Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kumagai, Yuta; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Watanabe, Masayuki
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 191, p.109831_1 - 109831_8, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Physical)In this study, we investigated and compared the effects of a high-silica zeolite (HMOR) on the radiation-induced degradation of three aromatic chlorides, 2-chlorophenol (2-ClPh), 2-chloroaniline (2-ClAn), and 2-chlorobenzoic acid (2-ClBA), in order to examine its potential to reduce the influence of ions in water matrix in the irradiation treatment of water-soluble organic compounds. In the presence of ions reactive to radicals, the degradation of 2-ClPh in water was inhibited, but the combined use of HMOR much improved the degradation yield. This improvement was attributed to high performance of HMOR in adsorption of 2-ClPh. Similarly, HMOR was effective for adsorption of 2-ClAn and facilitated the 2-ClAn degradation by irradiation. In contrast, HMOR was poor at adsorption of 2-ClBA and consistently the degradation of 2-ClBA in the water-HMOR mixture was inhibited by the radical scavenger. These results demonstrate that HMOR can mitigate the influence of radical scavengers in water.
Kumagai, Yuta; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Nishihara, Kenji; Yamagishi, Isao; Ogawa, Toru
Insights Concerning the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident, Vol.4; Endeavors by Scientists, p.37 - 45, 2021/10
Zeolite adsorbents are to be used for decontamination of radioactive water in Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station. Evaluation of hydrogen production by water radiolysis during decontamination is important for safe operation. Thus hydrogen production from the mixture of zeolite adsorbents and seawater was studied because seawater was urgently used as a coolant for the fuels. The hydrogen yield from the mixture decreased at a high weight fraction of zeolites. However, the measured yield was higher than the yield expected from the direct radiolysis of seawater in the mixture, which would decrease proportional to the weight fraction of seawater. The result suggests that the radiation energy deposited to zeolites was involved in the hydrogen formation. From the results, the hydrogen production rate was evaluated to be 3.6 mL/h per ton of radioactive water before decontamination. After the process, it was evaluated to be 1.5 L/h per ton of waste adsorbents due to the high dose rate.
Sato, Tomonori; Hata, Kuniki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Seito, Hajime*; Tada, Eiji*; Abe, Hiroshi*; Akiyama, Eiji*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-001, 123 Pages, 2021/06
In the implement of the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), there are many problems to be solved. Specially, the mitigation of the aging degradation by the corrosion of the structural materials is important to implement the decommissioning safely and continuously. However, there are limited data for the environmental factors of corrosion in 1F, and the condition of 1F is continuously changing. So, the literature data for the water radiolysis and the corrosion under irradiation are listed as the database of corrosion under irradiation in this report. And the new obtained radiolysis and corrosion data, which have not been reported in the literature and will be required in the decommissioning of 1F, are reported.
Omori, Atsushi*; Akiyama, Eiji*; Abe, Hiroshi*; Hata, Kuniki; Sato, Tomonori; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Seito, Hajime*; Tada, Eiji*; et al.
Zairyo To Kankyo, 69(4), p.107 - 111, 2020/04
To evaluate the effect of oxidants, which are formed by radiolysis of water under gamma ray irradiation, on the corrosion of a carbon steel in humid environment, ozone was introduced as a model oxidant in to humidity-controlled air at 50 C in a thermo-hygrostat chamber. Corrosion monitoring was performed by using an Atmospheric Corrosion Monitor-type (ACM) sensor consisting of a carbon steel anode and an Ag cathode. The output current of the ACM sensor was increased with the increase in relative humidity and it was obviously increased with the increase in the introduced ozone concentration at each relative humidity. The results indicate that ozone accelerates the corrosion of the carbon steel. The effect of ozone on the corrosion acceleration is attributed to the fast reduction reaction and fast dissolution reaction in to water compared to that of oxygen.
C in a thermo-hygrostat chamber. Corrosion monitoring was performed by using an Atmospheric Corrosion Monitor-type (ACM) sensor consisting of a carbon steel anode and an Ag cathode. The output current of the ACM sensor was increased with the increase in relative humidity and it was obviously increased with the increase in the introduced ozone concentration at each relative humidity. The results indicate that ozone accelerates the corrosion of the carbon steel. The effect of ozone on the corrosion acceleration is attributed to the fast reduction reaction and fast dissolution reaction in to water compared to that of oxygen.
 N]N
N]N gas for visualization of nitrogen fixation and translocation in nodulated soybean
gas for visualization of nitrogen fixation and translocation in nodulated soybeanYin, Y.-G.*; Ishii, Satomi*; Suzui, Nobuo*; Igura, Masato*; Kurita, Keisuke; Miyoshi, Yuta*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Kawachi, Naoki*
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 151, p.7 - 12, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:55.67(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Accurate analysis of N fixation in leguminous crops requires determination of N utilization within an intact plant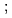 however, most approaches require tissue disassembly. We developed a simple and rapid technique to generate high-purity and high-yield [
however, most approaches require tissue disassembly. We developed a simple and rapid technique to generate high-purity and high-yield [ N]N
N]N gas and obtained real-time images of N fixation in an intact soybean plant. The purification efficiency was
gas and obtained real-time images of N fixation in an intact soybean plant. The purification efficiency was  81.6% after decay correction.
81.6% after decay correction.
Kumagai, Yuta; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Watanabe, Masayuki
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 316(1), p.341 - 348, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.93(Chemistry, Analytical)We studied effect of adsorption and condensation by zeolites on radiation-induced degradation of aqueous 2-chlorophenol (2-ClPh). This study aims to demonstrate that the solid-phase extraction using zeolites has potential advantage in treatments of aqueous organic pollutants. Among three zeolites examined in this study, a mordenite type zeolite (HMOR) that has a high Si to Al ratio (127  3) exhibited preferable performance as the matrix for the 2-ClPh degradation. HMOR adsorbed far more 2-ClPh than the other zeolites, which have lower Si/Al ratios. The irradiation of HMOR induced degradation of adsorbed 2-ClPh into Cl
3) exhibited preferable performance as the matrix for the 2-ClPh degradation. HMOR adsorbed far more 2-ClPh than the other zeolites, which have lower Si/Al ratios. The irradiation of HMOR induced degradation of adsorbed 2-ClPh into Cl and organic by-products. We found a significant increase in Cl
and organic by-products. We found a significant increase in Cl production by HMOR. The yield of Cl
production by HMOR. The yield of Cl production in the presence of HMOR was as high as the yield in aqueous solution of 2-ClPh at a concentration 10 times higher. The increased Cl
production in the presence of HMOR was as high as the yield in aqueous solution of 2-ClPh at a concentration 10 times higher. The increased Cl production indicates that the high concentration of adsorbed 2-ClPh led to effective use of the adsorbed energy of HMOR.
production indicates that the high concentration of adsorbed 2-ClPh led to effective use of the adsorbed energy of HMOR.
Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kimura, Atsushi*
IAEA-TECDOC-1855, p.106 - 116, 2018/00
The technology for the decomposition of trace amounts of halogenated pharmaceuticals/antibiotics was developed in wastewater by use of the combination method of zeolite adsorbent and ionizing radiation. HMOR, a hydrophobic high-silica mordenite-type zeolite, was employed to concentrate 2-chlorophenol (2-ClPh) as a simple model of halogenated pharmaceuticals/antibiotics. HMOR adsorbed above 99% of 2-ClPh from dilute aqueous solutions. The yield of Cl production in HMOR mixture corresponded to the aqueous solution containing 10 fold higher concentration of dissolved 2-ClPh. Clofibrate and triclosan, one of chlorinated pharmaceuticals/antibiotics, in real wastewater were treated by use of the combination method of HMOR and ionizing radiation. Production yield of Cl
production in HMOR mixture corresponded to the aqueous solution containing 10 fold higher concentration of dissolved 2-ClPh. Clofibrate and triclosan, one of chlorinated pharmaceuticals/antibiotics, in real wastewater were treated by use of the combination method of HMOR and ionizing radiation. Production yield of Cl by use of the adsorbent was about twice higher than that in aqueous solution, and HMOR was contributed for effective reduction of chlorinated pharmaceuticals/antibiotics in real wastewater.
by use of the adsorbent was about twice higher than that in aqueous solution, and HMOR was contributed for effective reduction of chlorinated pharmaceuticals/antibiotics in real wastewater.
 -ray irradiation from different types of zeolites in aqueous solution
-ray irradiation from different types of zeolites in aqueous solutionKumagai, Yuta; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Watanabe, Masayuki
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 121(34), p.18525 - 18533, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:26.48(Chemistry, Physical)H production by irradiation of zeolite-water mixtures was studied, to investigate effect of zeolites in the reaction process for H
production by irradiation of zeolite-water mixtures was studied, to investigate effect of zeolites in the reaction process for H . Four different types of zeolites were examined comparatively under anoxic and under aerated conditions. High production yields of H
. Four different types of zeolites were examined comparatively under anoxic and under aerated conditions. High production yields of H were observed for the zeolites of high Al contents at low water fraction and under anoxic condition, compared to zeolites having lower Al contents. A comparison of the H
were observed for the zeolites of high Al contents at low water fraction and under anoxic condition, compared to zeolites having lower Al contents. A comparison of the H yields in connection with chemical analysis of the zeolites suggests that extraframework Al species in the zeolites are involved in a reaction pathway for H
yields in connection with chemical analysis of the zeolites suggests that extraframework Al species in the zeolites are involved in a reaction pathway for H . Meanwhile, under aerated condition and at high mixing ratio of water, the difference in H
. Meanwhile, under aerated condition and at high mixing ratio of water, the difference in H yield among the zeolites was suppressed and the yields of H
yield among the zeolites was suppressed and the yields of H were lower than those under anoxic condition probably due to H
were lower than those under anoxic condition probably due to H O
O produced by water radiolysis. The comparable H
produced by water radiolysis. The comparable H yields suggest another reaction pathway for H
yields suggest another reaction pathway for H which is less dependent on the structure and composition of the zeolites.
which is less dependent on the structure and composition of the zeolites.
Kimura, Atsushi; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Shimada, Akihiko; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 124, p.130 - 134, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:64.88(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Yang, S.*; Katsumura, Yosuke*; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Matsuura, Chihiro*; Hiroishi, Daisuke*; Lertnaisat, P.*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 123, p.14 - 19, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.71(Chemistry, Physical) -radiolysis of boiling water has been investigated. The G-value of H
-radiolysis of boiling water has been investigated. The G-value of H evolution was found to be very sensitive to the purity of water. In high-purity water, both H
evolution was found to be very sensitive to the purity of water. In high-purity water, both H and O
and O gases were formed in the stoichiometric ratio of 2:1; a negligible amount of H
gases were formed in the stoichiometric ratio of 2:1; a negligible amount of H O
O remained in the liquid phase. The G-values of H
remained in the liquid phase. The G-values of H and O
and O gas evolution depend on the dose rate: lower dose rates produce larger yields. To clarify the importance of the interface between liquid and gas phase for gas evolution, the gas evolution under Ar gas bubbling was measured. A large amount of H
gas evolution depend on the dose rate: lower dose rates produce larger yields. To clarify the importance of the interface between liquid and gas phase for gas evolution, the gas evolution under Ar gas bubbling was measured. A large amount of H was detected, similar to the radiolysis of boiling water. The evolution of gas was enhanced in a 0.5 M NaCl aqueous solution. Deterministic chemical kinetics simulations elucidated the mechanism of radiolysis in boiling water.
was detected, similar to the radiolysis of boiling water. The evolution of gas was enhanced in a 0.5 M NaCl aqueous solution. Deterministic chemical kinetics simulations elucidated the mechanism of radiolysis in boiling water.
Iwamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Muroya, Yusa*; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 119, p.213 - 217, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.71(Chemistry, Physical)A quick measurement system of a continuous absorption spectrum covering a wide range from 200 to 950 nm was constructed by employing an optical multi-channel detector. Ion beam pulse radiolysis with 12.5 MeV/u He, 18.3 MeV/u C and 17.5 MeV/u Ne ions were performed with the measurement system. Transient absorption spectrum of (SCN)
 was clearly observed in KSCN aqueous solutions within a few minutes in spite of their very small absorbance, demonstrating high sensitivity of 0.001-0.003 in absorbance in the range from 260 to 660 nm as well as short measurement time of a few minutes. Two different absorption peaks attributed to Br
was clearly observed in KSCN aqueous solutions within a few minutes in spite of their very small absorbance, demonstrating high sensitivity of 0.001-0.003 in absorbance in the range from 260 to 660 nm as well as short measurement time of a few minutes. Two different absorption peaks attributed to Br
 and Br
and Br
 were observed simultaneously in NaBr aqueous solutions, showing powerfulness of the measurement system in overviewing chemical kinetics under ion beam irradiation especially in not well investigated chemical systems.
were observed simultaneously in NaBr aqueous solutions, showing powerfulness of the measurement system in overviewing chemical kinetics under ion beam irradiation especially in not well investigated chemical systems.
Koshimizu, Masanori*; Iwamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kimura, Atsushi; Yanagida, Takayuki*; Fujimoto, Yutaka*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Asai, Keisuke*
Journal of Luminescence, 169(Part B), p.678 - 681, 2016/01
We analyzed the effects of linear energy transfer (LET) on the scintillation properties of a Li glass scintillator, GS20. The scintillation time profiles were measured by using pulsed ion beams having different LETs. The rise in the scintillation time profiles was faster for higher LET, whereas the decay part was not significantly different for largely different LETs. The LET effects in the rise was ascribed to the effects of excited states interaction during the energy transfer process from the host glass to the luminescent centers, Ce ions. Supposing that the light yield decreases with LET, the fast rise at high LET was explained in terms of the competition between the energy transfer and the quenching due to the excited states interaction.
ions. Supposing that the light yield decreases with LET, the fast rise at high LET was explained in terms of the competition between the energy transfer and the quenching due to the excited states interaction.
Hiroki, Akihiro; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 365(Part B), p.583 - 586, 2015/12
Effects of liner energy transfer (LET) and dose rate on the optical property of polymer gel dosimeters were investigated. The dosimeter prepared by using a radiation-crosslinked hydroxypropyl cellulose gel and methacrylate monomers such as 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate and nonaethylene glycol dimethacrylate showed the color change from colorless to white with the He, C, Fe ions irradiation. Absorbance of the irradiated dosimeters increased with the dose up to 10 Gy. The absorbance of the dosimeters at the same total dose decreased with increasing dose rate in the range of 0.1 to 6.8 Gy/min. The absorbance decreased in order of He, C, Fe ions, which was in agreement with a change of LET. The increase in LET affected the decrease in the number of polymerization initiator such as OH radical and hydrated electron, resulting in the reduction of the absorbance of the dosimeters.
 crystals
crystalsYanagida, Takayuki*; Koshimizu, Masanori*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Iwamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Fujimoto, Yutaka*; Asai, Keisuke*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 365(Part B), p.529 - 532, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:67.3(Instruments & Instrumentation)We measured temporal profiles of scintillation of Ce-doped LiCaAlF scintillator crystals at different linear energy transfers (LETs). Based on the comparison of the high-LET temporal profiles with those at low LET, we found that a fast component was observed only at low LET. The disappearance of the fast component at high LET is tentatively ascribed to quenching of excited states at defects owing to the interaction between excited states via Auger process. In addition, the rise and the initial decay behavior was dependent on the LET. This LET-dependent behavior is explained by a seeming acceleration process and a slowing down process in energy transfer at high LET. The LET-dependent temporal profiles provide a basis of discrimination technique of
scintillator crystals at different linear energy transfers (LETs). Based on the comparison of the high-LET temporal profiles with those at low LET, we found that a fast component was observed only at low LET. The disappearance of the fast component at high LET is tentatively ascribed to quenching of excited states at defects owing to the interaction between excited states via Auger process. In addition, the rise and the initial decay behavior was dependent on the LET. This LET-dependent behavior is explained by a seeming acceleration process and a slowing down process in energy transfer at high LET. The LET-dependent temporal profiles provide a basis of discrimination technique of  -ray and neutron detection events using these scintillators based on the nuclear reaction,
-ray and neutron detection events using these scintillators based on the nuclear reaction,  Li(n,
Li(n, )t.
)t.
Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
Isotope News, (736), p.47 - 50, 2015/08
no abstracts in English
Kurashima, Satoshi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Okumura, Susumu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 86(7), p.073311_1 - 073311_8, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:51.15(Instruments & Instrumentation)The single-pulse formation technique using a beam chopping system consisting of two types of high-voltage beam kickers was modified to improve the quality and intensity of the single-pulse beam with pulse intervals over 1  s at TIARA cyclotron facility of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Reduction of the multi-turn extraction number for suppressing the neighboring beam bunch contamination was achieved by restriction of a beam phase width and precise optimization of a particle acceleration phase. In addition, the single-pulse beam intensity was increased by a factor of two or more by a combination of two types of beam bunchers using sinusoidal and saw-tooth voltage waveforms. As a result, a contamination rate of neighboring beam bunches in the single-pulse beam was reduced to less than 0.1 %. Long-term purification of the single pulse beam was guaranteed by the well-controlled magnetic field stabilization system for the TIARA cyclotron magnet. Provision of the high quality intense single-pulse beam contributes to improve the accuracy of experiments for investigation of scintillation light time-profile and for neutron energy measurement by a time-of-flight method.
s at TIARA cyclotron facility of Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Reduction of the multi-turn extraction number for suppressing the neighboring beam bunch contamination was achieved by restriction of a beam phase width and precise optimization of a particle acceleration phase. In addition, the single-pulse beam intensity was increased by a factor of two or more by a combination of two types of beam bunchers using sinusoidal and saw-tooth voltage waveforms. As a result, a contamination rate of neighboring beam bunches in the single-pulse beam was reduced to less than 0.1 %. Long-term purification of the single pulse beam was guaranteed by the well-controlled magnetic field stabilization system for the TIARA cyclotron magnet. Provision of the high quality intense single-pulse beam contributes to improve the accuracy of experiments for investigation of scintillation light time-profile and for neutron energy measurement by a time-of-flight method.
 -radiation effect on solvent extraction of minor actinide
-radiation effect on solvent extraction of minor actinideSugo, Yumi; Sasaki, Yuji; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Ishioka, Noriko
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1381 - 1384, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:25.85(Chemistry, Analytical)Yamashita, Shinichi*; Iwamatsu, Kazuhiro; Maehashi, Yuki*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Hata, Kuniki; Muroya, Yusa*; Katsumura, Yosuke*
RSC Advances (Internet), 5(33), p.25877 - 25886, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:38(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Pulse radiolysis experiments were carried out to observe transient absorptions of reaction intermediates produced in N O
O and Ar-saturated aqueous solutions containing 0.9-900 mM NaBr. The most important species among the reaction intermediates are BrOH
and Ar-saturated aqueous solutions containing 0.9-900 mM NaBr. The most important species among the reaction intermediates are BrOH 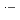 and Br
and Br
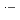 , which commonly have absorption peaks around 360 nm. The experimental results were compared with the results of simulation based on a spur diffusion model. Each of several complicated sequential radiation-induced chemical reactions was carefully considered, optimizing its rate constant within a range of reported values. All the experimental results were able to be universally reproduced by the simulation, assuming a reaction not yet reported, 2BrOH
, which commonly have absorption peaks around 360 nm. The experimental results were compared with the results of simulation based on a spur diffusion model. Each of several complicated sequential radiation-induced chemical reactions was carefully considered, optimizing its rate constant within a range of reported values. All the experimental results were able to be universally reproduced by the simulation, assuming a reaction not yet reported, 2BrOH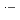
 Br
Br + 2OH
+ 2OH , with a rate constant of 3.8
, with a rate constant of 3.8  10
10 M
M s
s , which is significant only within 10 micro-s for rather high bromide concentrations (
, which is significant only within 10 micro-s for rather high bromide concentrations ( 10 mM). Primary
10 mM). Primary 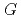 values, which are yields after sufficient diffusion from the spur to the perimeter region during 100 ns, of major water decomposition products, as well as of the reaction intermediates, were calculated for N
values, which are yields after sufficient diffusion from the spur to the perimeter region during 100 ns, of major water decomposition products, as well as of the reaction intermediates, were calculated for N O
O and Ar-saturated conditions as a function of NaBr concentration.
and Ar-saturated conditions as a function of NaBr concentration.
Hiroki, Akihiro; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 573(1), p.012028_1 - 012028_4, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:79.08(Engineering, Biomedical)Polymer gel dosimeters based on radiation-crosslinked hydroxypropyl cellulose gel were prepared, which comprised 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) and polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (9G) as less toxic monomers and tetrakis (hydroxymethyl) phosphoniumu chloride (THPC) as an antioxidant. The dosimeters exposed to  Co
Co  -rays became cloudy at only 1 Gy. The irradiated dosimeters were optically analyzed by using a UV-vis spectrophotometer to evaluate dose response. Absorbance of the dosimeters linearly increased in the dose range from 0 to 10 Gy. The dose sensitivity increased with increasing 9G concentration. The dosimeter with 2 wt% HEMA, 3 wt% 9G, and 0.16 wt% THPC exhibited about 0.04 Abs Gy
-rays became cloudy at only 1 Gy. The irradiated dosimeters were optically analyzed by using a UV-vis spectrophotometer to evaluate dose response. Absorbance of the dosimeters linearly increased in the dose range from 0 to 10 Gy. The dose sensitivity increased with increasing 9G concentration. The dosimeter with 2 wt% HEMA, 3 wt% 9G, and 0.16 wt% THPC exhibited about 0.04 Abs Gy of the dose sensitivity. The dose sensitivity of the dosimeters was also enhanced by increment in THPC, reached about 0.06 Abs Gy
of the dose sensitivity. The dose sensitivity of the dosimeters was also enhanced by increment in THPC, reached about 0.06 Abs Gy at 0.40 wt% THPC.
at 0.40 wt% THPC.
Koshimizu, Masanori*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Iwamatsu, Kazuhiro; Kimura, Atsushi; Asai, Keisuke*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 86(1), p.013101_1 - 013101_5, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:45.77(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have developed a system for measuring the temporal profiles of scintillation at high linear energy transfer (LET) by using pulsed ion beams from a cyclotron. The half width at half maximum time resolution was estimated to be 1.5-2.2 ns, which we attributed mainly to the duration of the pulsed ion beam and timing jitter between the trigger signal and the arrival of the ion pulse. The temporal profiles of scintillation of BaF at different LETs were successfully observed. These results indicate that the proposed system is a powerful tool for analyzing the LET effects in temporal profiles of scintillation.
at different LETs were successfully observed. These results indicate that the proposed system is a powerful tool for analyzing the LET effects in temporal profiles of scintillation.