Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Be and
Be and  Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxes
Al under direct muon-induced spallation in granite quartz and its implications for past high-energy cosmic ray fluxesSakurai, Hirohisa*; Kurebayashi, Yutaka*; Suzuki, Soichiro*; Horiuchi, Kazuho*; Takahashi, Yui*; Doshita, Norihiro*; Kikuchi, Satoshi*; Tokanai, Fuyuki*; Iwata, Naoyoshi*; Tajima, Yasushi*; et al.
Physical Review D, 109(10), p.102005_1 - 102005_18, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Secular variations of galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) are inseparably associated with the galactic activities and should reflect the environments of the local galactic magnetic field, interstellar clouds, and nearby supernova remnants. The high-energy muons produced in the atmosphere by high-energy GCRs can penetrate deep underground and generate radioisotopes in the rock. As long lived radionuclides such as  Be and
Be and  Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of
Al have been accumulating in these rocks, concentrations of  Be and
Be and  Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced
Al can be used to estimate the long-term variations in high-energy muon yields, corresponding to those in the high-energy GCRs over a few million years. This study measured the production cross sections for muon induced  Be and
Be and  Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
Al by irradiating positive muons with the momentum of 160 GeV/c on the synthetic silica plates and the granite core at the COMPASS experiment line in CERN SPS. In addition, it the contributions of the direct muon spallation reaction and the nuclear reactions by muon-induced particles on the production of long lived radionuclides in the rocks were clarified.
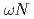 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.67(Physics, Nuclear) As
As using high-resolution inelastic X-ray scattering
using high-resolution inelastic X-ray scatteringMurai, Naoki*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Kobayashi, Tatsuya*; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Uchiyama, Hiroshi*; Ishikawa, Daisuke*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Miyasaka, Shigeki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 93(2), p.020301_1 - 020301_5, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:31.36(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) reflector and proton beam window
reflector and proton beam windowTeshigawara, Makoto; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Wakui, Takashi; Meigo, Shinichiro; Seki, Masakazu; Harada, Masahide; Ito, Manabu; Suzuki, Toru; Ikezaki, Kiyomi; Maekawa, Fujio; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2012-024, 303 Pages, 2012/07
3 GeV Protons with 1 MW beam power are irradiated to mercury target of spallation neutron source in Materials and Life science Facility (MLF), which is one of facilities of J-PARC. Irradiated components, such as target container, moderator, reflector and proton beam window, are needed to replace periodically due to irradiation damage of high energy protons and neutrons. These used components are replaced remotely because of highly activated. Maintenance scenario was settled so as to handle these components. Required remote handling machines were designed and installed in hot cell and other room of the MLF. We performed remote handling tests by using actual components to confirm the design. We report results, such as replacement procedure, trouble and its solution, etc., for moderator, reflector and proton beam window in order to provide the handling of actual used components.
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Suzuki, Masayuki*; Daito, Izuru; Okada, Hajime; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Sato, Masatoshi*; Tamaoki, Yoshinori*; Yoshii, Takehiro*; Maeda, Junya*; Matsuoka, Shinichi*; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 40(2), p.143 - 145, 2012/02
We demonstrate a compact, high-spatiotemporal-quality, high-intensity diode-pumped Yb:YAG thin-disk chirped-pulse amplification (CPA) laser system that incorporates a nonlinear preamplifier based on optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA). The stretched pulses are amplified in the OPCPA preamplifier and the following Yb:YAG main amplifier to  100 mJ at 10 Hz. The broadband amplified beam quality of 1.1 (horizontal direction) and 1.4 (vertical direction) times diffraction limited and pulse compression down to 470 fs with contrast of better than 10
100 mJ at 10 Hz. The broadband amplified beam quality of 1.1 (horizontal direction) and 1.4 (vertical direction) times diffraction limited and pulse compression down to 470 fs with contrast of better than 10 have been achieved successfully.
have been achieved successfully.
Isayama, Akihiko; Sakakibara, Satoru*; Furukawa, Masaru*; Matsunaga, Go; Yamazaki, Kozo*; Watanabe, Kiyomasa*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Tanaka, Kenji*; Tamura, Naoki*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 86(6), p.374 - 377, 2010/06
no abstracts in English
Sutherland, K.*; Miyajima, Satoshi*; Date, Hiroyuki*; Shirato, Hiroki*; Ishikawa, Masayori*; Murakami, Masao*; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Bolton, P.; Tajima, Toshiki
Radiological Physics and Technology, 3(1), p.16 - 22, 2010/01
Osakabe, Masaki*; Shinohara, Koji; Toi, Kazuo*; Todo, Yasushi*; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Murakami, Sadayoshi*; Yamamoto, Satoshi*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Tanaka, Kenji*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 85(12), p.839 - 842, 2009/12
no abstracts in English
Okada, Koichi*; Kondo, Keitaro; Ochiai, Kentaro; Sato, Satoshi; Konno, Chikara; Okamoto, Atsushi*; Kobuchi, Takashi*; Kitajima, Sumio*; Sasao, Mamiko*
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.8, p.666 - 669, 2009/09
Measurement of fuel ion density ratio, 
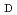 /
/
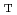 , is required for burning control on ITER. The measured
, is required for burning control on ITER. The measured 
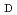 /
/
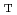 ratio must be fed back in real time. A neutron measurement system to measure
ratio must be fed back in real time. A neutron measurement system to measure 
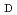 /
/
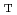 should be operable at high counting rate. It is estimated that the number of emitted DT neutrons is 200 times higher than that of DD neutrons under the condition of ITER standard operation. A neutron measurement system was developed using a DT/DD generator, where DT neutrons are dominant and DD neutrons are contaminated slightly in the neutron beam. The measurement instrument was a TOF spectrometer. Signals originating from each neutron must be distinguished in order to measure the fuel ratio. We developed a circuit system with discrimination windows to distinguish each signal pulse, and DT and DD neutrons were measured separately and simultaneously with this system. The experimental result indicates a possibility that this system is suitable for measurement of fuel ion density ratio on ITER.
should be operable at high counting rate. It is estimated that the number of emitted DT neutrons is 200 times higher than that of DD neutrons under the condition of ITER standard operation. A neutron measurement system was developed using a DT/DD generator, where DT neutrons are dominant and DD neutrons are contaminated slightly in the neutron beam. The measurement instrument was a TOF spectrometer. Signals originating from each neutron must be distinguished in order to measure the fuel ratio. We developed a circuit system with discrimination windows to distinguish each signal pulse, and DT and DD neutrons were measured separately and simultaneously with this system. The experimental result indicates a possibility that this system is suitable for measurement of fuel ion density ratio on ITER.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yoshida, Maiko; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Tanaka, Kenji*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Tamura, Naoki*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Urano, Hajime; Aiba, Nobuyuki; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 84(12), p.952 - 955, 2008/12
no abstracts in English
Murakami, Masao*; Hishikawa, Yoshio*; Miyajima, Satoshi*; Okazaki, Yoshiko; Sutherland, K.*; Abe, Mitsuyuki*; Bulanov, S. V.; Daido, Hiroyuki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Koga, J. K.; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1024, p.275 - 300, 2008/08
no abstracts in English
Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Mori, Michiaki; Nakai, Yoshiki; Shimomura, Takuya*; Tanoue, Manabu*; Akutsu, Atsushi; Okada, Hajime; Motomura, Tomohiro*; Kondo, Shuji; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2008-007, p.13 - 16, 2008/08
One of the main bottlenecks for the applications of ultrashort and ultrahigh-peak power lasers in high-field physics is a temporal contrast of the pulses. In ultrahigh-peak power lasers, a nanosecond background of the amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) is generated at the same time as the femtosecond pulse. This background is mostly generated in the preamplifier (regenerative, multipass amplifier). Even though the contrast level is usually in the range from 10 to 10
to 10 , this level is not sufficiently low at relativistic intensities greater than 10
, this level is not sufficiently low at relativistic intensities greater than 10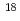 W/cm
W/cm to avoid unwanted pre-plasmas generation. We demonstrated a high-contrast, high-peak power laser with optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA). With the use of OPCPA, contrast is enhanced to better than 7
to avoid unwanted pre-plasmas generation. We demonstrated a high-contrast, high-peak power laser with optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification (OPCPA). With the use of OPCPA, contrast is enhanced to better than 7 10
10 in a few picoseconds before the main pulse, which corresponds to an improvement of three to four orders in magnitude compared with conventional systems.
in a few picoseconds before the main pulse, which corresponds to an improvement of three to four orders in magnitude compared with conventional systems.
Yogo, Akifumi; Daido, Hiroyuki; Bulanov, S. V.; Nemoto, Koshichi*; Oishi, Yuji*; Nayuki, Takuya*; Fujii, Takashi*; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
Physical Review E, 77(1), p.016401_1 - 016401_6, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:117 Percentile:97.10(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The duration-controlled amplified spontaneous emission with intensity of 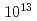 W/cm
W/cm is used to convert a 7.5
is used to convert a 7.5  m thick polyimide foil into a near-critical plasma, in which the
m thick polyimide foil into a near-critical plasma, in which the  -polarized, 45 fs,
-polarized, 45 fs, 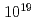 W/cm
W/cm laser pulse generates 3.8 MeV protons, emitted at some angle between the target normal and the laser propagation direction of 45
laser pulse generates 3.8 MeV protons, emitted at some angle between the target normal and the laser propagation direction of 45 . Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the efficient proton acceleration is due to generation of the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure inducing and sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
. Particle-in-cell simulations reveal that the efficient proton acceleration is due to generation of the quasistatic magnetic field on the target rear side with the magnetic pressure inducing and sustaining a charge separation electrostatic field.
Saito, Kimiaki; Saito, Hidetoshi*; Kunieda, Etsuo*; Narita, Yuichiro*; Myojoyama, Atsushi*; Fujisaki, Tatsuya*; Kawase, Takatsugu*; Kaneko, Katsutaro*; Ozaki, Masahiro*; Deloar, H. M.*; et al.
Joho Shori, 48(10), p.1081 - 1088, 2007/10
no abstracts in English
 beam line separation
beam line separationIshii, Yasuyuki; Chiba, Atsuya; Uno, Sadanori; Saito, Yuichi; Mizuhashi, Kiyoshi; Tajima, Satoshi*; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 260(1), p.15 - 19, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:13.89(Instruments & Instrumentation)Measurement of beam energy spreads caused by an accelerator are needed to evaluation the choromatic aberration when ion beams with micorometer or nanometer sizes are formed at a focusing point. A measurement method of the beam energy spreads without using a analyzing magnet with a high resolution was developed to evaluate the chromatic aberration in a light-ion micorbeam system connected to the 3MV JAEA single-ended accelerator. The accurate beam energy spread measurement method within a resolution of 10 was developed using resonance nuclear reactions with narrow energy spreads of
was developed using resonance nuclear reactions with narrow energy spreads of  A
A (p,
(p, )
) Si and
Si and  Mg(p,
Mg(p, )
) A
A in a MeV energy range. Furthermore, ion species separating method, in a 0-degree beam line connected to the accelerator, was developed using parmanent magnets attached on the accelerator tube in the accelerator. The two kinds of developmet resulted in measuring baem energy spreads generated from the accelerator directly.
in a MeV energy range. Furthermore, ion species separating method, in a 0-degree beam line connected to the accelerator, was developed using parmanent magnets attached on the accelerator tube in the accelerator. The two kinds of developmet resulted in measuring baem energy spreads generated from the accelerator directly.
Noda, Akira*; Nakamura, Shu*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Shirai, Toshiyuki*; Tongu, Hiromu*; Soda, Hikaru*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Mori, Michiaki; Kado, Masataka; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
International Journal of Modern Physics B, 21(3&4), p.319 - 330, 2007/02
Laser ion production has been studied for downsizing of the accelerator dedicated for cancer therapy. For optimization of various parameters such as pre-pulse condition, target position, laser spot size on target, laser pulse width and so on, time of flight (TOF) measurement utilizing the detected signal by a plastic scintillation counter played an essential role for real time measurement. Protons up to 900 keV and 600 keV are produced from the thin foil targets of Ti 3 micron and 5 micron in thickness, respectively. Modification of the energy distribution of the laser-produced ions with Maxwell distribution by utilizing an RF electric field synchronized to the pulse laser, which is the rotation of the ion beam in the longitudinal phase space (phase rotation), has been demonstrated for the first time.
Daido, Hiroyuki; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Mori, Michiaki; Ma, J.-L.; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
Proceedings of 7th Pacific Rim Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO-PR 2007) (CD-ROM), p.77 - 79, 2007/00
We are developing a proton accelerator using an intense lasers with a focused intensity of  10
10 W/cm
W/cm . To monitor proton energy spectra as well as plasma parameters at each laser shot, we are using real time detectors. The proton energy of MeV is stably obtained for applications.
. To monitor proton energy spectra as well as plasma parameters at each laser shot, we are using real time detectors. The proton energy of MeV is stably obtained for applications.
Daido, Hiroyuki; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Yogo, Akifumi; Mori, Michiaki; Li, Z.*; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Kanazawa, Shuhei; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2006; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.115, p.595 - 605, 2007/00
At present, using ultra-short high intensity lasers at APRC, JAEA Kansai photon research institute, we are developing laser driven multiple quantum beams such as protons, X-rays, electrons and THz waves. These beams are perfectly synchronized with each other. The pulse duration of each beam is lass than a pico-second. They have sharp directionality with high brightness. If we properly combined these, we have new pump-probe techniques for various applications.
Chiba, Atsuya; Saito, Yuichi; Tajima, Satoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 232(1-4), p.32 - 36, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:58.10(Instruments & Instrumentation)The structure of cluster ion may be important parameter for resolution of physical effect and interaction with cluster ion and solid. In this paper, we report a Coulomb explosion imaging of the constituent atoms of a swift carbon cluster (Cn, n=2, 3 and 6) passing through a thin foil and their average charge state that related with the structure of the cluster. The experimental setup is based on the 3MV TANDEM accelerator at the JAERI Takasaki. The cluster ion beam is pulsed by electrical deflection plates and an aperture. A few clusters pass trough the thin foil during 1 second, and the resulting are collected by the luminance plate detector. The average charge state was shown an almost same tendency as calculate theoretical value.
Okoshi, Kiyonori; Chiba, Atsuya; Mizuhashi, Kiyoshi; Tajima, Satoshi
JAERI-Review 2004-025, TIARA Annual Report 2003, p.324 - 325, 2004/11
no abstracts in English