Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -ray dust monitor for highly-concentrated airborne contaminants
-ray dust monitor for highly-concentrated airborne contaminantsSagawa, Naoki; Fujisawa, Makoto; Hosomi, Kenji; Morishita, Yuki; Takada, Chie
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 58(3), p.135 - 140, 2023/11
Radioactivity concentrations of airborne dust are important measurements because they are used to protect workers from intakes and to assess internal exposure doses. Therefore, we developed a portable  -ray dust monitor by using an ultra-thin plastic scintillator, which is designed for continuous monitoring of highly-concentrated airborne contaminants (
-ray dust monitor by using an ultra-thin plastic scintillator, which is designed for continuous monitoring of highly-concentrated airborne contaminants ( 10
10 Bq/cm
Bq/cm , equivalent to 30 times larger than the derived air concentration of
, equivalent to 30 times larger than the derived air concentration of  Sr) such as a decommissioning work in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. From the performance test results, it is evaluated that the developed portable
Sr) such as a decommissioning work in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. From the performance test results, it is evaluated that the developed portable  -ray dust monitor is functional in continuous monitoring with an airborne concentration of 1 Bq/cm
-ray dust monitor is functional in continuous monitoring with an airborne concentration of 1 Bq/cm .
.
Yokoyama, Hiroya; Maehara, Yushi; Fujita, Hiroki; Takada, Chie
KEK Proceedings 2023-2, p.126 - 131, 2023/11
no abstracts in English
 particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detector
particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detectorMorishita, Yuki; Sagawa, Naoki; Takada, Chie; Momose, Takumaro; Takasaki, Koji
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 199(13), p.1376 - 1383, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Environmental Sciences)It is very important to evaluate the diameters (activity median aerodynamic diameter) of Plutonium dioxide (PuO ) particles for internal exposure dose evaluation. In this study, a method of evaluating PuO
) particles for internal exposure dose evaluation. In this study, a method of evaluating PuO particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detector was developed. PuO
particle diameters using an alpha-particle imaging detector was developed. PuO particles with different diameters were modeled by Monte Carlo simulation, and the change in the shape of the energy spectrum for each particle diameter was evaluated. Two different patterns were modeled, namely, the case of
particles with different diameters were modeled by Monte Carlo simulation, and the change in the shape of the energy spectrum for each particle diameter was evaluated. Two different patterns were modeled, namely, the case of  PuO
PuO and the case of PuO
and the case of PuO (including isotopic composition of Pu). Multiple regression analysis was performed to determine the PuO
(including isotopic composition of Pu). Multiple regression analysis was performed to determine the PuO particle diameter from the obtained parameters. The simulated diameters and the diameters obtained with the regression model were in good agreement. The advantage of using the alpha-particle imaging detector is to measure the alpha energy spectrum for individual particle, and this allows accurate measurement of particle diameter distribution.
particle diameter from the obtained parameters. The simulated diameters and the diameters obtained with the regression model were in good agreement. The advantage of using the alpha-particle imaging detector is to measure the alpha energy spectrum for individual particle, and this allows accurate measurement of particle diameter distribution.
Fujii, Yutaka*; Takada, Chie
FBNews, (540), p.7 - 11, 2021/12
no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Makoto; Kinase, Sakae; Munakata, Masahiro; Murayama, Takashi; Takahashi, Masa; Takada, Chie; Okamoto, Akiko; Hayakawa, Tsuyoshi; Sukegawa, Masato; Kume, Nobuhide*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-071, 53 Pages, 2021/03
In the case of a nuclear accident or a radiological emergency, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), as a designated public corporation assigned in the Disaster Countermeasures Basic Act and the Armed Attack Situation Response Law, undertakes technical supports to the national government and local governments. The JAEA is requested to support to evaluate radiation doses to residents in a nuclear emergency, which is specified in the Basic Disaster Management Plan and the Nuclear Emergency Response Manual. For the dose evaluation, however, its strategy, target, method, structure and so on have not been determined either specifically or in detail. This report describes the results of investigation and consideration discussed in the "Working Group for Radiation Dose Evaluation at a Nuclear Emergency" established within the Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center to discuss technical supports for radiation dose evaluation to residents in the case of a nuclear emergency, and aims at contributing to specific and detailed discussion and activities in the future for the national government and local governments, also within the JAEA.
Tsujimura, Norio; Yamazaki, Takumi; Takada, Chie
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(1), p.40 - 44, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tsujimura, Norio; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Takada, Chie
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.148 - 151, 2019/01
Yamazaki, Takumi; Takada, Chie; Tsujimura, Norio; Okada, Kazuhiko
Hoken Butsuri, 52(3), p.167 - 170, 2017/09
At the JAEA MOX Fuel Facilities, a worker engaged in glove box operations uses two personal dosemeters, one worn on the trunk under a protective apron and the other at the collar over the apron. The recorded lens of the eye dose is based on the photon dose measured by the collar dosemeter plus the neutron dose measured by the under-apron dosemeter.
Takada, Chie; Kurihara, Osamu*; Kanai, Katsuta; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Tsujimura, Norio; Momose, Takumaro
NIRS-M-252, p.3 - 11, 2013/03
A massive earthquake and tsunami on March 11, 2011 resulted in an enormous amount of release of radioactivity to the environment. On the day after the earthquake occurrence, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) started emergency radiological monitoring. The measurements with whole body counter (WBC) for the staff members who had returned from Fukushima started at the end of March. The measured activity of  I due to inhalation for emergency staff varied from LLD to 7 kBq, which corresponded to a range of estimated initial intakes of
I due to inhalation for emergency staff varied from LLD to 7 kBq, which corresponded to a range of estimated initial intakes of  1 to 60 kBq when extrapolated back to the date on which the staff started the operation in Fukushima. The measured activity of
1 to 60 kBq when extrapolated back to the date on which the staff started the operation in Fukushima. The measured activity of  Cs and
Cs and  Cs were both in the ranges of LLD - 3 kBq. The range of initial intake of
Cs were both in the ranges of LLD - 3 kBq. The range of initial intake of  Cs to
Cs to  I was 11 when taking a median from all the measurements. The maximum committed effective dose of 0.8 mSv was recorded for a worker, a member of the 2nd monitoring team dispatched from March 13 to 14.
I was 11 when taking a median from all the measurements. The maximum committed effective dose of 0.8 mSv was recorded for a worker, a member of the 2nd monitoring team dispatched from March 13 to 14.
 I in the thyroids of employees involved in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident
I in the thyroids of employees involved in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accidentKurihara, Osamu*; Kanai, Katsuta; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takada, Chie; Tsujimura, Norio; Momose, Takumaro; Furuta, Sadaaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 50(2), p.122 - 129, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Takada, Chie
Radiation Measurements, 46(12), p.1720 - 1723, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)The authors investigated the performance of three commercially available electronic personal dosemeters (EPDs) in evaluating neutron dose equivalents and discussed their suitability to work environments in MOX fuel fabrication facilities. The EPDs selected for this study were NRY21 (Fuji Electric Systems), PDM-313 (Aloka) and DMC 2000 GN (MGP Instruments). All tests were conducted in moderated  Cf neutron fields with neutron spectral and dosimetric characteristics similar to those found in MOX fuel facilities. The test results revealed that all three models demonstrate a performance within a reasonably acceptable accuracy (a factor of 2) in practical use. The test results also suggested that the accuracy of some EPDs can be improved with a judicious selection of calibration sources.
Cf neutron fields with neutron spectral and dosimetric characteristics similar to those found in MOX fuel facilities. The test results revealed that all three models demonstrate a performance within a reasonably acceptable accuracy (a factor of 2) in practical use. The test results also suggested that the accuracy of some EPDs can be improved with a judicious selection of calibration sources.
Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takada, Chie; Tsujimura, Norio
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.140 - 143, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Radiation workers engaging in the fabrication of MOX fuels are exposed to neutrons, and hence thermoluminescent albedo dosemeters (TLAD) need to be used at JAEA-NCL. Because estimating the doses using TLADs are susceptible to the neutron energy spectrum, the authors have issued TLADs incorporating Solid-State Nuclear Tracks Detectors (SSNTDs) to selected workers who are routinely exposed to neutrons and been analyzing the relationship between the SSNTD and the TLAD (T/Rf) over the past 6 years. Consequently, the  /
/
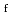 in each year was 10-20 (3.363 mm
in each year was 10-20 (3.363 mm )/(mSv
)/(mSv  Cs eq.), which is smaller than the data during 1991-1993, although the neutron spectra had not changed compared with that of the early 1990s. This decrease of the
Cs eq.), which is smaller than the data during 1991-1993, although the neutron spectra had not changed compared with that of the early 1990s. This decrease of the  /
/
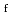 implies that the ratio of work carried out nearby the gloveboxes to total work decreased.
implies that the ratio of work carried out nearby the gloveboxes to total work decreased.
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Takada, Chie
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 146(1-3), p.198 - 201, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)To predict how accurately neutron dosemeters can measure the neutron dose equivalent (rate) in a MOX fuel fabrication facility work environments, the dose equivalent responses of neutron dosemeters were calculated by the spectral folding method. The dosemeters selected included two types of personal dosemeters, namely a thermoluminescent albedo neutron dosemeter and an electronic neutron dosemeter, three moderator-based neutron survey meters, and one special instrument called an 
 (10) monitor. The calculations revealed the energy dependences of the responses expected within the entire range of neutron spectral variations observed in neutron fields at workplaces.
(10) monitor. The calculations revealed the energy dependences of the responses expected within the entire range of neutron spectral variations observed in neutron fields at workplaces.
Takada, Chie
Hoken Butsuri, 46(1), p.18 - 21, 2011/03
The author participated IM2010 conference at Athens on March, 2010. The impression about the conference are described in this script.
Momose, Takumaro; Kurihara, Osamu; Takada, Chie; Furuta, Sadaaki
Proceedings of 1st International Symposium on Radiation Emergency Medicine at Hirosaki University, p.65 - 72, 2010/07
The basic principle of radiation control at plutonium facility such as characteristics of plutonium and relevant radionuclide which are operated in nuclear fuel cycle facilities is introduced and potential radioactive contaminations in accident is discussed. As a practice, decontamination procedure of skin at Tokai Reprocessing Plant, some of the operating principles and applications of various radiation detection and measurement instruments for contamination control and occupational monitoring for internal contamination are introduced. Special methods of measurement for alpha emitters for performing radiological monitoring such as radio autography of plutonium contamination on smear samples, nasal swab sampling and measurement, in vivo and in vitro analysis for plutonium and uranium have been improved and proven. The internal dose calculation code was originally developed in order to estimate retrospectively in case of accidental intake of plutonium.
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Takada, Chie
Proceedings of 3rd Asian and Oceanic Congress on Radiation Protection (AOCRP-3) (CD-ROM), 3 Pages, 2010/05
To predict how accurately the neutron dosemeters can measure the neutron dose equivalent (rate) in MOX fuel fabrication facility work environments, the calculations of the dose equivalent responses of neutron dosemeters were performed by the spectral folding method. The dosemeters selected included two types of personal dosemeters (a thermoluminescent albedo neutron dosemeter and an electronic neutron dosemeter), three moderator-based neutron survey meters and one special instrument called an 
 (10) monitor. The calculations revealed the energy dependences of the responses expected within the entire range of neutron spectral variation observed in neutron fields at workplaces.
(10) monitor. The calculations revealed the energy dependences of the responses expected within the entire range of neutron spectral variation observed in neutron fields at workplaces.
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Takada, Chie; Nunomiya, Tomoya*; Aoyama, Kei*
Proceedings of 12th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-12) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
The authors assessed performance of electronic personal neutron dosemeters (EPD). The EPD selected in this study is NRY21, manufactured by Fuji Electric Systems Co., Ltd. This dosemeter uses two silicon semiconductor detectors to provide wide measurable energy ranges from thermal to several tens of MeV. In the test, we focused on the energy and angular dependences of dose equivalent responses because it was of great importance in neutron dosimetry in work environments. Measurements of dose equivalent responses were performed in the moderated neutron field reproducing neutron spectra likely to be encountered in workplaces of MOX fuel facilities. Neutron dose equivalents given by EPD were compared with reference dose values. As a result, dose equivalent responses of this EPD were evaluated to be 0.7 to 1.1 for normal incidence of neutron irradiation. This is satisfactory performance required for personal neutron monitoring.
Kurihara, Osamu; Takada, Chie; Takasaki, Koji; Ito, Kimio; Momose, Takumaro; Miyabe, Kenjiro
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 127(1-4), p.411 - 414, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.97(Environmental Sciences)Practical action levels for beginning chelation therapy to remove plutonium in the body are now under discussion in Japan since there has been no experience in administrating agents to a subject in accidental intake in Japan although a first commercial reprocessing plant is about to start operation. Recently, International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) proposed some medical intervention levels for chelation therapy on ICRP Publication 96. These levels are determined based on internal dose however common monitoring methods such as lung counting or excreta analysis are not necessarily suitable in terms of both sensitivity and promptness. As an alternative, the authors paid attention to nose swabs and introduced the practical action levels.
Kurihara, Osamu; Hato, Shinji; Kanai, Katsuta; Takada, Chie; Takasaki, Koji; Ito, Kimio; Ikeda, Hiroshi*; Oeda, Mikihiro*; Kurosawa, Naohiro*; Fukutsu, Kumiko*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 44(10), p.1337 - 1346, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the case of internal contamination of radionuclides, it is necessary to perform internal dose assessment for radiation protection. For this purpose, the ICRP has given the dose coefficients and the retention and excretion rates for various radionuclides. However, these dosimetric quantities are calculated only in typical conditions, therefore, are not necessarily covered enough in the case of dose assessment in which specific information on the incident or/and individual biokinetic characteristics should be taken into account retrospectively. This paper describes a developed PC-based package of software REIDAC to meet the needs in retrospective dose assessment. REIDAC was verified by comparisons with dosimetric quantities given on the ICRP publications and several examples of practical use were also shown.
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Takada, Chie; Momose, Takumaro; Nunomiya, Tomoya*; Aoyama, Kei*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 126(1-4), p.261 - 264, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.94(Environmental Sciences)The authors developed a new neutron measuring-instrument that was designed to measure neutron personal dose equivalent, 
 (10). This detector is composed a central thermal neutron detector, a core-polyethylene moderator, a front-hemispherical polyethylene moderator and rear-hemispherical boron-contained polyethylene absorber. Dimensions of each part were determined so as to provide energy- and angular-responses close to energy- and angular-dependencies of neutron
(10). This detector is composed a central thermal neutron detector, a core-polyethylene moderator, a front-hemispherical polyethylene moderator and rear-hemispherical boron-contained polyethylene absorber. Dimensions of each part were determined so as to provide energy- and angular-responses close to energy- and angular-dependencies of neutron 
 (10), based on the Monte Carlo calculations.
(10), based on the Monte Carlo calculations.