This allows the acceleration of 15 H beamlets in SINGAP to be tested and a direct comparison between SINGAP and MAMuG to be made. High-voltage conditioning in the SINGAP configuration has been quite slow, with 581 kV in vacuum achieved after 140 hours of conditioning. With 0.1 Pa of H
beamlets in SINGAP to be tested and a direct comparison between SINGAP and MAMuG to be made. High-voltage conditioning in the SINGAP configuration has been quite slow, with 581 kV in vacuum achieved after 140 hours of conditioning. With 0.1 Pa of H gas present in the accelerator 787 kV could be achieved. The conditioning curve for MAMuG is 200 kV higher. A beamlet divergence better than 5 mrad was obtained. SINGAP accelerates electrons to a higher energy than MAMuG. Based on the experiments described here, electron production by a SINGAP accelerator scaled up to ITER size was estimated to be too high for comfort.
gas present in the accelerator 787 kV could be achieved. The conditioning curve for MAMuG is 200 kV higher. A beamlet divergence better than 5 mrad was obtained. SINGAP accelerates electrons to a higher energy than MAMuG. Based on the experiments described here, electron production by a SINGAP accelerator scaled up to ITER size was estimated to be too high for comfort.
Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Dairaku, Masayuki; DeEsch, H. P. L.*; Grisham, L. R.*; Svensson, L.*; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Umeda, Naotaka; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Sakamoto, Keishi; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
At JAEA, beam parameters achieved by the MAMuG (multi-aperture multi-grid) accelerator were increased to 0.32 A H at the ion current density of 140 A/m
at the ion current density of 140 A/m and 796 keV at the beam energy. This was achieved as the result of countermeasures to handle unexpected heat load by backstream positive ions. A test of SINGAP (single-aperture single-gap) accelerator, which was performed at JAEA under an ITER R&D task agreement. The objective of this study was to compare the two different accelerator concepts (SINGAP and MAMuG) at the same test facility. As the result, it was concluded that the MAMuG accelerator was more suitable for the ITER NBI because of its better voltage holding and less electron acceleration. A simulation is in progress for space charge repulsion of beamlets in the JT-60U accelerator. An aperture offset steering was suggested effective at exit of extractor for compensation of the beamlet deflection due to its own space charge.
and 796 keV at the beam energy. This was achieved as the result of countermeasures to handle unexpected heat load by backstream positive ions. A test of SINGAP (single-aperture single-gap) accelerator, which was performed at JAEA under an ITER R&D task agreement. The objective of this study was to compare the two different accelerator concepts (SINGAP and MAMuG) at the same test facility. As the result, it was concluded that the MAMuG accelerator was more suitable for the ITER NBI because of its better voltage holding and less electron acceleration. A simulation is in progress for space charge repulsion of beamlets in the JT-60U accelerator. An aperture offset steering was suggested effective at exit of extractor for compensation of the beamlet deflection due to its own space charge.
 /D
/D ) ion beams in negative ion source development for NBI
) ion beams in negative ion source development for NBIKashiwagi, Mieko; Amemiya, Toru*; Iga, Takashi*; Inoue, Takashi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Okumura, Yoshikazu; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Hanada, Masaya; Fujiwara, Yukio; Morishita, Takatoshi; et al.
Dai-12-Kai Ryushisen No Sentanteki Oyo Gijutsu Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu (BEAMS 2001) Hobunshu, p.37 - 40, 2001/11
no abstracts in English
Soler, J. M.*; L fgren, M.*; Nilsson, K.*; Lanyon, G. W.*; Gylling, B.*; Vidstrand, P.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Moreno, L.*; Liu, L.*; Meng, S.*; et al.
fgren, M.*; Nilsson, K.*; Lanyon, G. W.*; Gylling, B.*; Vidstrand, P.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Moreno, L.*; Liu, L.*; Meng, S.*; et al.
no journal, ,
The GWFTS Task Force is an international forum in the area of modeling of groundwater flow and solute transport in fractured rock. The WPDE experiments are matrix diffusion experiments in gneiss performed at the ONKALO underground facility in Finland. Synthetic groundwater containing several conservative and sorbing radiotracers was injected along a borehole interval. The objective of Task 9A of Task Force was the predictive modeling of the tracer breakthrough curves from the WPDE experiments. Several teams, using different modeling approaches, participated in this exercise. An important conclusion from this exercise is that the modeling results were very sensitive to the magnitude of dispersion in the borehole opening, which is related to the flow of water. Focusing on the tails of the breakthrough curves, which are more directly related to matrix diffusion and sorption, the results from the different teams were more comparable.
Son, N. T.*; Trinh, X. T.*; Suda, Jun*; Kimoto, Tsunenobu*; L vile, L. S.*; Svensson, B. G.*; Szasz, K.*; Hornos, T.*; Gali, A.*; Umeda, Takahide*; et al.
vile, L. S.*; Svensson, B. G.*; Szasz, K.*; Hornos, T.*; Gali, A.*; Umeda, Takahide*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English